Find Help
More Items From Ergsy search
-
Hives - Skin Condition
Relevance: 100%
-
Is it true that sunbeds can help treat skin conditions like psoriasis?
Relevance: 40%
-
Skin cancer education
Relevance: 33%
-
What is a skin cancer screening?
Relevance: 31%
-
Skin Cancer - How do I check if my mole is skin cancer? | NHS
Relevance: 31%
-

Are skin rashes a side effect of weight loss drugs?
Relevance: 29%
-

Are skin lightening kist safe to use?
Relevance: 29%
-
Do sunbeds help improve skin tone and texture?
Relevance: 28%
-

What SPF should I use if I have sensitive skin?
Relevance: 27%
-
Do sunbeds offer any anti-aging benefits for the skin?
Relevance: 27%
-

What are some common conditions treated with homeopathy?
Relevance: 26%
-

Does stress contribute to nettle rash?
Relevance: 26%
-

What causes nettle rash?
Relevance: 24%
-
Is pre-tanning in a sunbed a good way to prepare my skin for sun exposure?
Relevance: 24%
-

How important is it to keep the skin moisturised with psoriasis?
Relevance: 23%
-
Can nettle rash spread from person to person?
Relevance: 23%
-
Diabetic Foot Conditions Podiatrist
Relevance: 22%
-
Is tinnitus a common condition?
Relevance: 22%
-

Is asthma a serious condition?
Relevance: 21%
-

Is BPH a serious condition?
Relevance: 21%
-
What are the symptoms of scabies?
Relevance: 21%
-
Is health-related anxiety a common condition?
Relevance: 20%
-
Is postnatal depression a long-term condition?
Relevance: 20%
-

What are the symptoms of a nut allergy?
Relevance: 20%
-

What condition does Wegovy treat?
Relevance: 20%
-

What is a pre-existing condition waiver in travel insurance?
Relevance: 19%
-
Is thrombosis a common condition?
Relevance: 19%
-

Can an indefinite sentence end with a conditional release?
Relevance: 19%
-
What are common symptoms of nettle rash?
Relevance: 19%
-

Can self-testing detect all eye conditions?
Relevance: 19%
-
What conditions is ketamine used to treat?
Relevance: 19%
-

What is the eye condition hypotony?
Relevance: 19%
-

When should I see a doctor for nettle rash?
Relevance: 19%
-
How is nettle rash diagnosed?
Relevance: 19%
-

Can weather conditions contribute to dangerous driving?
Relevance: 18%
-

What foods can trigger nettle rash?
Relevance: 18%
-

Is it possible to be allergic to the sun?
Relevance: 18%
-
Is nettle rash contagious?
Relevance: 18%
-

Are pre-existing medical conditions covered by holiday insurance policies?
Relevance: 18%
-

Can homeopathy treat all medical conditions?
Relevance: 18%
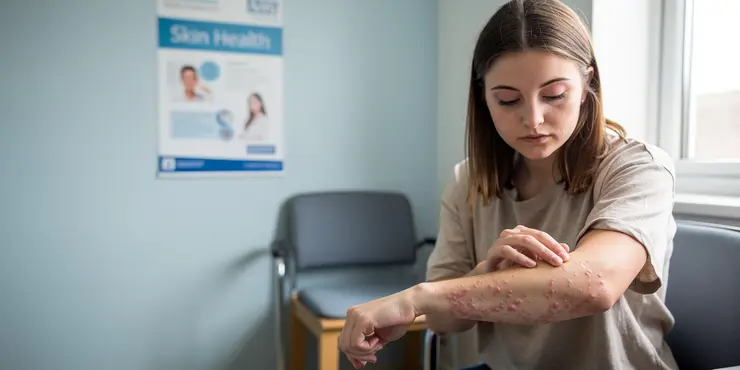
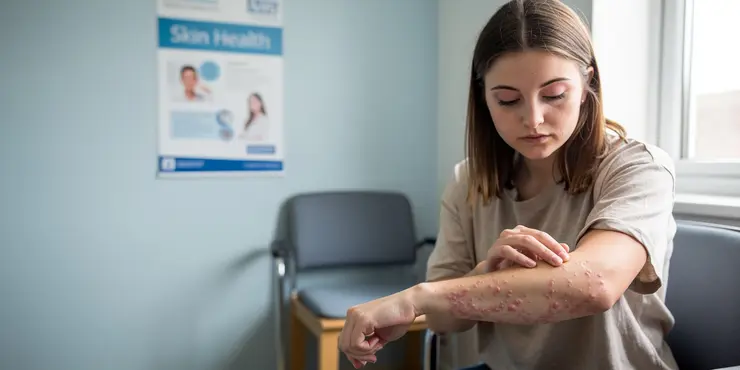
Hives - Skin Condition
Hives, also known as urticaria, are a common skin condition characterised by red, itchy welts that can appear anywhere on the body. These welts can vary in size and might merge to form larger areas of swelling. Although they are usually acute, lasting less than six weeks, chronic cases can persist for much longer, significantly impacting a person's daily life.
Causes of Hives
In the UK, hives can be triggered by a variety of factors. Common causes include allergic reactions to certain foods, medications, or insect stings. Environmental factors like extreme temperatures, stress, and infections can also lead to hives. Interestingly, for many individuals, the exact cause may remain unidentified, a condition known as idiopathic urticaria.
Symptoms and Appearance
The hallmark of hives is the appearance of wheals or welts on the skin. These welts can cause significant itching and discomfort. In some cases, individuals may experience angioedema, a more severe form of swelling that affects deeper layers of the skin, often around the eyes and lips. Symptoms can fluctuate rapidly, with welts disappearing in one area and emerging in another.
Treatment Options
Treatment for hives often involves addressing the underlying cause. In many instances, antihistamines are effective in reducing symptoms. Over-the-counter options are available, but more severe cases might require prescription-strength medications. For chronic hives, doctors may recommend corticosteroids or other immunosuppressive treatments. In the UK, people are advised to consult with a healthcare professional to devise an effective management plan.
Prevention and Management
Preventing hives can be challenging, but identifying and avoiding known triggers is key. Keeping a detailed diary of outbreaks can help pinpoint potential allergens or environmental factors. Wearing loose-fitting clothing and using mild soaps can reduce skin irritation. In cases of chronic hives, regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor the condition and adjust treatments as necessary.
When to Seek Medical Advice
While most cases of hives are mild and self-limiting, it is important to seek medical advice if you experience severe symptoms, such as difficulty breathing, which may indicate an allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) requiring immediate intervention. In the UK, such symptoms should prompt urgent medical care, either by calling emergency services or visiting the nearest hospital.
Hives - Skin Condition
Hives, also called urticaria, are a skin problem. They show up as red, itchy bumps on the skin. These bumps can be different sizes and might join together to make bigger swollen areas. Usually, hives last less than six weeks, but sometimes they last a lot longer and can make everyday life hard.
Causes of Hives
In the UK, lots of things can cause hives. Common causes are allergic reactions to some foods, medicines, or insect bites. Other causes can be extreme weather, stress, or illnesses. Sometimes, doctors can’t find the exact cause. This is called idiopathic urticaria.
Symptoms and Appearance
Hives show up as itchy bumps on the skin, called welts or wheals. These can be very itchy and uncomfortable. Some people might get a deeper swelling, especially around the eyes and lips, called angioedema. The bumps can come and go quickly, disappearing in one spot and showing up in another.
Treatment Options
To treat hives, it’s important to figure out what’s causing them. Many people find relief by taking antihistamines, which can be bought at the store. Sometimes stronger medicine from a doctor is needed. For long-lasting hives, doctors might suggest special medications like corticosteroids. In the UK, it’s best to talk to a doctor to make a good plan.
Prevention and Management
Stopping hives from happening can be tricky. It helps to know and avoid what triggers them. Keeping a diary of when hives happen can help find the cause. Wearing loose clothes and using gentle soap can help avoid skin irritation. For people with long-lasting hives, regular doctor visits are important to manage the condition.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Most hives are mild and go away on their own. But you should see a doctor if you have severe symptoms, like trouble breathing. This might mean an allergic reaction that needs fast help. In the UK, call emergency services or go to the hospital if this happens.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are hives?
Hives, also known as urticaria, is a skin condition characterised by red, itchy welts or swellings on the skin, often caused by an allergic reaction.
What causes hives?
Hives can be triggered by allergies to certain foods, medications, or insect stings, as well as stress, infections, or even changes in temperature.
Are hives contagious?
No, hives are not contagious. They are usually a reaction to an allergen or trigger specific to an individual.
How long do hives typically last?
Hives can last for a few hours or days. Acute hives typically resolve within six weeks, whereas chronic hives persist longer and may require medical attention.
What are common symptoms of hives?
Symptoms include red or skin-coloured welts, swelling, itching, and sometimes a burning sensation on the skin.
How are hives diagnosed?
A GP can often diagnose hives by examining the skin and assessing patient history. Further allergy testing may be conducted to identify specific triggers.
Can stress cause hives?
Yes, stress can trigger or worsen hives, as it can cause your body's immune system to act in unpredictable ways, potentially leading to outbreaks.
What treatment options are available for hives?
Treatments include antihistamines to relieve itching, corticosteroids for severe cases, and avoiding known triggers. Consultation with a healthcare provider is often recommended.
Are there any home remedies for managing hives?
Cold compresses, loose clothing, and taking cool showers can help alleviate discomfort. However, it is always advisable to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Can certain foods trigger hives?
Yes, common food triggers include nuts, shellfish, eggs, and some preservatives or additives. It's essential to identify and avoid these triggers if they are causing hives.
Is it possible to develop hives from exercise?
Yes, exercise-induced urticaria is a condition where physical activity can trigger hives in some individuals, often due to an increase in body temperature.
When should I see a doctor for hives?
You should see a doctor if hives persist for more than a few days, are severe, or are accompanied by difficulty breathing or other symptoms of anaphylaxis.
Can hives be prevented?
Preventing hives involves avoiding known triggers and managing stress. In some cases, a doctor may recommend medications or allergy management strategies to help prevent outbreaks.
Can hives occur in children and infants?
Yes, hives can occur in people of all ages, including children and infants. The causes may differ slightly, but management and treatment approaches are often similar.
Are there any long-term effects of hives?
Typically, hives do not have long-term effects, but chronic urticaria may require ongoing management. It's important to address any underlying causes, especially if hives occur frequently.
What are hives?
Hives are itchy, red bumps on the skin.
Hives can be a little or a lot. They might show up because you are allergic to something or because your skin is sensitive.
When you have hives, it can feel like you're itchy all over. Sometimes hives go away quickly, but sometimes they stay for a while.
If you have hives, it can help to tell a grown-up or a doctor. They can help you feel better.
You could use tools like pictures or videos to learn about hives. You can also ask someone to read to you or help you understand.
Hives is a skin problem. It is also called urticaria. When you have hives, you get red and itchy bumps on your skin. This can happen because of an allergy.
What makes hives happen?
Hives are red, itchy bumps on the skin. Here are some things that can cause hives:
- Eating certain foods like nuts or shellfish.
- Getting stung by a bee or bitten by a bug.
- Taking some medicines.
- Having a cold or an infection.
- Feeling stressed or nervous.
To help understand better, you can use:
- Pictures to show what hives look like.
- Stories or examples that explain what happens.
- Talking to someone who knows about hives, like a doctor.
Hives can happen because of allergies. This can be from some foods, medicines, or insect bites. Hives can also come when you are stressed, sick, or if the weather changes.
Can you catch hives from someone else?
You can't catch hives from another person. Hives are not spread like a cold or the flu.
If you have hives and need help, you can:
- Talk to a doctor.
- Use a cool, wet cloth to feel better.
- Stay away from things that make you itch.
No, you can't catch hives from someone else. Hives happen when your body reacts to something you are allergic to, or a special trigger that affects just you.
How long do hives usually last?
Hives are red, itchy bumps on your skin. They can come and go quickly or last longer.
Most hives last for a few hours or up to a day. Some hives can last for more than six weeks.
If you have hives for a long time or if they keep coming back, talk to a doctor. They can help you feel better.
If you find reading hard, you can:
- Ask someone to read with you.
- Use a tool to read the text out loud.
- Draw a picture to help you understand.
Hives are red, itchy spots on your skin. They can last a few hours or a few days. Hives that go away in less than six weeks are called acute hives. If hives last more than six weeks, they are called chronic hives. Chronic hives might need a doctor’s help.
What are common signs of hives?
Hives make your skin feel itchy. You might see red or white bumps on your skin. These bumps can come and go. They sometimes join together and get bigger.
If you have hives, it might help to:
- Put a cool, wet cloth on your skin
- Wear loose clothes
- Use special anti-itch cream
What you might feel:
1. Red bumps on your skin.
2. Bumps that are the same color as your skin.
3. Swelling.
4. Itchy skin.
5. Sometimes your skin might feel like it's burning.
It might help to use a cooling cream or talk to a grown-up about creams or medicines that can help.
How do doctors know if you have hives?
A doctor can usually tell if you have hives by looking at your skin and asking some questions about your health. Sometimes, they might do allergy tests to find out what is causing the hives.
Can stress cause hives?
Can feeling worried or upset make you get itchy bumps on your skin?
Feeling stressed can sometimes make your skin itchy and red. These are often called "hives."
If you get hives, try to relax and find ways to calm down.
Here are some things that might help:
- Take deep breaths.
- Listen to your favorite music.
- Talk to someone you trust about how you feel.
- Do something fun, like drawing or playing a game.
If the itchy bumps don't go away, it might be good to talk to a doctor.
Yes, stress can make hives start or get worse. Stress can make your body's defense system act in strange ways and cause hives.
What are the treatments for hives?
If you have hives, there are ways to help you feel better:
- Talk to a Doctor: A doctor can help you find out what is causing the hives.
- Medicine: Some medicines can make the itching and redness go away. Your doctor can tell you which ones to use.
- Cool your Skin: Put a cold, wet cloth on your skin to help with the itching.
- Avoid Hot Water: Try not to take hot showers or baths, as they can make hives worse.
- Calm Down: Try to stay calm, as stress can make hives worse. Breathing deeply or listening to quiet music might help.
If hives do not go away or you feel really unwell, tell an adult or go back to the doctor.
When we feel itchy, taking medicine called antihistamines can help us feel better. If it's very bad, doctors might give us a stronger medicine called corticosteroids. It's also important to stay away from things that make us feel itchy. Talking to a doctor can be a good idea to know what to do.
Can you treat hives at home?
Using cold packs, wearing loose clothes, and taking cool showers can help you feel better. But it's important to talk to a doctor or nurse to know what's wrong and how to fix it.
Can some foods make hives happen?
Sometimes, eating certain foods can make itchy bumps called hives appear on the skin. Eating food like nuts, eggs, or shellfish can do this. If you get hives after eating something, tell an adult. They might take you to see a doctor. The doctor can help you find out which foods to avoid. To remember which foods you might be allergic to, you can write them down or use a special app.
Yes, some foods can cause hives. These foods are nuts, shellfish, eggs, and some added chemicals in food. It's important to find out which food makes the hives and stay away from them.
Can you get itchy bumps from exercising?
When you exercise, your body gets hot and sweaty. Some people get itchy red bumps on their skin. These are called hives.
If you get hives, talking to a doctor can help. You can also try:
- Taking cool-down breaks while exercising
- Wearing loose clothes
- Showering quickly after exercising
- Using a soft cream or lotion for itchy skin
If you have trouble reading, you can ask someone to help. Listening to the text or using a tool to read it out loud can also help.
Yes, sometimes exercise can make a person's skin itchy and red. This can happen because their body gets warmer when they move a lot.
When do I need to see a doctor for hives?
If you have hives that last more than a few days, you should see a doctor. Go to the doctor if the hives are very bad or if you have trouble breathing or any other serious signs.
Can you stop hives from happening?
Hives are itchy, red bumps on your skin. They can be caused by allergies, stress, or heat.
You can try these things to stop hives:
- Stay away from things that give you allergies.
- Wear loose and comfy clothes.
- Use gentle soap and skin cream.
- Try to stay calm and not worry too much.
If you get hives a lot, talk to a doctor. They can help you find out what causes your hives and how to avoid them.
Ask an adult if you need help.
To stop hives, stay away from things that make them happen and try to keep calm. Sometimes, a doctor can suggest medicines or ways to handle allergies to stop hives from coming back.
Can children and babies get hives?
Yes, children and babies can get hives. Hives are red, itchy bumps on the skin. Here are some ways to help and check for hives: - Look for red, raised spots on the skin. - Ask the child if they feel itchy. - If the child is very uncomfortable, talk to a doctor. - You can calm itching with a cool, wet cloth. - Avoid scratching the spots to stop them from getting worse. Hives can sometimes happen because of things like certain foods, soap, or even weather changes. It is important to watch what your child touches or eats. If you need more help, there are some ways to understand more: - Use picture books to learn about skin and health. - Ask a doctor or a nurse for advice. - Use apps or videos made for kids to explain things simply. Remember to stay calm and patient while you help your child.Yes, people of all ages can get hives. This includes children and babies. The reasons for getting hives might be a little different, but how we take care of them is usually the same.
Can hives cause problems later on?
Hives can make your skin itchy and red. Most of the time, they go away after a while. But sometimes, they can come back or last a long time.
If you have hives often, it might help to talk to a doctor.
You can try these things to feel better:
- Avoid things that make your skin itchy.
- Wear loose clothes.
- Use a cool, damp cloth on your skin.
If reading is hard, try using an app that reads the text out loud or highlights words.
Hives usually do not cause problems that last for a long time. But if you get hives a lot, it can be something called chronic urticaria, and you might need to keep taking care of it. It's good to find out what is causing the hives, especially if you get them often.
Useful Links
This website offers general information and is not a substitute for professional advice.
Always seek guidance from qualified professionals.
If you have any medical concerns or need urgent help, contact a healthcare professional or emergency services immediately.
Some of this content was generated with AI assistance. We’ve done our best to keep it accurate, helpful, and human-friendly.
- Ergsy carfully checks the information in the videos we provide here.
- Videos shown by Youtube after a video has completed, have NOT been reviewed by ERGSY.
- To view, click the arrow in centre of video.
- Most of the videos you find here will have subtitles and/or closed captions available.
- You may need to turn these on, and choose your preferred language.
- Go to the video you'd like to watch.
- If closed captions (CC) are available, settings will be visible on the bottom right of the video player.
- To turn on Captions, click settings .
- To turn off Captions, click settings again.
More Items From Ergsy search
-

Hives - Skin Condition
Relevance: 100%
-
Is it true that sunbeds can help treat skin conditions like psoriasis?
Relevance: 40%
-

Skin cancer education
Relevance: 33%
-

What is a skin cancer screening?
Relevance: 31%
-

Skin Cancer - How do I check if my mole is skin cancer? | NHS
Relevance: 31%
-

Are skin rashes a side effect of weight loss drugs?
Relevance: 29%
-

Are skin lightening kist safe to use?
Relevance: 29%
-
Do sunbeds help improve skin tone and texture?
Relevance: 28%
-

What SPF should I use if I have sensitive skin?
Relevance: 27%
-
Do sunbeds offer any anti-aging benefits for the skin?
Relevance: 27%
-

What are some common conditions treated with homeopathy?
Relevance: 26%
-

Does stress contribute to nettle rash?
Relevance: 26%
-

What causes nettle rash?
Relevance: 24%
-
Is pre-tanning in a sunbed a good way to prepare my skin for sun exposure?
Relevance: 24%
-

How important is it to keep the skin moisturised with psoriasis?
Relevance: 23%
-

Can nettle rash spread from person to person?
Relevance: 23%
-

Diabetic Foot Conditions Podiatrist
Relevance: 22%
-
Is tinnitus a common condition?
Relevance: 22%
-

Is asthma a serious condition?
Relevance: 21%
-

Is BPH a serious condition?
Relevance: 21%
-

What are the symptoms of scabies?
Relevance: 21%
-
Is health-related anxiety a common condition?
Relevance: 20%
-
Is postnatal depression a long-term condition?
Relevance: 20%
-

What are the symptoms of a nut allergy?
Relevance: 20%
-

What condition does Wegovy treat?
Relevance: 20%
-

What is a pre-existing condition waiver in travel insurance?
Relevance: 19%
-

Is thrombosis a common condition?
Relevance: 19%
-

Can an indefinite sentence end with a conditional release?
Relevance: 19%
-

What are common symptoms of nettle rash?
Relevance: 19%
-

Can self-testing detect all eye conditions?
Relevance: 19%
-

What conditions is ketamine used to treat?
Relevance: 19%
-

What is the eye condition hypotony?
Relevance: 19%
-

When should I see a doctor for nettle rash?
Relevance: 19%
-

How is nettle rash diagnosed?
Relevance: 19%
-

Can weather conditions contribute to dangerous driving?
Relevance: 18%
-

What foods can trigger nettle rash?
Relevance: 18%
-

Is it possible to be allergic to the sun?
Relevance: 18%
-

Is nettle rash contagious?
Relevance: 18%
-

Are pre-existing medical conditions covered by holiday insurance policies?
Relevance: 18%
-

Can homeopathy treat all medical conditions?
Relevance: 18%


