
Find Help
More Items From Ergsy search
-

Are there any scientific studies supporting homeopathy?
Relevance: 100%
-

What is Homeopathy and Homeopathic Medecine?
Relevance: 59%
-

Is homeopathy widely used in the UK?
Relevance: 56%
-

Can homeopathy treat all medical conditions?
Relevance: 55%
-

Who founded homeopathy?
Relevance: 53%
-

How does homeopathy differ from conventional medicine?
Relevance: 52%
-

Is it necessary to stop conventional treatment when starting homeopathy?
Relevance: 47%
-

What are some common conditions treated with homeopathy?
Relevance: 46%
-

Is there any scientific evidence that links paracetamol use to autism?
Relevance: 38%
-

Can hypothesized variants be used in scientific modeling?
Relevance: 36%
-

Are homeopathic medicines safe?
Relevance: 35%
-

Do homeopathic medicines contain any active ingredients?
Relevance: 35%
-

What is the principle of 'like cures like'?
Relevance: 34%
-

Are homeopathic treatments covered by the NHS?
Relevance: 33%
-

Is there scientific evidence linking menopause to dementia?
Relevance: 32%
-

Is it possible to study nursing part-time?
Relevance: 28%
-

Where can I find research studies on air pollution and asthma in my area?
Relevance: 26%
-

Instructions for setting up your home sleep study
Relevance: 25%
-
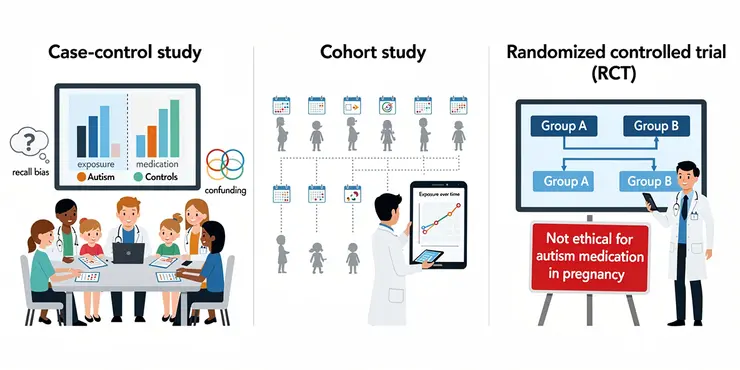
What kind of studies are conducted to investigate links between medications and autism?
Relevance: 24%
-

What is the main finding of the study linking screen time to sleep quality?
Relevance: 23%
-

New Study Links Diet Soda to Increased Risk of Heart Disease
Relevance: 23%
-

New Study Reveals Surprising Facts About Daily Step Counts
Relevance: 23%
-

Study Shows Link Between Screen Time and Sleep Quality
Relevance: 23%
-

Study Reveals Disparities in Welfare Support Between Urban and Rural Areas
Relevance: 23%
-

How are homeopathic medicines made?
Relevance: 22%
-
UK Study Links Poor Air Quality to Increased Asthma Cases in Urban Areas
Relevance: 22%
-
How long do studies suggest taking aspirin for cancer prevention?
Relevance: 21%
-

Who can prescribe homeopathic remedies?
Relevance: 21%
-
Are there ongoing studies about aspirin and colorectal cancer?
Relevance: 20%
-

Are there any long-term studies on the safety of nicotine pouches?
Relevance: 20%
-

How can I find a qualified homeopath in the UK?
Relevance: 20%
-

What are the limitations of studies examining paracetamol use and autism?
Relevance: 19%
-

Why is there concern about paracetamol and autism?
Relevance: 19%
-

Study Finds Alarming Increase in Childhood Obesity Rates Post-Pandemic
Relevance: 18%
-

Are there any studies that support the social media ban for under 16s?
Relevance: 18%
-

Is paracetamol linked to autism?
Relevance: 18%
-
Are vaccines linked to autism?
Relevance: 18%
-

What advancements have been made in understanding the bubonic plague?
Relevance: 15%
-

Is Paillon treatment used in any clinical trials?
Relevance: 14%
-

What research is being done on the Marburg virus?
Relevance: 14%
Scientific Evaluation of Homeopathy
Homeopathy, founded by Samuel Hahnemann in the 18th century, is based on two main principles: "like cures like" and the "law of minimum dose." It seeks to treat symptoms using highly diluted substances, with the belief that more dilute solutions tend to be more potent. However, the scientific community remains divided on the efficacy of homeopathy.
Clinical Trials and Meta-analyses
Several clinical trials have been conducted to evaluate the efficacy of homeopathy. However, the results are often mixed, varying in quality and consistency. A Cochrane systematic review, often cited as a rigorous standard for evidence-based medicine, has conducted analyses in this area. Some reviews suggest that homeopathy might have positive effects for certain conditions, yet they emphasize that these effects are difficult to distinguish from placebo responses. The British Medical Association has also highlighted the lack of scientific evidence to support homeopathy, and some meta-analyses conclude that homeopathy's effects are similar to placebo.
Mechanistic Studies of Homeopathic Solutions
While clinical outcomes are paramount, understanding the mechanisms behind homeopathy is also crucial. Current scientific research fails to provide a convincing mechanism of action for homeopathy that aligns with modern principles of chemistry and biology. Dilutions used in homeopathic preparations often exceed Avogadro's limit, which implies that these solutions contain no molecules of the original substance. This poses a significant challenge to the theoretical credence of homeopathy within traditional scientific frameworks.
Regulatory and Institutional Perspectives in the UK
In the UK, the National Health Service has been skeptical about the use of homeopathy. In recent years, the NHS has curtailed funding for homeopathic treatments due to insufficient evidence of their efficacy compared to cost. Furthermore, the House of Commons Science and Technology Committee has reported that homeopathic products should not be advocated as a treatment option until more robust evidence emerges.
Conclusion
Despite its popularity among some patient segments, homeopathy continues to be a contentious topic within the scientific community. In the UK, official perspectives lean towards a cautious approach, emphasizing the need for more extensive, rigorous scientific research to ascertain the practical utility of homeopathy in contemporary medical practice.
What is Homeopathy?
Homeopathy started a long time ago by a man named Samuel Hahnemann. It has two big ideas: "like cures like," and "use very small amounts." It tries to fix health problems by using things that are super tiny and diluted. Some people believe these tiny solutions work really well. But, many scientists do not agree on whether homeopathy works.
Homeopathy and Health Tests
Scientists have done many tests to see if homeopathy works. These tests have mixed results, which means sometimes they say it works, and other times it says it doesn't. Some studies suggest homeopathy might help with some health problems. But, it is hard to tell if it works better than pretend treatments like placebos. The British Medical Association says there is not enough strong proof that homeopathy works. Many studies say homeopathy works the same as placebos.
How Homeopathy Solutions Work
It is important to know how homeopathy is supposed to work. But right now, science does not have a good explanation for it. Homeopathy uses solutions that are so diluted, they might not have any of the original ingredient left. This makes it tricky for scientists to agree with how homeopathy works with what we know about chemistry and biology.
Homeopathy in the UK
In the UK, the National Health Service (NHS) is unsure about homeopathy. Lately, the NHS has stopped paying for homeopathy because there is not enough proof it works well. A group called the Science and Technology Committee says that homeopathy should not be used as a treatment until there is better proof it works.
The Last Word on Homeopathy
Even though some people like homeopathy, scientists still argue about it. In the UK, officials are careful and say more good research is needed before homeopathy can be used in modern medicine.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is homeopathy?
Homeopathy is an alternative medicine practice that involves using highly diluted substances with the aim of triggering the body's natural healing responses.
Are there any scientific studies supporting homeopathy?
There is limited scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of homeopathy. Most rigorous studies and systematic reviews have shown no significant benefit beyond placebo.
Is homeopathy regulated in the UK?
In the UK, homeopathic remedies are subject to regulation by the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA). They allow these products under specific regulations, but homeopathic products do not require proof of efficacy.
Why do some people believe in homeopathy?
Some people believe in homeopathy due to personal experiences, the placebo effect, or the appeal of natural treatments. Additionally, a holistic approach and the attention received from practitioners can contribute to perceived effectiveness.
What do major health organizations say about homeopathy?
Major health organizations like the NHS, World Health Organization (WHO), and the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) generally do not recommend homeopathy, citing insufficient evidence of effectiveness.
Has the NHS addressed the use of homeopathy?
The NHS in the UK has advised against the use of homeopathy due to lack of evidence supporting its effectiveness. In 2017, NHS England recommended that doctors stop prescribing homeopathic treatments.
What are some common conditions people use homeopathy for?
People commonly use homeopathy for conditions like allergies, asthma, chronic fatigue syndrome, migraines, rheumatoid arthritis, irritable bowel syndrome, and minor skin conditions.
Are there any safety concerns with homeopathy?
Homeopathy is generally considered safe since the remedies are highly diluted. However, safety concerns arise when people use homeopathy instead of proven medical treatments, potentially delaying effective care.
How does the scientific community evaluate homeopathy?
The scientific community generally evaluates homeopathy through controlled clinical trials and systematic reviews. Most of these evaluations have not demonstrated reliable evidence of efficacy beyond placebo effects.
What is the placebo effect, and how does it relate to homeopathy?
The placebo effect occurs when a patient experiences a perceived improvement in their condition due to their expectations, rather than the treatment itself. In homeopathy, many believe its effects can largely be attributed to placebo.
Are there any large-scale reviews of homeopathy?
Several large-scale reviews and meta-analyses, such as those conducted by the Cochrane Collaboration and the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, have concluded that there is no consistent evidence supporting homeopathy's efficacy.
How does homeopathy differ from conventional medicine?
Homeopathy differs from conventional medicine in its approach. Homeopathy uses highly diluted substances believed to trigger healing, whereas conventional medicine uses evidence-based practices and treatments backed by scientific research.
Can homeopathy be integrated with conventional treatment?
Some people choose to use homeopathy alongside conventional treatments, but it is important to consult with healthcare professionals to ensure it does not interfere with essential medical care.
Have any governmental bodies in the UK taken a stance on homeopathy?
Yes, the UK Parliament and NHS England have taken a stance against funding and recommending homeopathy due to a lack of scientific evidence supporting its effectiveness.
What should a patient consider before using homeopathy?
Patients considering homeopathy should assess the evidence, consult healthcare professionals, and ensure it does not replace proven medical treatments. They should be informed about possible placebo effects and the lack of scientific support.
What is homeopathy?
Homeopathy is a way to help people feel better. It uses very tiny amounts of natural things like plants and minerals. Some people believe it helps the body heal itself.
If you want to know more about homeopathy, you can:
- Ask a doctor or a nurse.
- Look at pictures or watch videos about it.
- Use a special app or tool that makes reading easier.
Homeopathy is a different way to treat people when they are sick. It uses tiny amounts of special things to help the body get better on its own.
Do scientists agree homeopathy works?
Scientists have not found much proof that homeopathy works. Most careful studies show that homeopathy is not better than a pretend treatment.
Is homeopathy controlled in the UK?
Homeopathy is a type of medicine. Is it checked or controlled by the government in the UK?
- Homeopathy is not checked by the government in the same way as other medicines.
- Some people think it helps. Others don't.
- If you want to try homeopathy, talk to your doctor first.
To understand better, you can:
- Ask someone you trust to explain it to you.
- Use apps that read texts out loud.
In the UK, there are rules for homeopathic medicines. The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) makes these rules. They say it is okay to sell these products, but homeopathic products do not have to show they work.
Here are some tips to help understand: - Break sentences into parts. Read one part at a time. - Use fingers to follow the words while reading. - Ask a friend to read with you and discuss what you read. - Look for picture books or videos about the topic to help you understand more.Why do some people like homeopathy?
Homeopathy is a way some people try to feel better when they are sick. It uses very tiny amounts of natural things like plants and minerals.
Here are some reasons why people like homeopathy:
- They believe it helps them feel better.
- They like natural ways to treat illness.
- They have had good experiences with homeopathy before.
- They know someone who used it and got better.
If you want to know more or try it, you can talk to a doctor or an expert. They can give you advice and help you make the best choice for your health.
Some people think homeopathy works because of their own experiences, or because they like natural treatments. Sometimes, if you think something will work, it feels like it does. This is called the placebo effect. Also, people like how homeopathy looks at the whole person and how much attention they get from the person giving the treatment.
What do big health groups think about homeopathy?
Big health groups like the NHS, World Health Organization (WHO), and the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) do not usually suggest homeopathy. They say there is not enough evidence to show it works well.
Is the NHS using homeopathy?
The NHS is the health service in the UK.
Homeopathy is a way some people try to get better using very small amounts of natural things.
The NHS has decided not to use homeopathy anymore because they say it does not work well enough.
If you have trouble reading, you might use tools like audiobooks or ask someone to read it to you.
It's always okay to ask for help if you need it!
The NHS is the UK's health service. They say not to use homeopathy because there is no proof it works. In 2017, NHS England told doctors to stop giving homeopathic treatments.
What problems do people try to fix with homeopathy?
People sometimes use homeopathy to help with common problems like:
- Feeling sad and worried (anxiety and depression)
- Allergies like sneezing and itching
- Headaches
- Colds and coughs
- Upset stomach
- Sore muscles or pain
Reading Tips:
- Use a finger or pencil to point at each word as you read.
- Read out loud to help you understand better.
- Use a ruler or paper to cover lines below the one you're reading. This helps you focus on one line at a time.
- Ask someone to read with you or help explain the words you don't know.
People often use homeopathy to help with things like allergies, asthma, feeling very tired, headaches, sore joints, tummy troubles, and small skin problems.
If you're finding it hard to read this, try using a finger or a ruler to follow along. You can also read out loud or use pictures to understand better.
Is homeopathy safe?
Homeopathy is usually safe because the medicine is very watered down. But there is a worry. If people use homeopathy instead of real medicine from the doctor, it could lead to problems because they might not get the right help in time.
What do scientists think about homeopathy?
Scientists study homeopathy to see if it works. They do tests to find out if taking homeopathy makes people better.
If you want help understanding this, you can:
- Ask someone to read it with you.
- Use a dictionary to learn new words.
- Watch videos that explain homeopathy.
Scientists check if homeopathy works by doing special tests and reviews. Most tests show that homeopathy works no better than a fake treatment that doesn't do anything.
What is the placebo effect, and how does it relate to homeopathy?
The placebo effect is when you feel better after taking a fake treatment, like a sugar pill, because you believe it will help you.
Homeopathy is a type of medicine that uses very tiny amounts of natural substances. People who use it sometimes feel better because of the placebo effect.
To help understand better, you can:
- Use pictures to explain ideas.
- Ask someone to read with you.
- Watch videos about the placebo effect and homeopathy.
The placebo effect happens when someone feels better because they believe they will, not because of the medicine. In homeopathy, many people think it works mainly because of the placebo effect.
Is there a big study about homeopathy?
Big studies by groups like the Cochrane Collaboration and the Australian Health Council looked at homeopathy. They found that homeopathy does not always work.
How is homeopathy different from regular medicine?
Homeopathy and regular medicine are two ways to help people feel better.
Homeopathy uses very tiny amounts of natural things, like plants and minerals, to help the body heal itself.
Regular medicine uses drugs and treatments tested by scientists to stop or fix what makes us sick.
If you have more questions, you can talk to a doctor or a nurse. They can help you understand more.
Homeopathy and regular medicine are different. Homeopathy uses tiny amounts of substances thought to help heal the body. Regular medicine uses methods proven by science and research.
Can homeopathy work with regular medicine?
Some people like to use homeopathy with their usual medicine. It is very important to talk to a doctor to make sure it is safe and does not stop the regular medicine from working.
What do UK government groups think about homeopathy?
Homeopathy is a way some people try to feel better using tiny amounts of natural things. Some people think it helps, and some do not. In the UK, there are government groups that share their thoughts about homeopathy.
If you want to understand what these groups say, you can:
- Ask someone you trust to explain it to you.
- Use apps that read the words out loud for you.
These can help make the information clearer and easier to understand.
Yes, the UK Parliament and NHS England decided not to pay for homeopathy. This is because there is no proof that it works.
Things to think about before using homeopathy
If you are thinking about trying homeopathy, here are some things to do:
- Look at the facts and evidence. This means checking if it really works.
- Talk to a doctor or nurse. They can give good advice.
- Remember, homeopathy should not take the place of real medicine.
- Know that homeopathy might work because you believe it will, not because it actually does.
- Understand that scientists do not have strong proof that homeopathy works.
Useful Links
This website offers general information and is not a substitute for professional advice.
Always seek guidance from qualified professionals.
If you have any medical concerns or need urgent help, contact a healthcare professional or emergency services immediately.
Some of this content was generated with AI assistance. We’ve done our best to keep it accurate, helpful, and human-friendly.
- Ergsy carfully checks the information in the videos we provide here.
- Videos shown by Youtube after a video has completed, have NOT been reviewed by ERGSY.
- To view, click the arrow in centre of video.
- Most of the videos you find here will have subtitles and/or closed captions available.
- You may need to turn these on, and choose your preferred language.
- Go to the video you'd like to watch.
- If closed captions (CC) are available, settings will be visible on the bottom right of the video player.
- To turn on Captions, click settings .
- To turn off Captions, click settings again.
More Items From Ergsy search
-

Are there any scientific studies supporting homeopathy?
Relevance: 100%
-

What is Homeopathy and Homeopathic Medecine?
Relevance: 59%
-

Is homeopathy widely used in the UK?
Relevance: 56%
-

Can homeopathy treat all medical conditions?
Relevance: 55%
-

Who founded homeopathy?
Relevance: 53%
-

How does homeopathy differ from conventional medicine?
Relevance: 52%
-

Is it necessary to stop conventional treatment when starting homeopathy?
Relevance: 47%
-

What are some common conditions treated with homeopathy?
Relevance: 46%
-

Is there any scientific evidence that links paracetamol use to autism?
Relevance: 38%
-

Can hypothesized variants be used in scientific modeling?
Relevance: 36%
-

Are homeopathic medicines safe?
Relevance: 35%
-

Do homeopathic medicines contain any active ingredients?
Relevance: 35%
-

What is the principle of 'like cures like'?
Relevance: 34%
-

Are homeopathic treatments covered by the NHS?
Relevance: 33%
-

Is there scientific evidence linking menopause to dementia?
Relevance: 32%
-

Is it possible to study nursing part-time?
Relevance: 28%
-

Where can I find research studies on air pollution and asthma in my area?
Relevance: 26%
-

Instructions for setting up your home sleep study
Relevance: 25%
-

What kind of studies are conducted to investigate links between medications and autism?
Relevance: 24%
-

What is the main finding of the study linking screen time to sleep quality?
Relevance: 23%
-

New Study Links Diet Soda to Increased Risk of Heart Disease
Relevance: 23%
-

New Study Reveals Surprising Facts About Daily Step Counts
Relevance: 23%
-

Study Shows Link Between Screen Time and Sleep Quality
Relevance: 23%
-

Study Reveals Disparities in Welfare Support Between Urban and Rural Areas
Relevance: 23%
-

How are homeopathic medicines made?
Relevance: 22%
-
UK Study Links Poor Air Quality to Increased Asthma Cases in Urban Areas
Relevance: 22%
-
How long do studies suggest taking aspirin for cancer prevention?
Relevance: 21%
-

Who can prescribe homeopathic remedies?
Relevance: 21%
-
Are there ongoing studies about aspirin and colorectal cancer?
Relevance: 20%
-

Are there any long-term studies on the safety of nicotine pouches?
Relevance: 20%
-

How can I find a qualified homeopath in the UK?
Relevance: 20%
-

What are the limitations of studies examining paracetamol use and autism?
Relevance: 19%
-

Why is there concern about paracetamol and autism?
Relevance: 19%
-

Study Finds Alarming Increase in Childhood Obesity Rates Post-Pandemic
Relevance: 18%
-

Are there any studies that support the social media ban for under 16s?
Relevance: 18%
-

Is paracetamol linked to autism?
Relevance: 18%
-

Are vaccines linked to autism?
Relevance: 18%
-

What advancements have been made in understanding the bubonic plague?
Relevance: 15%
-

Is Paillon treatment used in any clinical trials?
Relevance: 14%
-

What research is being done on the Marburg virus?
Relevance: 14%


