Find Help
More Items From Ergsy search
-

What is Cancer?
Relevance: 100%
-

Ovarian Cancer
Relevance: 100%
-

Vaginal Cancer
Relevance: 100%
-

Endometrial Cancer
Relevance: 100%
-

Vulval Cancer
Relevance: 99%
-

Endometrial Cancer
Relevance: 99%
-

Endometrial Cancer
Relevance: 99%
-
What is the difference between colon cancer and rectal cancer?
Relevance: 97%
-
What is cancer screening?
Relevance: 95%
-

What is testicular cancer?
Relevance: 95%
-

What is colorectal cancer?
Relevance: 95%
-

What is Bowel Cancer?
Relevance: 95%
-

Treating prostate cancer
Relevance: 95%
-

Mouth Cancer Awareness
Relevance: 95%
-

What is testicular cancer?
Relevance: 95%
-

What is Prostate Cancer?
Relevance: 95%
-

What is testicular cancer?
Relevance: 95%
-

Is testicular cancer treatable?
Relevance: 94%
-
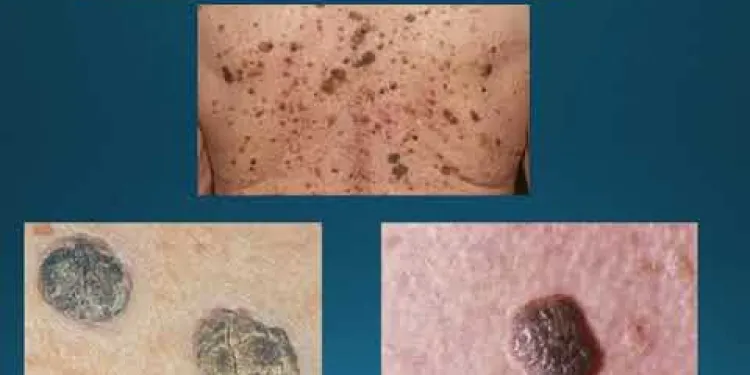
Skin cancer education
Relevance: 94%
-

Living with prostate cancer
Relevance: 94%
-

What is Pancreatic Cancer?
Relevance: 94%
-

Mouth Cancer Infomercial
Relevance: 94%
-
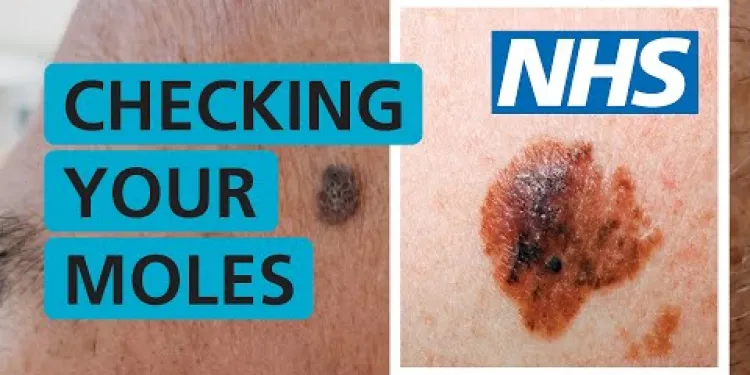
Skin Cancer - How do I check if my mole is skin cancer? | NHS
Relevance: 93%
-

Breakthrough in Cancer Treatment Offers Hope for Prostate Cancer Patients
Relevance: 93%
-
AI Breast Cancer Screening in the UK
Relevance: 92%
-

How common is testicular cancer?
Relevance: 91%
-
What causes testicular cancer?
Relevance: 91%
-

What is a skin cancer screening?
Relevance: 91%
-

Raising awareness of ovarian cancer
Relevance: 90%
-

What are the stages of testicular cancer?
Relevance: 90%
-

How is prostate cancer treated?
Relevance: 90%
-

Who is at risk for testicular cancer?
Relevance: 90%
-

Am I more at risk of prostate cancer?
Relevance: 90%
-

Can HPV lead to cancer?
Relevance: 90%
-

How to do the FIT bowel cancer screening test | Cancer Research UK
Relevance: 90%
-

What are the symptoms of testicular cancer?
Relevance: 90%
-
How common is bowel cancer?
Relevance: 90%
-

Head and Neck Cancer Diagnosis
Relevance: 90%
-

Can bowel cancer be prevented?
Relevance: 90%
-

How is bowel cancer diagnosed?
Relevance: 90%
Cancer is a complex and multifaceted disease characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells in the body. Normal cells in the body grow, divide, and die in a controlled manner as part of the natural process of tissue renewal and repair. However, in cancer, this orderly process goes awry, leading to the formation of tumors or the invasion of nearby tissues and organs by malignant cells.
There are over 100 different types of cancer, each with its own set of causes, risk factors, and characteristics. Cancer can arise from virtually any type of cell in the body, and its development often involves a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
The process of cancer formation, known as carcinogenesis, typically involves multiple stages, starting with the initiation of genetic mutations or alterations that disrupt normal cellular functions. These mutations can be caused by various factors, including exposure to carcinogens (such as tobacco smoke or ultraviolet radiation), genetic predisposition, infections, and hormonal imbalances.
As cancer progresses, cells acquire additional mutations that enable them to proliferate uncontrollably, evade the body's immune defenses, and invade surrounding tissues and organs. Ultimately, cancer can metastasize, spreading to distant parts of the body via the bloodstream or lymphatic system, and forming secondary tumors. Despite significant advances in cancer research and treatment, cancer remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide, underscoring the importance of continued efforts to better understand and combat this devastating disease.
Treatment options for cancer vary widely depending on the type and stage of the cancer, as well as individual patient factors. Here is a general list of common treatment modalities:
- Surgery: Surgical removal of tumors or cancerous tissue is often the primary treatment for localized cancers.
- Chemotherapy: Drugs are used to kill cancer cells or slow their growth. Chemotherapy can be given orally, intravenously, or through other methods.
- Radiation therapy: High-energy radiation beams are targeted at the cancer to destroy cancer cells or stop their growth. It may be administered externally (external beam radiation) or internally (brachytherapy).
- Immunotherapy: This treatment harnesses the power of the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. It includes therapies such as checkpoint inhibitors, CAR-T cell therapy, and cancer vaccines.
- Targeted therapy: Drugs specifically target abnormalities in cancer cells, such as gene mutations or protein overexpression, to disrupt their growth and survival.
- Hormone therapy: Hormone-blocking drugs or surgery may be used to inhibit hormone-sensitive cancers, such as breast or prostate cancer.
- Stem cell transplant: Also known as bone marrow transplant, this procedure replaces diseased or damaged bone marrow with healthy stem cells to treat certain blood cancers or other conditions.
- Precision medicine: Treatment plans are tailored based on the unique genetic makeup of the cancer through techniques such as molecular profiling and genomic testing.
- Palliative care: Focuses on symptom management and improving quality of life for patients with advanced cancer, often provided alongside curative treatments.
- Clinical trials: Investigational treatments are tested in clinical trials to evaluate their safety and effectiveness, offering potential access to cutting-edge therapies.
Treatment plans are typically individualized based on the specific characteristics of the cancer, including its type, stage, and molecular profile, as well as the patient's overall health and preferences. A multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals collaborates to develop the most appropriate and effective treatment strategy for each patient.
What is Cancer?
Cancer is a disease characterised by the rapid and uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells. If the growth spreads to other parts of the body, it can be life-threatening. In the United Kingdom, cancer remains one of the leading causes of mortality, affecting hundreds of thousands of people each year.
How Does Cancer Develop?
Cancer develops when genetic mutations within cells cause them to grow and divide uncontrollably. These abnormal cells can aggregate to form a mass called a tumour. Not all tumours are cancerous; benign tumours do not spread to other parts of the body, whereas malignant tumours do.
Common Types of Cancer
In the UK, the most common types of cancer are breast cancer, lung cancer, prostate cancer, and bowel cancer. Each type affects different parts of the body and has distinct risk factors and symptoms.
Symptoms of Cancer
Symptoms vary widely depending on the type and stage of cancer. Common symptoms include unexplained weight loss, persistent fatigue, unusual bleeding, and lumps or swelling. Early detection through screening and awareness of these symptoms is crucial for effective treatment.
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing cancer. These include lifestyle factors like smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, poor diet, and lack of physical activity. Genetic factors and exposure to certain chemicals or radiation also contribute to cancer risk.
Treatment Options
Treatment for cancer varies based on the type, location, and stage of the disease. Common treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted drug therapy. In the UK, the NHS provides comprehensive care and support for cancer patients, aiming for early diagnosis and prompt treatment.
Prevention and Early Detection
Prevention strategies are crucial in reducing the incidence of cancer. These include a healthy lifestyle, vaccinations (e.g., HPV vaccine for cervical cancer), and regular screenings like mammograms and colonoscopies. Early detection significantly improves the chances of successful treatment and survival.
Cancer is a disease that happens when bad cells in the body grow too fast and don't stop. Normal cells grow, divide, and die in a controlled way, which helps our body stay healthy. But in cancer, this process doesn't work right, and bad cells can form lumps called tumors or spread to other parts of the body.
There are more than 100 types of cancer. Each type has different causes and risks. Cancer can start in any cell in the body. It often happens because of a mix of gene problems, things in the environment, and how we live our lives.
Cancer starts when something changes in the genes and makes cells act differently. These changes, called mutations, can be caused by things like smoking, too much sun, our family history, infections, or hormone changes.
As cancer grows, cells change more and grow faster. They can hide from the body's defense system and invade other parts of the body. Cancer can spread to far places in the body through blood or the lymph system. While we know a lot about cancer, it is still one of the main causes of death in the world. That's why learning more and fighting cancer is very important.
There are many ways to treat cancer. The treatment depends on the type of cancer, how far it has spread, and the person’s health. Here are some common treatments:
- Surgery: Doctors remove the tumor or cancer cells from the body.
- Chemotherapy: Special medicine kills cancer cells or slows them down. It can be taken by mouth or through a needle.
- Radiation therapy: Strong energy beams are aimed at the cancer to destroy it or stop it from growing.
- Immunotherapy: Uses the body's defense system to fight cancer cells. Includes special treatments like vaccines or cell therapy.
- Targeted therapy: Uses drugs that focus on what's wrong in cancer cells to stop them growing.
- Hormone therapy: Blocks hormones to slow some cancers, like breast or prostate cancer.
- Stem cell transplant: Replaces damaged bone marrow with healthy cells. Helps certain blood cancers.
- Precision medicine: Looks at the cancer's genes to find the best treatment for each person.
- Palliative care: Helps make people feel better. Focuses on reducing symptoms and making life more comfortable for those with serious cancers.
- Clinical trials: Tests new treatments to see if they work well and are safe. People may try these to access new therapies.
Treatment plans are made just for each person. They look at the type and stage of cancer and what the person prefers. A team of doctors and healthcare workers work together to decide the best treatment plan.
For help understanding information, tools like audiobooks or simple explanation videos can be helpful. Also, talking with healthcare providers who can explain things in simple words is a good idea.
What is Cancer?
Cancer is a very serious illness. It happens when bad cells in the body grow fast and spread. If the bad cells move to other parts of the body, it can be very dangerous. Many people in the UK get cancer every year.
How Does Cancer Develop?
Cancer starts when something inside the cells goes wrong. This makes them grow and divide too much. These cells can form a lump called a tumour. Some tumours are not harmful and do not spread. But bad tumours can spread to other parts of the body.
Common Types of Cancer
There are different kinds of cancer. The most common in the UK are breast cancer, lung cancer, prostate cancer, and bowel cancer. Each one affects different parts of the body and has its own signs and risks.
Symptoms of Cancer
Signs of cancer can be different for each person. Some common signs are losing weight without trying, feeling very tired, bleeding that is not normal, and finding lumps or swellings. It is important to know these signs and see a doctor early.
Risk Factors
Some things make it more likely to get cancer. These include smoking, drinking too much alcohol, eating unhealthy food, and not exercising. Other things like family history and being around certain chemicals can also increase the risk.
Treatment Options
The way cancer is treated depends on where it is and how serious it is. Doctors may use surgery, drugs like chemotherapy, and therapy with radiation. In the UK, the NHS helps people with cancer get good care and treatment.
Prevention and Early Detection
There are ways to lower the chance of getting cancer. These include living a healthy life, getting vaccinations like the HPV vaccine, and going for health checks like mammograms. Finding cancer early makes it easier to treat and gives a better chance of getting well.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is cancer?
Cancer is a disease where abnormal cells divide uncontrollably and destroy body tissue. It can start almost anywhere in the body.
How many types of cancer are there?
There are over 200 different types of cancer, each classified by the type of cell that initially becomes cancerous.
What are the common symptoms of cancer?
Common symptoms can include lumps, weight loss, fatigue, skin changes, and persistent pain or cough, but symptoms vary widely depending on the type of cancer.
How is cancer diagnosed?
Cancer is diagnosed through various tests such as blood tests, imaging (like X-rays, CT scans, MRI), and biopsies where a tissue sample is examined.
What causes cancer?
Cancer can be caused by genetic factors, lifestyle choices (like smoking and diet), infections, environmental exposures to chemicals and radiation, and other factors.
Can cancer be prevented?
While not all cancers can be prevented, reducing risk factors such as avoiding tobacco, eating a healthy diet, exercising, and protecting against infections can help lower the risk.
What treatments are available for cancer?
Treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and hormone therapy, depending on the cancer type and stage.
Is cancer contagious?
No, cancer is not contagious. It cannot be spread from person to person.
What is staging in cancer?
Staging describes the extent of cancer in the body, including the size of the tumor and whether it has spread. Commonly used systems include TNM (Tumor, Nodes, Metastasis) and number stages (1 through 4).
How important is early detection in cancer treatment?
Early detection significantly improves the chances of successful treatment and survival, as cancer caught at an early stage is often easier to treat.
What is metastasis?
Metastasis occurs when cancer cells spread from the primary site to other parts of the body, forming new tumors.
Are there any side effects to cancer treatments?
Yes, treatments can have side effects such as fatigue, nausea, hair loss, and increased susceptibility to infection. These vary based on the type and duration of treatment.
Can lifestyle changes help to manage cancer?
Yes, maintaining a healthy diet, exercising, reducing stress, and avoiding tobacco can help manage cancer and improve quality of life during and after treatment.
How can someone support a loved one with cancer?
Offering emotional support, helping with daily tasks, attending medical appointments, and listening can be very helpful to someone going through cancer treatment.
Where can I find reliable information about cancer in the UK?
Reliable information can be found through organisations like Cancer Research UK, Macmillan Cancer Support, the NHS, and the British Cancer Foundation.
What is cancer?
Cancer is a disease. It happens when some cells in the body grow too much and too fast. These cells can make lumps called tumors. Sometimes, cancer can spread to other parts of the body.
It is important to talk to a doctor if you have questions about cancer. They can help you understand it more.
Using pictures and videos can help make this information clearer.
Cancer is a sickness. It happens when bad cells grow too fast. These cells can hurt the body.
What different kinds of cancer are there?
There are more than 200 kinds of cancer. Each kind is named after the cell where the cancer starts.
What are the signs that someone might have cancer?
Cancer is a sickness. Here are some signs that could mean someone has cancer:
- A lump or bump in the body.
- Feeling very tired all the time.
- Losing weight without trying.
- Pain that doesn’t go away.
- Coughing that doesn’t stop or a croaky voice.
- Changes when going to the toilet, like a tummy ache or diarrhea.
- Unexplained bleeding or bruising.
- Skin changes, like a sore that doesn’t heal.
If you see these signs, talk to a doctor.
Using pictures and saying things out loud can help understand better. You can ask someone to read it with you.
Cancer can make you feel different in your body. You might see or feel a lump. You could lose weight without trying. Sometimes, you feel very tired. Your skin might look different. You might have pain that won't go away or a cough that sticks around. These signs can be different for each type of cancer.
How do doctors find out if someone has cancer?
Doctors use special tests to find out if a person has cancer. Here are some ways they do it:
- Talking and checking: The doctor asks questions about how you feel and checks your body.
- Pictures: They might take special pictures of the inside of your body, like X-rays or scans.
- Lab tests: Sometimes they test your blood or urine in a lab.
- Biopsy: The doctor might take a small piece of body tissue to look at under a microscope.
Tools to help:
- Ask for help: Talk to an adult you trust if you need help understanding.
- Use simple words: Ask doctors to explain things in simple words.
- Take notes: Write down or draw pictures about what you learn to remember better.
Doctors check for cancer using different tests. These include blood tests, pictures of the inside of your body (like X-rays, CT scans, and MRI), and biopsies. A biopsy is when doctors take a tiny piece of your body to look at it closely.
What makes cancer happen?
Cancer is when cells in the body grow in a way that is not normal.
Here are some things that can make cancer start:
- Smoking or breathing in smoke from others.
- Being in the sun too much without skin protection.
- Eating unhealthy food often.
- Some germs and viruses.
- Cancer can also run in families.
You can try to stay healthy by:
- Not smoking.
- Wearing sunscreen when outside.
- Eating lots of fruits and vegetables.
- Seeing a doctor for check-ups.
If you want to know more, you can use a book or a tool that reads text out loud.
Cancer can happen because of different reasons. Some reasons are in your genes, things you do (like smoking and what you eat), germs, things around you like chemicals and radiation, and other things too.
Can we stop cancer before it starts?
Cancer is a big illness. But there are ways to help stop it before it happens. Here are some things you can do:
- Eat healthy foods like fruits and vegetables.
- Move your body by playing or exercising every day.
- Don't smoke or be around people who smoke.
- Wear sunscreen to protect your skin from the sun.
- Go to the doctor for check-ups to stay healthy.
These tips can help keep you strong and healthy. If you want more help, ask a parent, teacher, or doctor. They can give you more ideas and support.
You can't stop all cancers from happening. But you can do things to make it less likely. Don't use tobacco. Eat healthy food. Exercise and move your body. Keep away from things that can make you sick. These things can help lower your risk.
What treatments can help with cancer?
If someone is sick with cancer, there are ways to help them feel better. Here are some ways:
- Medicine: There are special drugs that doctors can give to kill cancer cells.
- Radiation: This uses powerful rays to destroy cancer cells.
- Surgery: Sometimes doctors need to remove the cancer with an operation.
- Healthy Eating: Eating good food can make you stronger.
- Support Groups: Talking to others can help people feel less alone.
It's important to talk to a doctor about what is best. They know how to help. Using pictures, videos, or talking to someone can also make it easier to understand.
Doctors can help treat cancer in different ways. What they do depends on what type of cancer it is and how serious it is. Here are some ways they might help:
- They might do an operation to take out the cancer. This is called surgery.
- They might give you strong medicine to kill the cancer cells. This is called chemotherapy.
- They might use special rays to kill cancer cells. This is called radiation therapy.
- They might help your body fight cancer by using its own defenses. This is called immunotherapy.
- They might give you medicine that targets cancer cells specifically. This is called targeted therapy.
- They might use medicine to change hormones that can help cancer grow. This is called hormone therapy.
It’s important to talk with your doctor about which treatment is best for you. .
Can you catch cancer from someone?
No, you cannot catch cancer from someone else. Cancer is not like a cold or flu that spreads from one person to another.
If you are worried or want to learn more, you can:
- Talk to a doctor or nurse.
- Read books or look online for easy information about cancer.
- Ask an adult to help explain things to you.
No, cancer is not something you can catch. You can't get it from someone else.
What does staging in cancer mean?
"Staging" tells us how big cancer is and if it has spread in the body. It's like a map that helps doctors understand the cancer. This way, they know the best way to treat it.
To help with reading:
- Use a ruler or finger to keep your place.
- Read out loud slowly.
- Ask someone to read with you.
Staging tells us how big the cancer is and if it has spread to other parts of the body. We use systems like TNM (which stands for Tumor, Nodes, Metastasis) and number stages from 1 to 4 to describe it.
Why is it good to find cancer early?
Finding cancer early is very important. It helps doctors treat it better. If we find cancer early, there are more ways to help. People can get well faster.
Here are some things that can help:
- Regular check-ups with the doctor.
- Talking to the doctor about any changes in your body.
- Using tools like apps or reminders to keep track of doctor visits.
Remember to see your doctor if you feel something is wrong. They are there to help you.
Finding cancer early can help doctors treat it better. When cancer is found early, it is often easier to make the person healthy again. This can help people live longer.
What is metastasis?
Metastasis is when cancer spreads to other parts of the body. Cancer can move from the place it started to a new place. This can happen through the blood or lymph system.
It is important to talk to a doctor to understand more. Doctors can explain what this means for you or someone you know.
Using pictures, diagrams, or a simple video can help explain how cancer moves. If you find it hard to understand, ask someone you trust to help you learn more.
Cancer can move to other parts of the body. This is called metastasis. When this happens, small cancer cells travel from the first place where cancer started. Then, they make new lumps in other parts of the body.
Do cancer treatments have side effects?
Cancer treatments might have some side effects, like feeling tired or feeling sick. It's important to talk to a doctor or nurse about how you are feeling.
Using pictures, videos, or asking someone to explain in simple words can help you understand better.
Yes, treatments can have side effects. These are things that might happen because of the treatment. You might feel very tired, feel sick in your tummy, lose your hair, or get sick more easily. These side effects can be different depending on the kind of treatment and how long you have it.
Can changing how we live help with cancer?
Yes, sometimes changing how we live can help. Here are some ways:
- Eat Healthy: Eating good food helps our bodies. Try fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Exercise: Moving our bodies is good. Try to walk, run, or play outside.
- Rest Well: Sleeping enough helps us feel strong. Try to go to bed at the same time every night.
- Stay Calm: Feeling less worried is good. Try deep breathing or gentle stretches.
- Talk to Your Doctor: They can give you the best ideas for staying healthy.
If reading is hard, you can ask someone to read with you. Using pictures or videos can also help you understand better. You can also use tools that read text out loud. These tips can help you learn about cancer and feel better.
Yes, eating healthy food, moving your body, staying calm, and not smoking can help you feel better if you have cancer. It can also help you feel good when getting better.
How can you help someone you love who has cancer?
When someone you care about has cancer, you can help them feel better. Here are some easy ways to help:
1. Be There to Listen: Let them talk about their feelings. Just listening can help a lot.
2. Help with Daily Tasks: Offer to help with things like making meals or cleaning the house. It can make their day easier.
3. Go to Appointments: If they want, go with them to see the doctor. You can help them remember what the doctor says.
4. Send Notes or Cards: Write a nice note or card to cheer them up and show you care.
5. Learn About Cancer: Read simple books or use websites with easy information to understand what they are going through.
6. Be Patient: They might have good days and bad days. Be understanding and patient with them.
If you need more help, ask a nurse or doctor for advice. They have good ideas on how to support your loved one.
You can help a friend with cancer in these ways:
- Be there to listen and show you care.
- Help them with things like cooking or cleaning.
- Go with them to see the doctor.
- Be kind and supportive. Let them know you’re there for them.
Where can I find good and trusted information about cancer in the UK?
If you want to learn more about cancer, there are places you can go for good information:
- Check the NHS website. It has lots of information about health.
- The Macmillan Cancer Support website is another good place to look.
- You can also visit the Cancer Research UK website for details.
Using support tools can help:
- Ask a friend or family member to help you read.
- You can also use text-to-speech tools that read the words out loud.
- Look for pictures or videos that explain things.
You can find good information from places like Cancer Research UK, Macmillan Cancer Support, the NHS, and the British Cancer Foundation.
Useful Links
- Ergsy carfully checks the information in the videos we provide here.
- Videos shown by Youtube after a video has completed, have NOT been reviewed by ERGSY.
- To view, click the arrow in centre of video.
- Most of the videos you find here will have subtitles and/or closed captions available.
- You may need to turn these on, and choose your preferred language.
- Go to the video you'd like to watch.
- If closed captions (CC) are available, settings will be visible on the bottom right of the video player.
- To turn on Captions, click settings .
- To turn off Captions, click settings again.
More Items From Ergsy search
-

What is Cancer?
Relevance: 100%
-

Ovarian Cancer
Relevance: 100%
-

Vaginal Cancer
Relevance: 100%
-

Endometrial Cancer
Relevance: 100%
-

Vulval Cancer
Relevance: 99%
-

Endometrial Cancer
Relevance: 99%
-

Endometrial Cancer
Relevance: 99%
-

What is the difference between colon cancer and rectal cancer?
Relevance: 97%
-

What is cancer screening?
Relevance: 95%
-

What is testicular cancer?
Relevance: 95%
-

What is colorectal cancer?
Relevance: 95%
-

What is Bowel Cancer?
Relevance: 95%
-

Treating prostate cancer
Relevance: 95%
-

Mouth Cancer Awareness
Relevance: 95%
-

What is testicular cancer?
Relevance: 95%
-

What is Prostate Cancer?
Relevance: 95%
-

What is testicular cancer?
Relevance: 95%
-

Is testicular cancer treatable?
Relevance: 94%
-

Skin cancer education
Relevance: 94%
-

Living with prostate cancer
Relevance: 94%
-

What is Pancreatic Cancer?
Relevance: 94%
-

Mouth Cancer Infomercial
Relevance: 94%
-

Skin Cancer - How do I check if my mole is skin cancer? | NHS
Relevance: 93%
-

Breakthrough in Cancer Treatment Offers Hope for Prostate Cancer Patients
Relevance: 93%
-

AI Breast Cancer Screening in the UK
Relevance: 92%
-

How common is testicular cancer?
Relevance: 91%
-

What causes testicular cancer?
Relevance: 91%
-

What is a skin cancer screening?
Relevance: 91%
-

Raising awareness of ovarian cancer
Relevance: 90%
-

What are the stages of testicular cancer?
Relevance: 90%
-

How is prostate cancer treated?
Relevance: 90%
-

Who is at risk for testicular cancer?
Relevance: 90%
-

Am I more at risk of prostate cancer?
Relevance: 90%
-

Can HPV lead to cancer?
Relevance: 90%
-

How to do the FIT bowel cancer screening test | Cancer Research UK
Relevance: 90%
-

What are the symptoms of testicular cancer?
Relevance: 90%
-

How common is bowel cancer?
Relevance: 90%
-

Head and Neck Cancer Diagnosis
Relevance: 90%
-

Can bowel cancer be prevented?
Relevance: 90%
-

How is bowel cancer diagnosed?
Relevance: 90%


