
Find Help
More Items From Ergsy search
-

How is testicular cancer diagnosed?
Relevance: 100%
-
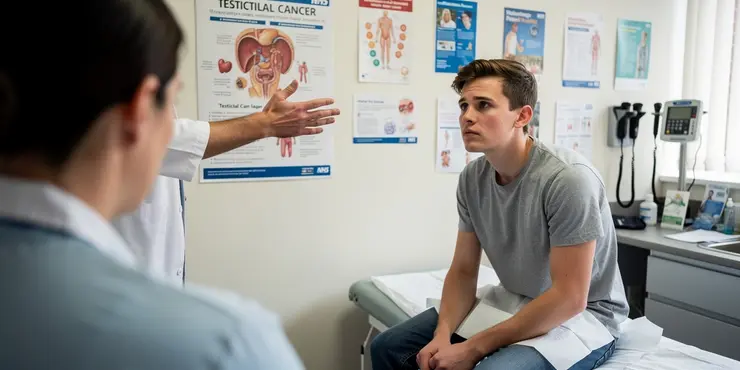
What is testicular cancer?
Relevance: 96%
-

What is testicular cancer?
Relevance: 96%
-
What is testicular cancer?
Relevance: 95%
-

Is testicular cancer treatable?
Relevance: 94%
-

Can testicular cancer spread to other parts of the body?
Relevance: 89%
-

What are the stages of testicular cancer?
Relevance: 88%
-

What is the survival rate for testicular cancer?
Relevance: 88%
-

What are the symptoms of testicular cancer?
Relevance: 88%
-

How common is testicular cancer?
Relevance: 87%
-

What causes testicular cancer?
Relevance: 87%
-
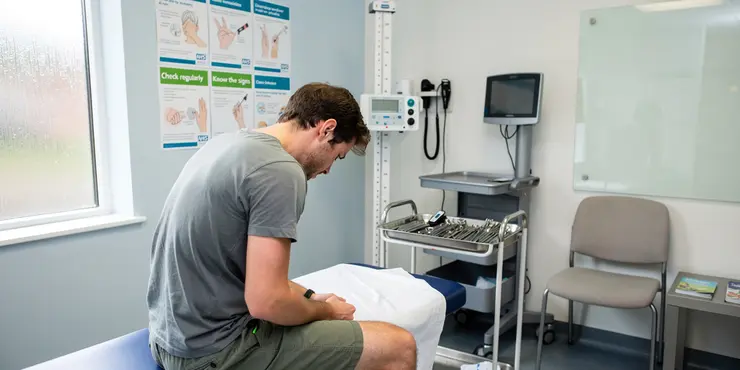
Who is at risk for testicular cancer?
Relevance: 86%
-

What role do tumor markers play in testicular cancer?
Relevance: 86%
-

Is fertility affected by testicular cancer?
Relevance: 85%
-

Are there support groups for those affected by testicular cancer?
Relevance: 84%
-

Getting to know your Testicles: Testicular Cancer Awareness with Dr James Howarth, Spilsby Surgery
Relevance: 83%
-

What types of treatments are available for testicular cancer?
Relevance: 82%
-

Can lifestyle changes help prevent testicular cancer?
Relevance: 80%
-

Can testicular cancer recur after treatment?
Relevance: 80%
-

How can I perform a testicular self-exam?
Relevance: 61%
-
Prostate cancer diagnosis and tests
Relevance: 58%
-
Are AI systems used alone in lung cancer diagnosis or alongside human radiologists?
Relevance: 58%
-

Head and Neck Cancer Diagnosis
Relevance: 57%
-

What is a seminoma?
Relevance: 43%
-

When should I see a doctor about potential testicular cancer?
Relevance: 43%
-

What's the difference between seminomas and non-seminomas?
Relevance: 42%
-
How is bowel cancer diagnosed?
Relevance: 41%
-

What are the risk factors for bowel cancer?
Relevance: 40%
-
What is the purpose of a bone scan in prostate cancer treatment?
Relevance: 40%
-

What support is available for individuals diagnosed with bowel cancer?
Relevance: 40%
-

Vulval Cancer
Relevance: 39%
-

Vaginal Cancer
Relevance: 39%
-
How can AI improve patient outcomes in lung cancer?
Relevance: 39%
-
What is Pancreatic Cancer?
Relevance: 39%
-

Endometrial Cancer
Relevance: 39%
-

What is Bowel Cancer?
Relevance: 39%
-

Endometrial Cancer
Relevance: 39%
-

Ovarian Cancer
Relevance: 38%
-

Mouth Cancer Infomercial
Relevance: 37%
-

Worried about signs that could be cancer? Contact your GP practice | NHS
Relevance: 37%
Introduction to Testicular Cancer Diagnosis
Testicular cancer, while relatively rare compared to other forms of cancer, typically affects younger men, particularly those aged between 15 and 49. Early diagnosis significantly increases the chances of successful treatment and recovery. In the UK, healthcare providers follow a systematic approach to diagnose this condition, ensuring timely and accurate identification.
Recognising Initial Symptoms
The diagnosis often begins with the patient noticing symptoms themselves. Common early signs include a lump or swelling in one of the testicles, which may or may not be accompanied by pain. Some individuals may also experience a feeling of heaviness in the scrotum or a dull ache in the lower abdomen. If these symptoms are observed, it is crucial for the individual to consult a GP promptly.
GP Consultation and Examination
During the initial GP visit, the doctor will conduct a thorough physical examination. This includes checking for lumps or abnormalities in both testicles. The GP will also ask about the patient’s medical history, looking at any relevant familial history of testicular or other cancers. If the GP suspects testicular cancer, they will refer the patient to a specialist for further tests.
Ultrasound Scan
An ultrasound scan is usually the first-line imaging test used to investigate suspected testicular cancer. This non-invasive procedure uses high-frequency sound waves to create a detailed image of the testicles. It helps distinguish between cysts, which are fluid-filled and usually harmless, and solid lumps, which are more likely to be cancerous.
Blood Tests for Tumour Markers
Blood tests are essential in diagnosing and managing testicular cancer. These tests measure the levels of certain proteins known as tumour markers, which are often elevated when cancer is present. Common markers include alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). Elevated levels can support a diagnosis, though not all tumours produce these markers.
Orchidectomy and Histological Examination
If imaging and blood tests suggest the presence of testicular cancer, a surgical procedure called an orchidectomy is performed. This involves the removal of the affected testicle and provides a definitive diagnosis. The removed tissue is examined under a microscope to confirm cancer and determine its type, which is crucial for planning further treatment.
Staging and Further Imaging
Once a diagnosis is confirmed, additional imaging tests, such as CT scans, may be conducted to determine if the cancer has spread beyond the testicle. Staging helps guide treatment decisions and provides information on prognosis. Early-stage cancers, where the disease is confined to the testicle, have a very high cure rate.
Conclusion
Early diagnosis and treatment are key to effectively managing testicular cancer. In the UK, a combination of physical examination, ultrasound, blood tests, and histological analysis form a comprehensive approach to identifying this cancer. If you notice any symptoms, seek medical advice promptly to ensure the best possible outcome.
What is Testicular Cancer?
Testicular cancer is a type of cancer that happens in the testicles. It is not very common, but it usually affects younger men aged 15 to 49. Finding it early makes it easier to treat. In the UK, doctors have a plan to find and treat testicular cancer quickly and correctly.
How to Spot Early Signs
Most times, the person with testicular cancer notices something is wrong first. Look for these signs: a lump or swelling in one testicle, which might hurt or not. Sometimes, you might feel your scrotum is heavy or have a dull pain in your lower belly. If you see any of these signs, talk to your doctor right away.
Seeing Your Doctor (GP)
When you visit your doctor (GP), they will check you carefully. They will look for lumps or anything unusual in both testicles. The doctor also asks about your health and your family's history with cancer. If the GP thinks it might be cancer, they will send you to a specialist for more tests.
Ultrasound Test
An ultrasound test is often the first test to check for testicular cancer. It does not hurt and uses sound waves to make pictures of your testicles. The pictures help the doctor see if there are cysts (harmless fluid-filled lumps) or solid lumps that might be cancer.
Blood Tests
Blood tests help find and treat testicular cancer. These tests look for special proteins called tumour markers. If these markers are high, it might mean there is cancer. Some common markers doctors check are AFP, HCG, and LDH. Not all testicular cancers make these markers, but when they do, it helps with diagnosis.
Orchidectomy Surgery
If tests show there might be cancer, a surgery called orchidectomy is done. This surgery removes the testicle with cancer. After removal, the tissue is looked at under a microscope to see if there is cancer and what type it is. This step is important to plan the right treatment.
Checking If Cancer Has Spread
If cancer is found, more tests like CT scans can show if it has spread. This step is called staging and helps to know how far the cancer has gone and what treatment is needed. If cancer is only in the testicle, treatment success is very likely.
Conclusion
Finding and treating testicular cancer early is very important. In the UK, doctors use several ways to check for this cancer. This includes checking your body, doing an ultrasound, blood tests, and looking at tissue under a microscope. If you see any unusual symptoms, talk to a doctor quickly to get help.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the first step in diagnosing testicular cancer?
The first step is usually a physical examination by a doctor to check for lumps, swelling, or other abnormalities in the testicles.
What imaging tests are used to diagnose testicular cancer?
An ultrasound of the testicles is the primary imaging test used to diagnose testicular cancer.
Why is an ultrasound used for testicular cancer diagnosis?
An ultrasound helps visualize the structure of the testicles and detect any tumors.
Are blood tests used in diagnosing testicular cancer?
Yes, blood tests can be used to check for tumor markers such as AFP, HCG, and LDH, which may be elevated in testicular cancer.
What are tumor markers?
Tumor markers are substances, often proteins, found at higher levels in the blood when cancer is present.
Can a biopsy be used to diagnose testicular cancer?
A needle biopsy is usually not done because it can risk spreading cancerous cells. Instead, the affected testicle may be surgically removed and examined if cancer is highly suspected.
What is the role of a CT scan in diagnosing testicular cancer?
A CT scan can be used to determine if cancer has spread to other parts of the body, such as the abdomen and pelvis.
What does an orchiectomy involve?
An orchiectomy is a surgical procedure to remove one or both testicles, and it is often performed if testicular cancer is suspected.
When is a PET scan recommended?
A PET scan may be used in some cases to evaluate the spread of cancer after the initial diagnosis and treatment.
What symptoms might lead to testing for testicular cancer?
Symptoms include a lump or swelling in the testicle, discomfort or pain in the scrotum, and a feeling of heaviness in the scrotum.
How important is self-examination for early detection?
Regular self-examinations can help individuals detect changes early, which can lead to earlier diagnosis and treatment.
Is testicular cancer screening recommended for all men?
There is no standard screening for testicular cancer for asymptomatic men, but awareness of risk factors and symptoms is advised.
How does a doctor determine if a testicular lump is cancerous?
A doctor will evaluate symptoms, conduct imaging tests like an ultrasound, and may conduct blood tests to look for tumor markers.
What information can be obtained from blood tests in diagnosing testicular cancer?
Blood tests can provide information on the presence and levels of tumor markers, which can suggest the presence and extent of cancer.
What role does family history play in diagnosing testicular cancer?
Family history may be taken into account as it can be a risk factor for testicular cancer, although most cases occur without a family history.
Does age affect the likelihood of testicular cancer?
Yes, testicular cancer is most common in young and middle-aged men, particularly those between the ages of 15 and 35.
Can testicular cancer be detected through a routine physical exam?
Yes, lumps or abnormalities may be discovered during routine physical exams and are often the first step in further testing.
Why might an MRI be used in the diagnosis of testicular cancer?
An MRI may be used as an adjunct to ultrasound to further characterize testicular masses or when other imaging is inconclusive.
What are the limitations of ultrasound in diagnosing testicular cancer?
While ultrasound is excellent for detecting masses, it cannot definitively determine if a mass is cancerous; further testing is usually required.
How quickly should a man see a doctor if he notices a lump in his testicle?
It's important to see a doctor as soon as possible if any changes or lumps are detected, as early diagnosis can lead to better outcomes.
How do doctors find out if someone has testicular cancer?
The first thing the doctor does is look at and feel your testicles. They are checking for any bumps, swelling, or anything that seems different.
What pictures do doctors use to find out if someone has testicular cancer?
An ultrasound is a special picture that helps doctors look inside the body. Doctors use an ultrasound to check the testicles for cancer. Testicles are part of the male body.
To help understand this, you can use tools like picture cards or watch simple videos about how ultrasounds work.
Why do doctors use ultrasound to check for testicular cancer?
Doctors use a special machine called an ultrasound. It helps them look inside your body. It does not hurt and is very safe. The ultrasound shows pictures of your testicles. This helps doctors see if there is a lump that might be cancer. Using ultrasound is a good way to find out what is happening inside. If you have trouble reading or understanding, you can ask someone to explain it to you. You can also use an app that reads text out loud.
An ultrasound is a special test. It takes pictures of the inside of the body. It helps doctors look at the testicles to see if there are any lumps or bumps.
Do doctors use blood tests to find testicular cancer?
Yes, doctors can use blood tests to look for special signs in the blood called tumor markers. These signs have names like AFP, HCG, and LDH. If these signs are high, it might mean someone has testicular cancer.
What are tumor markers?
Tumor markers are things in your body that can help doctors find out if you have cancer. These can be in your blood, pee, or tissues. Doctors use tests to look for these markers. Tumor markers can also help doctors see if cancer treatment is working.
Here are some helpful tools and tips:
- Picture charts to show what tumor markers are.
- Talk to your doctor for more information.
- Use apps that read text out loud to you.
Tumor markers are things in the blood that we can measure. They are usually proteins. When someone has cancer, these markers can be higher than normal.
Can a biopsy help find out if someone has testicular cancer?
A needle biopsy is not usually done because it might spread cancer cells. Instead, if doctors think there might be cancer, they will take out the testicle in an operation and look at it closely.
What does a CT scan do to find out about testicular cancer?
A CT scan is a special kind of picture of the inside of the body. It helps doctors see if cancer has moved to other places, like the tummy (abdomen) or the lower tummy (pelvis).
What happens in an orchiectomy?
An orchiectomy is an operation to take out one or both testicles. Doctors might do this if they think someone has testicular cancer.
When should you get a PET scan?
A doctor might say you need a PET scan for different reasons:
- If they want to see how well your body is working.
- If they are trying to find out more about a sickness you have.
- If they want to check if a treatment is working.
You can use these tools to help understand:
- Pictures or videos that show how PET scans work.
- Someone to talk to, like a friend or helper, to explain things.
A PET scan is a special test that doctors use. It helps them look at the spread of cancer in the body. Doctors might use it after they first find cancer and begin treatment.
What are the signs to check for testicular cancer?
Signs of a problem can be a bump or swelling in the ball, a sore feeling in the pouch, or feeling like the pouch is heavy.
Why is checking your body early important?
Checking your body regularly is important. It can help you find any changes early. This means you can see a doctor sooner and get help if you need it.
Should every man get checked for testicular cancer?
Doctors don't do regular checks for testicular cancer if you don't have any symptoms. But it's good to know what could increase the risk and what signs to look for.
How does a doctor know if a lump on the testicle is cancer?
A doctor can check a lump using special tools. - They might use an ultrasound. This is a machine that looks inside the body to see the lump. - They may also feel the lump with their hands. - Sometimes, they do a blood test. This checks for signs of cancer. If the doctor is worried, they might send you to a specialist who knows more about this. It’s important to see a doctor if you find a lump. Always ask questions if you don’t understand something. You can use pictures or videos to help explain things.A doctor will check how you are feeling. They might use a camera to look inside your body, called an ultrasound. They might also test your blood to look for signs of a tumor.
What can a blood test tell us about testicular cancer?
A blood test can give doctors important clues. It can help find things that might mean testicular cancer.
Doctors check for special markers in the blood. These are like little signs that help doctors know if something is wrong.
If the blood test shows these markers, it might mean there is a problem with the testicles.
A blood test is just one tool doctors use. It's like a puzzle piece. They use other tests and exams to be sure.
If you want to know more, it's good to ask a doctor. They can explain more about what your blood test shows.
Blood tests can show if there are signs of cancer. They can also help doctors understand how much cancer is in the body.
How can your family history help doctors find testicular cancer?
Your family's medical history can help doctors check if you might get testicular cancer. If someone in your family had testicular cancer, you might need to get checked more often.
If you have trouble reading, you can ask someone to help you understand. You can also use audiobooks or apps that read out loud.
Having someone in your family who had testicular cancer might mean you have a higher chance of getting it too. But most people who get this cancer did not have anyone in their family with it before.
To help with reading, you can use tools like audiobooks to listen instead of reading, or apps that highlight words as you read. This can make it easier to understand the information.
Does age change the chance of getting testicular cancer?
As you get older, does the chance of having testicular cancer go up or down?
Using tools like picture cards or a simple story can help you understand more about testicular cancer and age.
Yes, testicular cancer happens most often in men who are young or middle-aged. It is most common in men who are between 15 and 35 years old.
Can a doctor find testicular cancer during a regular check-up?
Yes, doctors can find lumps or something unusual during a check-up. This is the first step to see if more tests are needed.
Why do doctors use an MRI to check for testicular cancer?
Doctors use a special machine called an MRI when they want to see inside the body. An MRI takes pictures of the inside of your body without hurting you.
If a doctor thinks a person might have testicular cancer, they use an MRI to take pictures of the testicles. This helps doctors see if there is anything wrong.
It is important to find out if there is cancer because it can help doctors decide the best way to make someone healthy again.
If reading is hard, you can ask someone to read this to you or use a computer program that reads out loud.
An MRI scan can help doctors look at testicular lumps more closely. This is often used after an ultrasound if doctors need more information or if the results are not clear.
What can't ultrasound do when checking for testicular cancer?
Ultrasound is a tool doctors use to look inside the body. It helps find things like testicular cancer. But, sometimes ultrasound has limits. This means it can't do everything. Here are some things it can't do:
- Can't See Everything: Ultrasound might miss very small lumps or cancers.
- Might Not Be Clear: Sometimes, it's hard to tell the difference between cancer and something else.
- Needs More Tests: Doctors may need other tests, like blood tests or a biopsy, to make sure it's cancer.
It's okay to ask the doctor questions if you don't understand. They can help explain things in a way that's easy to get. You can also use tools like drawings or videos to help learn more. It's important to take your time and ask for help if you need it.
Ultrasound is good at finding lumps. But it cannot tell if a lump is cancer or not. More tests are needed to find out for sure.
When should a man go to the doctor if he finds a bump on his testicle?
If a man finds a bump on his testicle, he should see a doctor soon. It is important to get it checked. The doctor can help find out what it is.
If you have trouble reading, ask someone you trust to read it with you. You can also use a reading tool on a computer or phone. These tools can read out loud to you.
If you find any lumps or changes in your body, it's a good idea to see a doctor quickly. Finding problems early can make things better.
Useful Links
This website offers general information and is not a substitute for professional advice.
Always seek guidance from qualified professionals.
If you have any medical concerns or need urgent help, contact a healthcare professional or emergency services immediately.
Some of this content was generated with AI assistance. We’ve done our best to keep it accurate, helpful, and human-friendly.
- Ergsy carfully checks the information in the videos we provide here.
- Videos shown by Youtube after a video has completed, have NOT been reviewed by ERGSY.
- To view, click the arrow in centre of video.
- Most of the videos you find here will have subtitles and/or closed captions available.
- You may need to turn these on, and choose your preferred language.
- Go to the video you'd like to watch.
- If closed captions (CC) are available, settings will be visible on the bottom right of the video player.
- To turn on Captions, click settings .
- To turn off Captions, click settings again.
More Items From Ergsy search
-

How is testicular cancer diagnosed?
Relevance: 100%
-

What is testicular cancer?
Relevance: 96%
-

What is testicular cancer?
Relevance: 96%
-
What is testicular cancer?
Relevance: 95%
-

Is testicular cancer treatable?
Relevance: 94%
-

Can testicular cancer spread to other parts of the body?
Relevance: 89%
-

What are the stages of testicular cancer?
Relevance: 88%
-

What is the survival rate for testicular cancer?
Relevance: 88%
-

What are the symptoms of testicular cancer?
Relevance: 88%
-

How common is testicular cancer?
Relevance: 87%
-

What causes testicular cancer?
Relevance: 87%
-

Who is at risk for testicular cancer?
Relevance: 86%
-

What role do tumor markers play in testicular cancer?
Relevance: 86%
-

Is fertility affected by testicular cancer?
Relevance: 85%
-

Are there support groups for those affected by testicular cancer?
Relevance: 84%
-

Getting to know your Testicles: Testicular Cancer Awareness with Dr James Howarth, Spilsby Surgery
Relevance: 83%
-

What types of treatments are available for testicular cancer?
Relevance: 82%
-

Can lifestyle changes help prevent testicular cancer?
Relevance: 80%
-

Can testicular cancer recur after treatment?
Relevance: 80%
-

How can I perform a testicular self-exam?
Relevance: 61%
-

Prostate cancer diagnosis and tests
Relevance: 58%
-

Are AI systems used alone in lung cancer diagnosis or alongside human radiologists?
Relevance: 58%
-

Head and Neck Cancer Diagnosis
Relevance: 57%
-

What is a seminoma?
Relevance: 43%
-

When should I see a doctor about potential testicular cancer?
Relevance: 43%
-

What's the difference between seminomas and non-seminomas?
Relevance: 42%
-

How is bowel cancer diagnosed?
Relevance: 41%
-

What are the risk factors for bowel cancer?
Relevance: 40%
-

What is the purpose of a bone scan in prostate cancer treatment?
Relevance: 40%
-

What support is available for individuals diagnosed with bowel cancer?
Relevance: 40%
-

Vulval Cancer
Relevance: 39%
-

Vaginal Cancer
Relevance: 39%
-

How can AI improve patient outcomes in lung cancer?
Relevance: 39%
-

What is Pancreatic Cancer?
Relevance: 39%
-

Endometrial Cancer
Relevance: 39%
-

What is Bowel Cancer?
Relevance: 39%
-

Endometrial Cancer
Relevance: 39%
-

Ovarian Cancer
Relevance: 38%
-

Mouth Cancer Infomercial
Relevance: 37%
-

Worried about signs that could be cancer? Contact your GP practice | NHS
Relevance: 37%


