Find Help
More Items From Ergsy search
-

Diabetes: How to inject insulin | NHS
Relevance: 100%
-
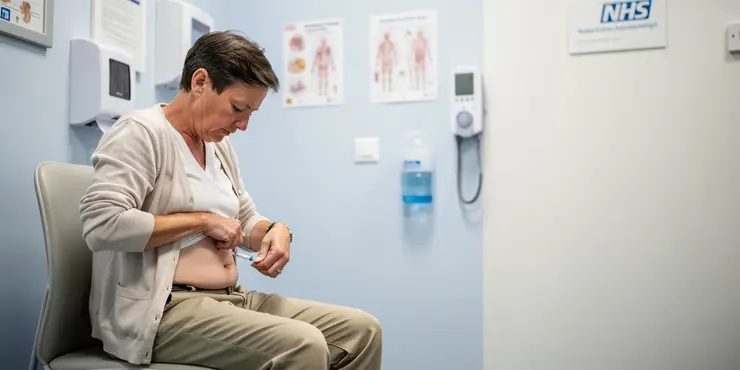
How to inject insulin
Relevance: 91%
-

What is the role of insulin in Type 2 Diabetes?
Relevance: 75%
-

Can Mounjaro be mixed with insulin?
Relevance: 62%
-

Is Ozempic a form of insulin?
Relevance: 61%
-

Are GLP-1 medications injectable?
Relevance: 56%
-

Is Ozempic suitable for type 1 diabetes?
Relevance: 52%
-

What is the connection between GLP-1 and insulin?
Relevance: 52%
-

What is type 1 diabetes?
Relevance: 52%
-
What is the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
Relevance: 50%
-
What is type 1 diabetes?
Relevance: 48%
-

Can Mounjaro be used in type 1 diabetes?
Relevance: 48%
-

Can I take Ozempic with other diabetes medications?
Relevance: 47%
-

How is Type 2 Diabetes treated?
Relevance: 47%
-

What Is Type 2 Diabetes? | 2 Minute Guide | Diabetes UK
Relevance: 46%
-
Eye Injections at Royal Bournemouth Hospital
Relevance: 44%
-

How to manage type 2 diabetes
Relevance: 44%
-

Gestational diabetes | NHS
Relevance: 44%
-
What is Barbie Doll Diabetes?
Relevance: 43%
-

Eye Injections at Royal Bournemouth Hospital
Relevance: 43%
-
Is Teplizumab used to treat diabetes?
Relevance: 42%
-

What causes Type 2 Diabetes?
Relevance: 42%
-

Type 1 Diabetes supporting adults to manage Type 1 diabetes
Relevance: 42%
-

Is Wegovy used for type 2 diabetes management?
Relevance: 41%
-

Gestational Diabetes during pregnancy
Relevance: 40%
-
What support is available for families dealing with type 1 diabetes?
Relevance: 39%
-

What role does GLP-1 play in diabetes management?
Relevance: 39%
-
Does Botox injection hurt?
Relevance: 38%
-

How is Type 2 Diabetes diagnosed?
Relevance: 38%
-

Can Type 2 Diabetes be prevented?
Relevance: 38%
-

Improving outcomes for people with diabetes
Relevance: 38%
-
Is there a genetic predisposition to type 1 diabetes?
Relevance: 38%
-
What are the benefits of early detection of type 1 diabetes?
Relevance: 38%
-
Is Type 2 Diabetes hereditary?
Relevance: 37%
-

Can Type 2 Diabetes go away?
Relevance: 37%
-
Should I screen my child for type 1 diabetes?
Relevance: 36%
-

Sarah and Glinys Managing Diabetes into remission Jan2019
Relevance: 35%
-

How does Ozempic work?
Relevance: 35%
-

Can exercise help prevent gestational diabetes?
Relevance: 35%
-
What does screening for type 1 diabetes involve?
Relevance: 34%
Diabetes: How to Inject Insulin | NHS
Introduction to Insulin Injections
For individuals diagnosed with diabetes, especially type 1 diabetes, insulin injections are an essential part of managing blood glucose levels. The NHS provides guidelines to ensure that patients in the UK administer insulin correctly and safely. Proper technique can improve insulin absorption and maintain blood sugar control, thereby enhancing overall health and wellness.Preparing for an Insulin Injection
Before injecting insulin, it's important to gather all necessary supplies: insulin pen or syringe, insulin vial, an alcohol swab, and a sharps disposal container. Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water to prevent any infection. Next, if you are using a new insulin vial, gently roll it between your hands to mix the insulin. Always check the expiration date and inspect the insulin for any cloudiness or particles if it's supposed to be clear.Choosing the Injection Site
Insulin can be injected into the fatty tissue just under the skin. Common injection sites include the abdomen, thighs, buttocks, and upper arms. Rotating your injection sites is crucial to prevent lipodystrophy (lumpiness or scarring of fatty tissue). For example, if you inject into your abdomen for one injection, consider using your outer thigh for the next.Administering the Insulin
1. **Clean the Injection Site:** Use an alcohol swab to clean the chosen area. Let the alcohol dry to prevent stinging. 2. **Prepare the Insulin:** If you are using an insulin pen, attach a new, sterile needle. Prime the pen by dialing up a small dose (usually 2 units) and pressing the plunger to expel air bubbles. 3. **Inject the Insulin:** Pinch the skin lightly, and insert the needle at a 90-degree angle if the needle is short (4-6 mm). For longer needles, you may need to insert at a 45-degree angle to avoid injecting into the muscle. 4. **Deliver the Dose:** Press the plunger or the button on the pen fully until the dose is completely delivered. Hold the needle in place for about 10 seconds to ensure all the insulin has been injected. 5. **Withdraw the Needle:** Remove the needle and gently apply pressure to the injection site with a swab for a few seconds.After the Injection
Dispose of the used needle and syringe or pen needle in a designated sharps disposal container. Do not throw these items in the household waste to avoid injury and contamination. Monitor your blood glucose levels regularly as per your GP’s recommendations and adjust your insulin dosage if advised.Conclusion
Injecting insulin can seem daunting, but with practice and adherence to NHS guidelines, it becomes a routine part of diabetes management. If you have any concerns or experience complications, contact your healthcare provider for advice. Proper insulin administration helps keep diabetes under control, leading to a healthier and more active life.Diabetes: How to Give Insulin Shots | NHS
What Insulin Shots Are
If you have diabetes, especially type 1 diabetes, you need insulin shots to keep your blood sugar levels right. Insulin helps keep you healthy. The NHS gives advice on how to give insulin safely.Getting Ready for an Insulin Shot
Before you give an insulin shot, get everything you need: an insulin pen or syringe, insulin vial, an alcohol wipe, and a special bin for sharp things. Wash your hands well with soap and water. If you have a new vial of insulin, roll it gently between your hands to mix it. Check the date on the vial and make sure the insulin is clear and not cloudy or lumpy.Where to Give the Shot
You inject insulin into the fatty part just under the skin. You can use your belly, thighs, buttocks, or upper arms. Change where you inject each time. This helps stop lumps or bumps under your skin. For example, if you use your belly today, use your thigh next time.How to Give the Insulin Shot
1. **Clean the Skin:** Wipe the area with an alcohol swab and wait for it to dry. 2. **Get the Insulin Ready:** If you use an insulin pen, put on a new, clean needle. Prime the pen by dialing a little insulin (2 units) and pressing to get rid of any air bubbles. 3. **Give the Shot:** Pinch the skin a little and put the needle in straight if it is short (4-6 mm). If the needle is longer, you might need to angle it a bit. 4. **Press the Plunger:** Push the plunger or button all the way to give the insulin. Keep the needle in place for 10 seconds to make sure all the insulin goes in. 5. **Take Out the Needle:** Take out the needle and press the spot with a clean swab for a few seconds.What to Do After the Shot
Put the used needle and syringe in the special sharps bin. Don’t throw them in the regular trash. Check your blood sugar levels often, as your doctor says, and change your insulin if you need to.Finishing Up
Giving insulin can feel tricky at first, but with practice, it becomes easy. Follow the NHS rules and talk to your doctor if you have problems. Using insulin the right way helps you stay healthy and enjoy life.Frequently Asked Questions
What is insulin and why do I need to inject it?
Insulin is a hormone that helps control blood sugar levels. People with diabetes may need to inject insulin because their pancreas doesn't produce enough insulin or their body doesn't use it effectively.
Where on my body should I inject insulin?
Common injection sites include the abdomen, thighs, buttocks, and upper arms. Rotate injection sites to avoid skin problems.
How do I prepare my skin before injecting insulin?
Clean the injection site with soap and water or an alcohol swab to reduce the risk of infection.
What type of insulin syringe or pen should I use?
Your healthcare provider will recommend the best type of syringe or pen for you based on your insulin dosage and personal preferences.
How do I draw insulin into the syringe?
If using a vial and syringe, insert air into the vial, then draw the insulin by pulling back the plunger to the correct dosage.
How do I administer an insulin injection with a pen?
Attach a new needle, dial your dose, clean the skin, and insert the needle at a 90-degree angle. Press the button to inject.
How do I store my insulin?
Unopened insulin should be kept in the refrigerator. Once opened, it can be kept at room temperature but should be used within 28 days.
Can I reuse insulin syringes or needles?
It's recommended to use a new syringe or needle for each injection to reduce the risk of infection and ensure proper dosing.
What should I do if I accidentally inject into a blood vessel?
If you see blood in the syringe, withdraw it immediately and try again with a new needle and new insulin.
What should I do if I experience a painful injection?
Try changing the site of injection, ensuring the needle is the correct size, and injecting at the proper angle.
How do I dispose of used insulin needles and syringes?
Place them in a sharps disposal container and follow your local regulations for disposal.
What should I do if I miss a dose of insulin?
Contact your healthcare provider for specific instructions as it depends on the type of insulin and your blood sugar levels.
Can I inject insulin through my clothes?
It's not recommended. Injecting through clothing can increase the risk of infection and may not ensure proper delivery of insulin.
How can I reduce the pain from insulin injections?
Let insulin come to room temperature before injecting, use a new needle for each injection, and ensure proper technique.
What are the symptoms of low blood sugar after an injection?
Symptoms can include sweating, dizziness, hunger, irritability, and confusion. It's important to monitor your blood sugar levels regularly.
What is insulin and why do I need to take it?
Insulin is something in our body that helps use the sugar from food for energy.
Some people need extra insulin to stay healthy. This is when they might need to take it with a needle.
Ask a grown-up or a doctor to help you understand more.
Insulin is a special thing in your body that helps control sugar in your blood. People with diabetes might need to take insulin shots. This is because their bodies don't make enough insulin, or their bodies don't use insulin the right way.
Where should I inject insulin in my body?
Here is how you can do it:
- You can inject insulin into your tummy, but not near your belly button.
- You can also use the top part of your legs or the back of your arms.
- Make sure to use a different spot each time so your skin stays healthy.
If you need help, ask a doctor, nurse, or an adult you trust.
When you need to give an injection (a shot), you can use these places on the body: tummy, legs, bum, and top of arms. Make sure to change the spot where you give the shot each time. This helps stop skin problems.
How can I get my skin ready to inject insulin?
Wash the place where you will give the injection. Use soap and water or an alcohol wipe to keep it clean and safe.
What kind of insulin syringe or pen is best for me?
It can be tricky to pick the right insulin syringe or pen. Here's how to make it simpler:
- Talk to your doctor or nurse. They can help you choose.
- Think about what is easy for you to use.
- Some tools talk and tell you what to do. These might help.
- Ask a family member or friend for support.
Remember, you are not alone. There are people and tools to help you.
Your doctor or nurse will help you choose the right needle or pen for your insulin. They will pick what works best for you and how much insulin you need.
How do I put insulin into the needle?
If you are using a bottle and needle:
1. First, put air into the bottle.
2. Next, pull the plunger back to get the right amount of insulin.
Make sure you have someone to help if needed, like a parent or a nurse.
Pictograms or step-by-step images can make it easier to follow the steps.
How do I give an insulin shot with a pen?
Put on a new needle. Choose how much medicine you need. Clean your skin. Push the needle straight in. Press the button to give the medicine.
You can use tools like a timer to help you remember each step. You can also ask someone to help you.
How do I keep my insulin safe?
Here is how to keep your insulin:
- Put insulin in the fridge before you open it. Keep it cool.
- If you open it, you can keep it at room temperature, but use it in 28 days.
- Do not freeze insulin. It will not work.
- Keep it away from sunlight and heat. Light and heat can spoil it.
- Check the expiry date. Do not use if it's past the date.
If you need help, ask a carer or a family member. Use a visual chart to remember these rules.
Keep insulin that is not open in the fridge. When you open it, you can keep it in a cool, dry place, but use it in 28 days.
Can I use insulin syringes or needles more than once?
No, you should not use insulin syringes or needles more than one time. It is safer to use a new one each time. This helps stop germs from making you sick.
If you have trouble with reading, you can ask a caregiver for help or use a voice-to-text app to read out loud.
Use a new syringe or needle each time you have an injection. This helps stop infections and makes sure you get the right amount of medicine.
What should I do if I put a needle in a blood vessel by mistake?
If you put a needle in a blood vessel by mistake, stay calm. Here is what you can do:
- Take the needle out right away.
- Press on the spot where the needle was to stop bleeding.
- If you feel unwell, tell an adult or call a doctor.
- You can call emergency services if you need help fast.
It might help to have a friend or adult with you if you feel nervous.
If you see blood in the needle, take it out right away. Then, try again with a new needle and new insulin.
What can I do if an injection hurts?
If an injection hurts, here are some simple steps you can try:
- Stay calm: Take deep breaths to help relax.
- Tell someone: Let a nurse or doctor know it hurts.
- Try to relax your arm: Keep it loose and not tense.
- Put something cold on it: Use an ice pack to feel better.
If it keeps hurting, ask for help from a grown-up or a doctor.
You can use tools like picture guides or videos to learn more about injections and what to do.
Try using a different spot for the injection. Make sure the needle is the right size. Hold the needle at the right angle when you inject.
What do I do with used insulin needles and syringes?
Here is how to get rid of used insulin needles and syringes safely:
- Put them in a strong, plastic container with a lid, like a bottle or a special sharps box.
- Make sure the lid is tight so nothing can spill out.
- Do not throw them in the trash or recycling bin.
- Take the container to a pharmacy, hospital, or special disposal place.
Ask a grown-up for help if you need it.
Put them in a special container for sharp things. Follow your local rules to throw them away safely.
What to Do If You Forget Your Insulin
Did you forget to take your insulin? That's okay. Here’s what you can do:
- Stay calm and don’t worry.
- Check your blood sugar level if you can.
- Ask an adult, like a parent or teacher, for help.
- Call or talk to your doctor or nurse. They know what to do.
- Write down what happened so you remember for next time.
If you need help, try these tips:
- Set a reminder alarm to take your insulin.
- Use a checklist to track your doses.
Remember, your doctor can give you the best advice for you.
Ask your doctor or nurse what to do. This is because it depends on the type of insulin you use and your blood sugar levels.
Can I give myself an insulin shot through my clothes?
Yes, you can give yourself an insulin shot through your clothes. But it might be better to do it on clean skin to avoid any dirt.
Suggestions: Start by making sure your clothes and skin are clean. You might find it helpful to use a mirror to see better. If you are unsure, ask an adult or a nurse for help.
It is not a good idea. Putting a needle through clothes can make it easier to get germs and you might not get the insulin the right way.
How can I make insulin shots hurt less?
Wait for the insulin to warm up a bit before using it. Use a new needle for every shot. Make sure you are doing it the right way.
What happens if your blood sugar is too low after a shot?
Sometimes after you get a shot, your blood sugar can get too low. This can make you feel:
- Shaky
- Weak
- Hungry
- Sweaty
- Dizzy
- Mood changes
- Tired
If you feel like this, tell an adult. Eating or drinking something sweet can help. Try talking to a doctor for more advice.
Signs you might notice are sweating, feeling dizzy, being very hungry, getting grumpy, or feeling confused. It's important to check your blood sugar often.
Useful Links
This website offers general information and is not a substitute for professional advice.
Always seek guidance from qualified professionals.
If you have any medical concerns or need urgent help, contact a healthcare professional or emergency services immediately.
Some of this content was generated with AI assistance. We’ve done our best to keep it accurate, helpful, and human-friendly.
- Ergsy carfully checks the information in the videos we provide here.
- Videos shown by Youtube after a video has completed, have NOT been reviewed by ERGSY.
- To view, click the arrow in centre of video.
- Most of the videos you find here will have subtitles and/or closed captions available.
- You may need to turn these on, and choose your preferred language.
- Go to the video you'd like to watch.
- If closed captions (CC) are available, settings will be visible on the bottom right of the video player.
- To turn on Captions, click settings .
- To turn off Captions, click settings again.
More Items From Ergsy search
-

Diabetes: How to inject insulin | NHS
Relevance: 100%
-

How to inject insulin
Relevance: 91%
-

What is the role of insulin in Type 2 Diabetes?
Relevance: 75%
-

Can Mounjaro be mixed with insulin?
Relevance: 62%
-

Is Ozempic a form of insulin?
Relevance: 61%
-

Are GLP-1 medications injectable?
Relevance: 56%
-

Is Ozempic suitable for type 1 diabetes?
Relevance: 52%
-

What is the connection between GLP-1 and insulin?
Relevance: 52%
-

What is type 1 diabetes?
Relevance: 52%
-
What is the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
Relevance: 50%
-
What is type 1 diabetes?
Relevance: 48%
-

Can Mounjaro be used in type 1 diabetes?
Relevance: 48%
-

Can I take Ozempic with other diabetes medications?
Relevance: 47%
-

How is Type 2 Diabetes treated?
Relevance: 47%
-

What Is Type 2 Diabetes? | 2 Minute Guide | Diabetes UK
Relevance: 46%
-

Eye Injections at Royal Bournemouth Hospital
Relevance: 44%
-

How to manage type 2 diabetes
Relevance: 44%
-

Gestational diabetes | NHS
Relevance: 44%
-
What is Barbie Doll Diabetes?
Relevance: 43%
-

Eye Injections at Royal Bournemouth Hospital
Relevance: 43%
-

Is Teplizumab used to treat diabetes?
Relevance: 42%
-

What causes Type 2 Diabetes?
Relevance: 42%
-

Type 1 Diabetes supporting adults to manage Type 1 diabetes
Relevance: 42%
-

Is Wegovy used for type 2 diabetes management?
Relevance: 41%
-

Gestational Diabetes during pregnancy
Relevance: 40%
-
What support is available for families dealing with type 1 diabetes?
Relevance: 39%
-

What role does GLP-1 play in diabetes management?
Relevance: 39%
-

Does Botox injection hurt?
Relevance: 38%
-

How is Type 2 Diabetes diagnosed?
Relevance: 38%
-

Can Type 2 Diabetes be prevented?
Relevance: 38%
-

Improving outcomes for people with diabetes
Relevance: 38%
-
Is there a genetic predisposition to type 1 diabetes?
Relevance: 38%
-
What are the benefits of early detection of type 1 diabetes?
Relevance: 38%
-

Is Type 2 Diabetes hereditary?
Relevance: 37%
-

Can Type 2 Diabetes go away?
Relevance: 37%
-
Should I screen my child for type 1 diabetes?
Relevance: 36%
-

Sarah and Glinys Managing Diabetes into remission Jan2019
Relevance: 35%
-

How does Ozempic work?
Relevance: 35%
-

Can exercise help prevent gestational diabetes?
Relevance: 35%
-
What does screening for type 1 diabetes involve?
Relevance: 34%


