Find Help
More Items From Ergsy search
-
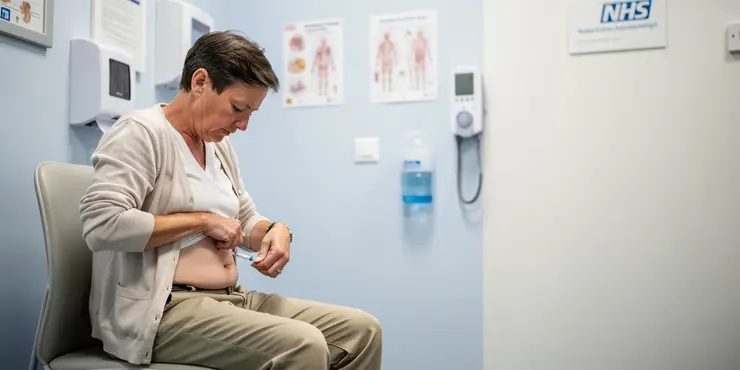
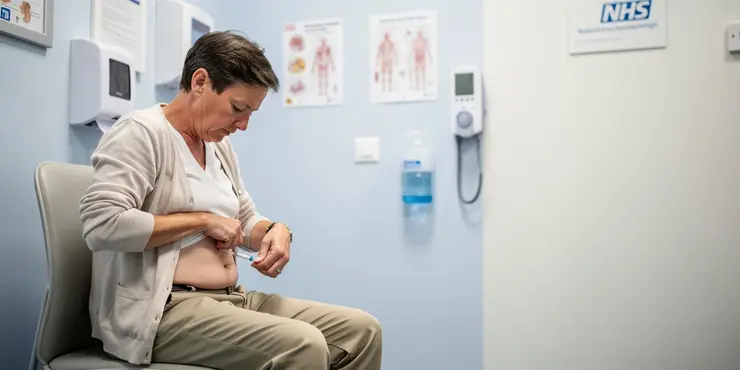
How to inject insulin
Relevance: 100%
-

Diabetes: How to inject insulin | NHS
Relevance: 91%
-

Can Mounjaro be mixed with insulin?
Relevance: 60%
-

Are GLP-1 medications injectable?
Relevance: 58%
-

Is Ozempic a form of insulin?
Relevance: 58%
-

What is the role of insulin in Type 2 Diabetes?
Relevance: 55%
-

What is the connection between GLP-1 and insulin?
Relevance: 47%
-
Does Botox injection hurt?
Relevance: 45%
-
Eye Injections at Royal Bournemouth Hospital
Relevance: 43%
-

Eye Injections at Royal Bournemouth Hospital
Relevance: 43%
-
Evidence-Based Interventions: injections for non-specific low back pain without sciatica
Relevance: 37%
-

What should I do if I experience side effects after a Botox injection?
Relevance: 35%
-

Do I need any vaccine injections for EU countries?
Relevance: 30%
-

How do weight loss jabs work?
Relevance: 29%
-

How does Ozempic work?
Relevance: 28%
-

How should I inject Mounjaro?
Relevance: 26%
-

What is Mounjaro?
Relevance: 26%
-
What is the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
Relevance: 26%
-

Is Ozempic suitable for type 1 diabetes?
Relevance: 26%
-

Can I take Ozempic with other diabetes medications?
Relevance: 24%
-

What is type 1 diabetes?
Relevance: 24%
-

How is Ozempic administered?
Relevance: 24%
-

Are there any GLP-1 medications that are taken orally?
Relevance: 23%
-

What is Ozempic?
Relevance: 23%
-

What is GLP-1?
Relevance: 23%
-

Can Mounjaro be used in type 1 diabetes?
Relevance: 23%
-

How do GLP-1 receptor agonists work?
Relevance: 22%
-

How does Ozempic affect blood sugar levels?
Relevance: 22%
-

How is Type 2 Diabetes treated?
Relevance: 21%
-

How is Mounjaro administered?
Relevance: 20%
-
What is type 1 diabetes?
Relevance: 20%
-

What does GLP-1 stand for?
Relevance: 20%
-

Is GLP-1 related to any other hormones?
Relevance: 19%
-
How is Wegovy administered?
Relevance: 18%
-

How is Ozempic administered?
Relevance: 18%
-

What impact does GLP-1 have on glucose metabolism?
Relevance: 18%
-

How to manage type 2 diabetes
Relevance: 17%
-

What are the common side effects of Ozempic?
Relevance: 17%
-

Can GLP-1 be used as a medication?
Relevance: 17%
-

Does Botox hurt?
Relevance: 17%
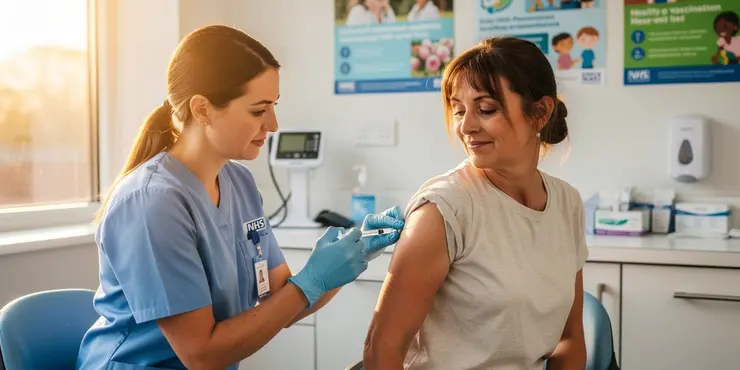
How to Inject Insulin
Understanding Your Equipment
Before you start injecting insulin, it's crucial to understand the equipment you will be using. Insulin is typically administered using a syringe, insulin pen, or an insulin pump. Make sure your hands and the injection site are clean to reduce the risk of infection. The insulin pen or syringe should be calibrated to ensure you are taking the correct dosage as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
Selecting the Injection Site
The most common sites for insulin injections in the UK are the abdomen, thighs, buttocks, and upper arms. Rotate your injection sites to prevent lipohypertrophy, which is thickening of the fatty tissue that can interfere with insulin absorption. The abdomen is often the preferred site because it allows for consistent absorption.
Preparing for Injection
First, inspect the insulin for any changes in colour or clarity, especially if you’re using insulin that should appear clear. If using a syringe, draw air into the syringe equal to your insulin dose. Inject the air into the insulin vial, then draw the correct dosage of insulin into the syringe. If using an insulin pen, attach a new needle, prime the pen to remove any air bubbles, and set the dosage.
Injecting Insulin
Pinch the skin around your selected injection site to create a fold. Holding the syringe or pen like a dart, insert the needle at a 90-degree angle if you have more subcutaneous fat, or at a 45-degree angle if you have less. Depress the plunger slowly and steadily until the insulin is fully injected. Wait for about 10 seconds before removing the needle to ensure all the insulin has dispersed into the tissue.
After Injection Care
Once the needle is out, dispose of it in a sharps container. Do not massage the injection site as this can interfere with absorption. Monitor your blood sugar levels as advised by your healthcare provider to ensure that your insulin dosage is effective. Keep an eye out for any redness, swelling, or signs of infection at the injection site, and consult your healthcare provider if you have any concerns.
Conclusion
Administering insulin correctly is vital for effective diabetes management. By understanding your equipment, preparing thoroughly, selecting appropriate injection sites, and following post-injection care guidelines, you can ensure you are administering your insulin safely and effectively. Always consult with your healthcare provider for any questions or concerns specific to your treatment plan. In the UK, resources such as the NHS provide additional support and guidance for individuals managing diabetes.
How to Inject Insulin
Preparation
Before injecting insulin, ensure you have all necessary supplies: insulin vial or pen, syringe or pen needles, alcohol swabs, and a proper container for sharps disposal. Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water to maintain hygiene.
Selecting the Injection Site
Popular insulin injection sites include the abdomen, thighs, buttocks, and upper arms. Rotate the injection site within the same general area to prevent lipodystrophy, a condition where fatty tissue breaks down or builds up under the skin.
Preparing the Insulin
If using a vial and syringe, roll the vial between your palms gently to mix the insulin. For insulin pens, follow the manufacturer’s instructions to prime the pen by expelling a small amount of insulin to ensure it’s working properly.
Injecting the Insulin
Clean the selected injection site with an alcohol swab and allow it to dry. If using a syringe, draw the recommended dose of insulin, ensuring no air bubbles are present. Pinch a fold of skin, insert the needle at a 90-degree angle if using a short needle or at a 45-degree angle if using a longer needle. For pen users, insert the needle straight into the pinched skin.
Slowly push the plunger or press the button on the insulin pen to inject the insulin. After injecting, count to ten before removing the needle to ensure the full dose is delivered.
Post-Injection Care
Dispose of the syringe or pen needle in a designated sharps container. Do not reuse needles. Make sure to store your insulin as per the instructions—generally in the refrigerator for unopened vials or pens and at room temperature once opened.
Important Considerations
Always follow your healthcare provider’s instructions regarding insulin dosage and injection techniques. Consult with your healthcare team if you experience any issues such as unexpected changes in blood glucose levels or skin reactions at the injection site.
How to Inject Insulin
Understanding Your Equipment
Before you start injecting insulin, it is important to know about the tools you will use. Insulin is usually given with a syringe, insulin pen, or an insulin pump. Keep your hands and the place where you will inject clean to avoid germs. Make sure you use the right amount of insulin as your doctor told you.
Selecting the Injection Site
The most common places to inject insulin in the UK are the tummy, thighs, bottom, and upper arms. Change where you inject each time to keep your skin healthy. The tummy is often the best place because it helps insulin work well.
Preparing for Injection
Check the insulin to make sure it looks right. If you use a syringe, pull in air equal to your insulin dose, and then put the air in the insulin bottle. Pull the correct insulin amount into the syringe. If you have an insulin pen, put on a new needle, get rid of air bubbles, and set your dose.
Injecting Insulin
Pinch the skin where you will inject. Hold the syringe or pen like a dart. If you have more fat, push the needle in straight (90 degrees). If you have less fat, angle the needle a bit (45 degrees). Push the insulin in slowly. Wait 10 seconds before taking the needle out to make sure all the insulin goes in.
After Injection Care
After taking out the needle, put it in a special box for sharp things (sharps container). Do not rub where you injected. Check your blood sugar as your doctor says. If you see redness, swelling, or any problems, tell your doctor.
Conclusion
Giving insulin the right way is very important for managing diabetes. Know your tools, get ready, pick good places to inject, and take care of your skin after. Always talk to your doctor if you have questions. In the UK, you can get more help from the NHS for managing diabetes.
How to Inject Insulin
Getting Ready
Before you inject insulin, make sure you have everything you need. You will need: insulin vial or pen, syringe or pen needles, alcohol wipes, and a special container to throw away sharps (used needles). Wash your hands well with soap and water to keep everything clean.
Choosing Where to Inject
You can inject insulin in different places like your belly, thighs, buttocks, and upper arms. Use a different spot each time in the same area so your skin stays healthy.
Getting the Insulin Ready
If you are using a vial and syringe, roll the vial gently between your hands to mix the insulin. If you have an insulin pen, follow the instructions to make sure it works. You might need to push out a little insulin first.
Injecting the Insulin
Clean where you will inject with an alcohol wipe and let it dry. If you are using a syringe, fill it with the right amount of insulin. Make sure there are no air bubbles. Pinch some skin, and then push the needle in. If the needle is short, go straight in. If it's longer, go at an angle. If you use a pen, go straight in.
Push the plunger or press the button on the pen slowly to inject. Count to ten before you take out the needle to make sure all the insulin goes in.
After You Inject
Put the syringe or pen needle in the special sharps container. Do not use needles more than once. Store insulin correctly. Unopened vials or pens go in the fridge. Once opened, keep them at room temperature.
Things to Remember
Always do what your doctor tells you about how much insulin to use and how to inject it. Talk to your healthcare team if you have any problems, like your blood sugar changing a lot or if your skin gets sore where you inject.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is insulin injection?
Insulin injection is a method to deliver insulin, a hormone required for controlling blood glucose levels, directly into the body through a syringe, pen, or pump.
Why do I need to inject insulin?
People with diabetes may need insulin injections to help keep their blood sugar levels within the target range. This is especially true for people with Type 1 diabetes.
When should I inject my insulin?
The timing of insulin injections depends on the type of insulin you are using. Some insulins are taken before meals, others once or twice daily. Always follow your healthcare provider's instructions.
Where can I inject insulin on my body?
Common injection sites include the abdomen, thighs, buttocks, and upper arms. Rotating the injection sites helps to avoid tissue damage and lumps.
How do I prepare an insulin injection?
Wash your hands, gather supplies (insulin pen/syringe, needle, alcohol swabs), check the insulin for clarity (except cloudy insulins that need rolling), and prepare the dose as directed.
How do I inject insulin using a syringe?
Pinch the skin, insert the needle at a 90-degree angle, release the pinch, push the plunger to inject the insulin, count to five, and remove the needle.
How do I inject insulin using an insulin pen?
Attach a new needle, prime the pen to remove air bubbles, dial up your dose, clean the injection site, insert the needle, and administer the dose by pressing the button.
Can I reuse insulin needles?
No, using a new needle for each injection helps prevent infections, ensures the needle is sharp, and reduces discomfort.
What should I do if I see bubbles in the syringe?
Tap the syringe to make the bubbles rise to the top, then push the plunger slightly to remove them. It's essential to remove these to ensure accurate dosing.
Do insulin injections hurt?
You might feel a slight prick when the needle goes in, but most people find it relatively painless. Rotate injection sites to minimize discomfort.
How do I store insulin?
Unopened insulin should be stored in the refrigerator. Once in use, it can be kept at room temperature for a specific period, as stated on the packaging.
What should I do if I miss an insulin dose?
If you miss a dose, follow your healthcare provider's advice. It may vary depending on your insulin regimen and blood sugar readings.
How do I dispose of used insulin needles?
Place used needles in a sharps container or a hard, puncture-proof container with a secure lid, and follow local guidelines for disposal.
Can I travel with my insulin?
Yes, keep your insulin and supplies in your hand luggage, along with a doctor's letter explaining your need for insulin. Store insulin within the recommended temperature range.
What should I do if my insulin looks cloudy or discolored?
Do not use insulin if it looks cloudy or discolored, except for certain types like NPH insulin, which need to be mixed before use. Contact your pharmacist or healthcare provider for a replacement.
What are the different types of insulin delivery devices?
The most common insulin delivery devices in the UK are insulin pens, insulin pumps, and syringes.
How do I prepare an insulin pen for injection?
First, wash your hands. Remove the cap of the pen and attach a new needle. Prime the pen by dialling 2 units and pressing the button until you see a drop of insulin.
What are the recommended injection sites for insulin?
Common injection sites include the abdomen, upper arms, thighs, and buttocks. It's important to rotate sites to avoid tissue damage.
How do I measure the correct dose of insulin?
Follow your healthcare provider's instructions. If you're using a pen, dial the dose. If using a syringe, draw up the correct amount from the vial.
How should I inject insulin?
Pinch the skin, insert the needle at a 90-degree angle, and press the plunger or button. Hold for a few seconds before removing the needle.
What should I do if I experience pain during injection?
Ensure the needle is sharp and not bent. Try relaxing the muscle, and rotate injection sites. If pain persists, consult your healthcare provider.
How do I store insulin?
Unopened insulin should be kept in the refrigerator. Opened insulin pens or vials can be stored at room temperature, away from heat and light, usually for up to 28 days.
What should I do if I accidentally miss a dose?
Contact your healthcare provider for advice. Do not double your next dose unless instructed.
What are the possible side effects of insulin injections?
Possible side effects include hypoglycemia, weight gain, and local reactions such as redness, swelling, or itching at the injection site.
Can I reuse insulin syringes or needles?
Reusing needles or syringes is not recommended as it can cause infection and dull the needle, increasing pain.
What should I do if I inject too much insulin?
Monitor your blood sugar levels closely and consume carbohydrates to prevent hypoglycemia. Seek medical help if necessary.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
The frequency will depend on your individual treatment plan. Consult your healthcare provider for specific instructions.
What type of needle should I use for insulin injections?
Use a single-use, fine-gauge (usually 31 to 32 gauge) needle. The length may vary; common lengths are 4mm to 12.7mm. Consult your provider for recommendations.
Can I travel with insulin?
Yes, you can travel with insulin. Keep it in a cooler case if traveling long distances and carry a letter from your doctor for airport security.
What should I do with used needles and syringes?
Place used needles and syringes in a proper sharps disposal container. Do not throw them in the bin. Check with your local council for disposal guidelines.
What is an insulin injection?
An insulin injection is a way to help people with diabetes. It gives them the insulin they need because their body can't make enough of it.
Insulin is a medicine that helps keep blood sugar levels normal.
If someone needs to use insulin, a doctor or nurse can show them how to give the injection safely.
Using fun activities or picture guides can make learning about insulin easier.
An insulin injection is a way to put insulin into the body. Insulin is needed to keep blood sugar levels just right. You can do this with a needle, a pen, or a pump.
Why do I need to take insulin?
Sometimes our bodies need a little help to work properly. Insulin is a medicine that helps control sugar in our blood. If your doctor says you need insulin, it helps your body handle sugar in the right way.
If you have questions or need help, you can:
- Ask a doctor or nurse to explain it in simple words.
- Use pictures to understand better.
- Watch videos made for kids to see how insulin works.
People who have diabetes might need to have insulin injections. This helps keep their blood sugar at the right level. This is very important for people with Type 1 diabetes.
When do I take my insulin?
When you take your insulin shot depends on the kind of insulin you use. Some insulin needs to be taken before you eat. Other types are taken once or twice a day. Always listen to what your doctor or nurse tells you to do.
Where can I inject insulin in my body?
You can put insulin in different places on your body.
Here are some spots:
- Your belly (tummy), but stay away from the belly button.
- The top part of your legs (thighs).
- The back of your upper arms.
- Your buttocks (bottom).
Remember:
- Try to change spots each time you inject.
- Ask a grown-up or a nurse to help if needed.
- Use a pen or needle that feels comfy in your hand.
If you need help, you can use tools like a mirror or talk to your doctor or nurse.
You can give an injection in these places: belly, thighs, bottom, and top of arms. Change where you give the injection each time. This stops damage and lumps under the skin.
How do I get ready to give an insulin shot?
Here is how you can get ready to give an insulin shot:
- Wash your hands: Use soap and water to clean your hands.
- Gather your supplies: You will need insulin, a syringe or pen, and a clean area.
- Check the insulin: Make sure the insulin is not cloudy or past its use-by date.
- Prepare the syringe or pen: Take off the cap and attach a new needle.
- Get the right dose: Use the pen or syringe to get the amount of insulin you need.
- Pick a spot on your skin: Choose a clean area, like your belly or thigh.
- Give the shot: Put the needle in the skin and push the plunger to give the insulin.
- Take out the needle: Remove the needle and throw it away safely.
Helpful tools: You can use reminder apps or alarms to help you remember to take your insulin. Use a sharps container to throw away needles safely.
First, wash your hands to keep them clean. Next, get what you need: an insulin pen or syringe, a needle, and alcohol wipes. Check your insulin to make sure it is clear. Some insulin can be cloudy, and those need to be rolled gently. Now, get the right dose ready like your doctor told you.
How can I use a needle to take insulin?
Pinch the skin, put the needle straight in, let go of the pinch, push the plunger to give the insulin, count to five, and take the needle out.
How do I use an insulin pen?
Do you need to use an insulin pen? Here is how you can do it:
- Wash your hands with soap and water.
- Take the cap off the insulin pen.
- Check that the insulin is clear. If it is cloudy, roll it gently to mix it.
- Put a new needle on the pen.
- Set the right dose of insulin. You can use a pen with a dial to choose your dose.
- Pick a spot on your body to inject. Good places are your belly, thigh, or arm.
- Clean the skin with an alcohol wipe.
- Pinch the skin gently and push the needle in straight.
- Push the button on the pen to inject the insulin.
- Count to 10 before pulling the needle out.
- Remove the needle from the pen and throw it away safely.
- Put the cap back on the pen and store it as directed.
Tools to help you:
- Get a helper to practice with you.
- Use a timer to count to 10.
- Sticker charts can remind you where to inject next.
Put a new needle on the pen. Get rid of air bubbles by pressing the pen. Choose how much medicine you need. Clean the place where the needle will go. Put the needle in your skin. Press the button to give the medicine.
You can use tools like a magnifying glass to help see better. Ask someone you trust to help if you need it.
Can I use insulin needles more than once?
No, it is not safe to use insulin needles again. You should always use a new needle.
Here are some tips to help:
- Ask your doctor or nurse for more needles if you need them.
- Use a special container to throw away old needles safely.
- Make sure to check your needle before using it each time.
No, you should use a new needle every time you have an injection. This stops infections, keeps the needle sharp, and makes it hurt less.
What to do if you see bubbles in the syringe?
If you see bubbles in the syringe, don’t worry. Here is what you can do:
Steps to take:
- Hold the syringe upright with the needle pointing up.
- Tap the syringe gently with your finger to move the bubbles to the top.
- Press the plunger slowly to push the air out.
Tools that can help you:
- Use a magnifying glass if you have trouble seeing the bubbles.
- Ask someone for help if you are unsure.
If you need help, talk to your doctor or nurse.
Gently tap the syringe so the bubbles move up to the top. Then push the plunger a little bit to get rid of the bubbles. It is important to do this so you can give the right amount of medicine.
Do insulin injections hurt?
Getting an insulin injection might feel like a little pinch. Everyone feels things differently. Some people say it doesn't hurt at all, while others might feel a tiny bit of pain. Using ice or a numbing cream can help if you are worried. It's okay to feel nervous, and talking to a doctor or nurse can make you feel better. They can also show you the best way to do it.
You might feel a little pinch when the needle goes in, but most people say it does not hurt much. Use different places on your body for injections to make it feel better.
How do I keep insulin safe?
Here is how you can keep insulin safe:
- Keep insulin in the fridge, but not too cold.
- Don't put insulin in the freezer.
- If you are using insulin, you can keep it at room temperature for a short time.
- Keep insulin away from sunlight and heat.
- Check the expiry date before using insulin.
If you need help, ask a grown-up or use a picture chart to remember.
Keep unopened insulin in the fridge. When you start using it, you can leave it out of the fridge for a while. Check the package to see how long you can do this.
What if I forget my insulin?
If you forget your insulin shot, don't worry.
Here is what you can do:
- Take your insulin as soon as you remember.
- If it's almost time for your next dose, wait and take that one instead.
- Ask an adult or a doctor if you are unsure.
Tools that can help:
- Set an alarm to remind you.
- Use a pillbox to keep track.
- Ask someone to remind you.
If you forget to take your medicine, ask your doctor or nurse what to do. What you need to do can change based on the type of insulin you use and your blood sugar levels.
How do I get rid of used insulin needles?
Getting rid of used insulin needles can be easy. Follow these steps:
1. Use a sharps container: Put the needle in a special container called a sharps container. You can get one from a pharmacy or your doctor's office.
2. Don't throw in the trash: Do not put used needles in the regular trash or recycling bins.
3. Find a drop-off place: Look for a place where you can take the full sharps container. This could be a pharmacy or a local health clinic.
4. Ask for help: If you are not sure what to do, ask a nurse or a doctor for help.
It is important to be safe and careful when getting rid of needles. This helps keep everyone safe.
Put used needles in a special container called a 'sharps container.' You can also use a strong, hard container with a secure lid. Make sure to follow the rules for throwing them away in your area.
Can I take my insulin when I travel?
Yes, keep your insulin and things you need in your carry-on bag. Make sure you have a letter from your doctor that says you need insulin. Keep insulin at the right temperature.
What should I do if my insulin looks cloudy or the wrong color?
If your insulin looks cloudy or a strange color, don't use it. Insulin should usually be clear or a little cloudy, but it should not be very cloudy or have changed color.
Tell an adult you trust like a parent, teacher, or nurse. They can help you know what to do next.
Here are some tools that might help you:
- Use a picture checklist of how insulin should look.
- Watch a simple video on how to check insulin.
Do not use insulin if it looks cloudy or the wrong color. This does not include some kinds like NPH insulin that need to be mixed first. If you are unsure, talk to your pharmacist or a doctor for new insulin.
What are the different types of insulin delivery devices?
Here are the types of tools people use to take insulin:
- Insulin Pens: These look like a pen. You can use them to inject insulin into your body.
- Insulin Pumps: These are small machines. They give insulin through a tiny tube in your skin.
- Syringes: Traditional way to inject insulin using a needle and a tube.
- Insulin Inhalers: You breathe in insulin with this device.
If it is hard to understand, ask someone to explain it to you. You can also use picture guides to help.
The main ways people in the UK get insulin are insulin pens, insulin pumps, and syringes.
How do I get an insulin pen ready to use?
First, wash your hands to make sure they are clean. Take off the pen's cap. Put on a new needle. Get the pen ready by turning it to 2 and pressing the button. Keep pressing until you see a drop of insulin come out.
If reading is hard, try listening to someone read it to you. You can also use a pen or highlighter to focus on one part at a time.
Where should you put an insulin injection?
You can give injections in the belly, upper arms, legs, and bottom. It is important to use different spots each time so the skin stays healthy.
How do I measure the right amount of insulin?
Here's how to do it:
- Ask a grown-up or a doctor to show you how to measure insulin.
- Use an insulin pen or syringe to get the right amount.
- Check the numbers on the pen or syringe carefully.
- If you are not sure, ask for help!
Tools and tips:
- Use a magnifying glass to see the numbers better.
- Have a chart or picture guide to follow.
- Practice with a nurse or doctor.
Listen to what your doctor or nurse says. If you have a pen, turn the dial to the right dose. If you have a syringe, take the right amount from the bottle.
How do I take insulin?
Here is how you can take your insulin injection safely and easily:
- Get ready: Wash your hands with soap and water. Make sure the insulin is not too hot or too cold.
- Choose a spot: Pick a different spot on your belly, thigh, or arm each time. This helps protect your skin.
- Use the right tools: Use a clean needle and the insulin your doctor gave you.
- Ask for help: If you find it hard, ask a family member or nurse to help you.
Remember, always follow what your doctor says about how much insulin to use.
Tools that can help:
- Insulin pens: These are easier to use than syringes.
- Reminders: Set alarms to help you remember when to take your insulin.
- Apps: There are phone apps to track your insulin schedule.
Grab the skin gently. Put the needle straight in. Push the button or plunger. Wait for a few seconds, then take the needle out.
What to Do if an Injection Hurts
If an injection causes pain, here are some simple tips:
- Stay Calm: Try to relax your body.
- Talk to Someone: Tell a doctor or nurse if it hurts.
- Breathe Deeply: Take slow, deep breaths to feel better.
- Ask for Help: You can ask if there is something to make it hurt less.
These steps can help you feel better.
Make sure the needle is sharp and not bent. Relax your muscle and change where you inject each time. If it still hurts, talk to your doctor or nurse.
How do I keep insulin?
Here is how to keep insulin safe:
- Keep insulin in the fridge until you use it.
- Don't let insulin get too hot or too cold.
- When you start using a bottle, you can keep it at room temperature.
- Check the expiry date. Don't use it after this date.
If you need help, ask a doctor or nurse. They can give you tips on keeping insulin safe.
Keep insulin that hasn't been opened in the fridge. Once you open insulin pens or bottles, you can keep them at room temperature. Make sure they are away from heat and light. You can usually use them for up to 28 days after opening.
Make reading easier with these tools: - **Text-to-Speech**: Have text read out loud to help understand better. - **Highlighting**: Use a yellow pen to mark important parts. - **Chunking**: Break big information into smaller bits. - **Pictures**: Use pictures to help explain words.What if I forget to take my medicine?
If you forget to take your medicine, don’t worry.
Here’s what you can do:
- Take it as soon as you remember.
- If it’s nearly time for the next dose, skip the dose you missed. Just take the next one.
- Never take two doses at once to make up for the one you missed.
If you’re worried, you can:
- Ask an adult you trust.
- Talk to your doctor.
Tools that can help:
- Use an alarm or a phone reminder to help you remember.
- Keep a medicine chart or checklist.
Ask your doctor or nurse what to do. Do not take two doses next time unless they tell you to.
What can happen if you take insulin injections?
Insulin injections can help people with diabetes, but sometimes they might cause other changes in your body. Here are some things that might happen:
- Your skin might get a bit red or sore where you had the injection.
- You might feel a bit dizzy or shaky if your blood sugar gets too low.
- Some people might gain a little weight.
- There could be small lumps or bumps where you inject.
If you feel worried, it's a good idea to talk to a doctor or nurse. They can help you feel better.
Some things might happen when you use this medicine. You might have low blood sugar, gain some weight, or get redness, swelling, or itchiness where you got the shot.
Can I use insulin syringes or needles more than once?
It is not safe to use syringes or needles more than once. Always use a new syringe and needle each time. It helps keep you healthy.
Here are some tools and tips to help you:
- Ask someone you trust for help if you are not sure what to do.
- Keep new syringes and needles in a clean, safe place.
- Put used syringes and needles in a special container for sharp things.
Remember, if you have questions, ask your doctor or nurse for help.
You should not use needles or syringes more than once. This can cause infections and make the needle less sharp, which can hurt more.
What if I use too much insulin?
Did you use too much insulin by accident? Here is what you can do:
- Tell someone you trust, like a family member or friend.
- Eat or drink something sweet, like candy or juice. It helps you feel better.
- Keep special sugar tablets. You can use them if you feel dizzy or shaky.
- You might need help from a doctor or nurse. Ask for help if you feel very bad.
It can help to keep a diary. Write down when you take insulin and how much.
Check your blood sugar often. Eat foods with carbohydrates like bread, rice, or fruit to stop your blood sugar from getting too low. Get help from a doctor if you need it.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
It is important to check your blood sugar to stay healthy. Here are some tips:
1. You might need to check your blood sugar every day.
2. Some people check their blood sugar a few times a day, like before meals and at bedtime.
3. Talk to your doctor or nurse. They can tell you how often is best for you.
Tools to help you:
- Use a blood sugar meter. It will tell you your blood sugar level.
- Keep a notebook. Write down your blood sugar numbers.
- Use reminders. Set alarms to help you remember to check your blood sugar.
How often you need treatment will depend on your own plan. Talk to your doctor or nurse to find out what is right for you.
What Needle Should I Use for Insulin Shots?
If you need insulin shots, you should use a special needle. These needles are small and thin.
Using the right needle makes taking insulin easier and less painful. Here are some tips to help:
- Talk to your doctor or nurse. They can help you choose the best needle.
- Look for needles that are short and thin. They hurt less.
- Use a new needle each time to keep things clean.
If you find it hard to read this, try these tools:
- Ask someone to read with you.
- Use a magnifying glass if the print is too small.
- Listen to the text using a screen reader.
Use a needle one time only. The needle should be very small and thin. It is usually size 31 or 32. The needle can be different lengths. It is often between 4mm and 12.7mm long. Ask your doctor or nurse what is best for you.
Can I take insulin when I travel?
Yes, you can travel with insulin. If your trip is long, keep it in a cool bag. Bring a letter from your doctor for the airport. A doctor’s letter will help with security checks.
What should I do with used needles and syringes?
When you are done using needles and syringes, put them in a special container. This container is called a "sharps bin." You can ask your doctor or pharmacy for one.
Do not throw needles or syringes in the trash. They can hurt other people. Always use the sharps bin to keep everyone safe.
When the sharps bin is full, take it back to your doctor or pharmacy. They will help you dispose of it safely.
You can also watch videos online to learn how to use a sharps bin. These videos can make it easier to understand.
Put used needles and syringes in a special sharps disposal box. Do not throw them in the regular trash. Ask your local council how to get rid of them safely.
Useful Links
This website offers general information and is not a substitute for professional advice.
Always seek guidance from qualified professionals.
If you have any medical concerns or need urgent help, contact a healthcare professional or emergency services immediately.
Some of this content was generated with AI assistance. We’ve done our best to keep it accurate, helpful, and human-friendly.
- Ergsy carfully checks the information in the videos we provide here.
- Videos shown by Youtube after a video has completed, have NOT been reviewed by ERGSY.
- To view, click the arrow in centre of video.
- Most of the videos you find here will have subtitles and/or closed captions available.
- You may need to turn these on, and choose your preferred language.
- Go to the video you'd like to watch.
- If closed captions (CC) are available, settings will be visible on the bottom right of the video player.
- To turn on Captions, click settings .
- To turn off Captions, click settings again.
More Items From Ergsy search
-

How to inject insulin
Relevance: 100%
-

Diabetes: How to inject insulin | NHS
Relevance: 91%
-

Can Mounjaro be mixed with insulin?
Relevance: 60%
-

Are GLP-1 medications injectable?
Relevance: 58%
-

Is Ozempic a form of insulin?
Relevance: 58%
-

What is the role of insulin in Type 2 Diabetes?
Relevance: 55%
-

What is the connection between GLP-1 and insulin?
Relevance: 47%
-

Does Botox injection hurt?
Relevance: 45%
-

Eye Injections at Royal Bournemouth Hospital
Relevance: 43%
-

Eye Injections at Royal Bournemouth Hospital
Relevance: 43%
-

Evidence-Based Interventions: injections for non-specific low back pain without sciatica
Relevance: 37%
-

What should I do if I experience side effects after a Botox injection?
Relevance: 35%
-

Do I need any vaccine injections for EU countries?
Relevance: 30%
-

How do weight loss jabs work?
Relevance: 29%
-

How does Ozempic work?
Relevance: 28%
-

How should I inject Mounjaro?
Relevance: 26%
-

What is Mounjaro?
Relevance: 26%
-
What is the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
Relevance: 26%
-

Is Ozempic suitable for type 1 diabetes?
Relevance: 26%
-

Can I take Ozempic with other diabetes medications?
Relevance: 24%
-

What is type 1 diabetes?
Relevance: 24%
-

How is Ozempic administered?
Relevance: 24%
-

Are there any GLP-1 medications that are taken orally?
Relevance: 23%
-

What is Ozempic?
Relevance: 23%
-

What is GLP-1?
Relevance: 23%
-

Can Mounjaro be used in type 1 diabetes?
Relevance: 23%
-

How do GLP-1 receptor agonists work?
Relevance: 22%
-

How does Ozempic affect blood sugar levels?
Relevance: 22%
-

How is Type 2 Diabetes treated?
Relevance: 21%
-

How is Mounjaro administered?
Relevance: 20%
-
What is type 1 diabetes?
Relevance: 20%
-

What does GLP-1 stand for?
Relevance: 20%
-

Is GLP-1 related to any other hormones?
Relevance: 19%
-

How is Wegovy administered?
Relevance: 18%
-

How is Ozempic administered?
Relevance: 18%
-

What impact does GLP-1 have on glucose metabolism?
Relevance: 18%
-

How to manage type 2 diabetes
Relevance: 17%
-

What are the common side effects of Ozempic?
Relevance: 17%
-

Can GLP-1 be used as a medication?
Relevance: 17%
-

Does Botox hurt?
Relevance: 17%


