Find Help
More Items From Ergsy search
-
What impact do screw worms have on livestock?
Relevance: 100%
-

What are Screw Worms parasites?
Relevance: 83%
-

Can screw worm infestations be prevented?
Relevance: 81%
-

Are there any natural predators of screw worms?
Relevance: 80%
-

How do screw worms reproduce?
Relevance: 79%
-

How do screw worms infest their hosts?
Relevance: 78%
-
Can screw worms cause zoonotic disease?
Relevance: 75%
-

What are the symptoms of a screw worm infestation?
Relevance: 75%
-
Where are screw worms found geographically?
Relevance: 74%
-
Has the screw worm been eradicated in some areas?
Relevance: 74%
-

What methods are used to control screw worm populations?
Relevance: 73%
-
Are screw worms dangerous to humans?
Relevance: 72%
-

What measures are taken during a screw worm outbreak?
Relevance: 71%
-
How are screw worm infestations treated?
Relevance: 69%
-
How long do screw worm larvae typically infest a host?
Relevance: 66%
-

What species of flies produce screw worms?
Relevance: 64%
-

What economic impact do screw worms have?
Relevance: 42%
-
What animals can be affected by screw worms?
Relevance: 37%
-

How can individuals help in the fight against screw worms?
Relevance: 32%
-

How do hosepipe bans affect farmers?
Relevance: 17%
-

Why is screw worm eradication important?
Relevance: 16%
-

How do I install a Ring Doorbell Camera?
Relevance: 12%
-

Is there an impact on short-term rentals?
Relevance: 11%
-

How will the cuts impact landlords?
Relevance: 10%
-
Can whiplash occur at low-speed impacts?
Relevance: 10%
-

What is the impact of director disputes on company morale?
Relevance: 10%
-

What are the environmental impacts of cremation?
Relevance: 10%
-

Impact of Housing Shortage on Local Communities
Relevance: 10%
-

Does screen time impact REM sleep?
Relevance: 10%
-

How can drug offences impact future opportunities?
Relevance: 10%
-

Can diet impact BPH?
Relevance: 10%
-

Can a wealth tax impact economic behavior?
Relevance: 10%
-

What are the health impacts of the US leaving WHO?
Relevance: 10%
-

Impact of Rising Energy Costs on Family Budgets
Relevance: 10%
-

What are the potential long-term impacts of housing benefit cuts?
Relevance: 10%
-

Can sewage pollution impact marine wildlife?
Relevance: 10%
-

Can diet impact postnatal depression?
Relevance: 9%
-

How does the type of case impact the court schedule?
Relevance: 9%
-

What is the impact of obesity on mental health?
Relevance: 9%
-

How Rising Living Costs Are Impacting Family Wellbeing
Relevance: 9%
Introduction to Screw Worms
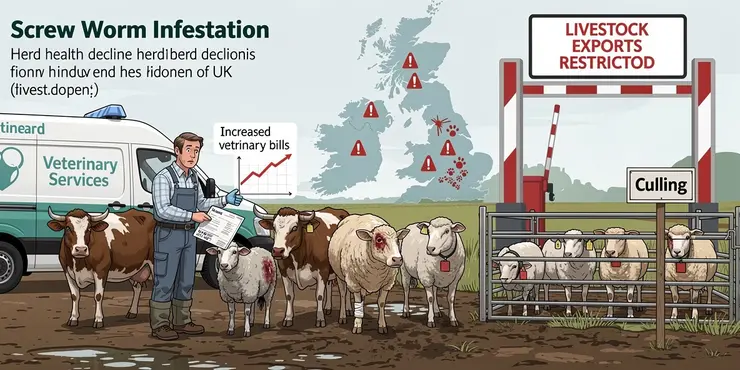
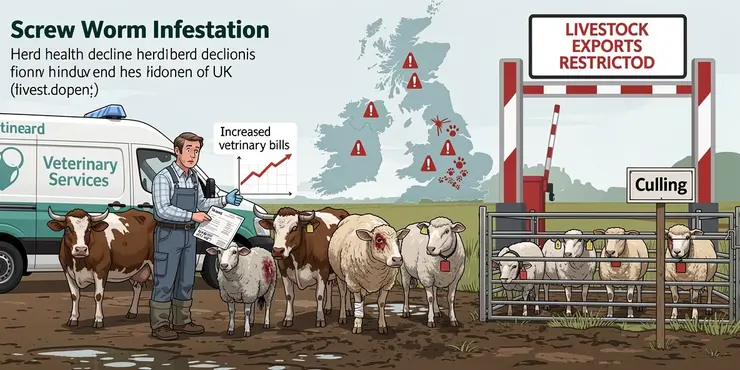
Screw worms are parasitic fly larvae that infest and consume the living tissue of warm-blooded animals. The presence of screw worms is a serious threat to livestock, causing significant economic and welfare issues. Although not currently present in the UK, understanding the impact of screw worms is crucial for prevention and management strategies should they be introduced.
Biology and Lifecycle of Screw Worms
Screw worms belong to the fly family Calliphoridae, with the primary species being the New World Screwworm (Cochliomyia hominivorax) and the Old World Screwworm (Chrysomya bezziana). The flies lay eggs in open wounds on animals. The larvae hatch and feed on the host's tissue, causing severe injuries and leading to secondary infections. The lifecycle from egg to adult can be completed in weeks, leading to rapid population increases in suitable climates.
Economic Impact on Livestock
Screw worms pose a considerable economic threat to the livestock industry due to the costs associated with treatment, loss of livestock, and production inefficiencies. Infestations can lead to significant weight loss in animals, decreased milk production, and, ultimately, death if left untreated. The presence of screw worms necessitates expensive veterinary care and management programs, which increase operational costs for farmers.
Welfare Concerns for Animals
The welfare implications of screw worm infestation are severe. Affected animals experience extreme discomfort and pain due to the larvae feeding on their tissue. Open wounds attract further infestations and can result in debilitating conditions or death. Preventative and responsive measures must prioritize animal welfare through regular inspection, early detection, and timely treatment to mitigate suffering.
Environmental Factors and Risks
Screw worms thrive in warm, humid conditions, posing a higher risk in regions with favorable climates. Although not currently found in the UK, climate change could alter habitat suitability. International trade and movement of animals increase the risk of accidental introduction, warranting stringent import controls and monitoring programs to prevent an outbreak.
Prevention and Control Strategies
Effective control of screw worms relies on a combination of strategies. Surveillance programs, including monitoring of livestock and wildlife, are essential for early detection. The Sterile Insect Technique (SIT) has been successful in eradicating populations in affected areas by releasing sterile males to disrupt breeding. Quarantine measures and education of farmers about symptoms and preventive measures are critical components of an integrated approach.
Conclusion
The impact of screw worms on livestock extends beyond economic losses, significantly affecting animal welfare and requiring strategic management to prevent potential outbreaks. Awareness and preparedness are key to protecting the UK's livestock industry and maintaining high welfare standards. Collaborative efforts between government, researchers, and farmers will ensure effective responses to this threat.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are screw worms?
Screw worms are fly larvae (maggots) that infest and feed on the living tissue of warm-blooded animals, including livestock.
How do screw worms affect livestock?
Screw worms cause severe pain, distress, and can lead to secondary infections or even death if not treated, impacting livestock health and productivity.
What species of screw worms are most harmful to livestock?
The primary species harmful to livestock are the New World screw worm (Cochliomyia hominivorax) and the Old World screw worm (Chrysomya bezziana).
What are the signs of screw worm infestation in livestock?
Signs include wounds that don't heal and may have a foul smell, irritation, inflammation, and larvae visible in wounds.
How do screw worms enter livestock?
Adult flies lay eggs on open wounds or mucous membranes, and the larvae burrow into the flesh of their host.
Can screw worm infestations spread among livestock?
Yes, infestations can spread through open wounds on different animals, especially in warm, humid conditions.
How do screw worm infestations impact livestock production?
Infestations can reduce weight gain, milk production, and overall animal health, leading to economic losses in livestock production.
Can screw worms transmit diseases to livestock?
While screw worms themselves do not transmit diseases, they can lead to secondary bacterial infections in livestock.
How can screw worm infestations be prevented in livestock?
Prevention includes maintaining hygiene, treating wounds promptly, and using insect repellents or insecticides.
What treatments are available for livestock infested with screw worms?
Treatments include removing larvae manually, applying insecticidal dressings, and providing supportive care with antibiotics for infections.
Are there any biological control methods for managing screw worms in livestock?
Yes, the sterile insect technique (SIT) is a biological control method where sterile males are released to reduce the breeding population.
How does screw worm infestation affect animal welfare?
Screw worm infestations cause significant pain and suffering, leading to distress, poor quality of life, and potentially death if untreated.
What economic impacts do screw worms have on livestock farming?
Economic impacts include treatment costs, reduced productivity, death of animals, and potential trade restrictions due to infestations.
Where are screw worms commonly found?
Screw worms are commonly found in tropical and subtropical regions, but efforts like SIT have eradicated them in areas such as the U.S.
How quickly can screw worms kill livestock?
Screw worms can cause severe infestations within a few days, leading to rapid deterioration and death if untreated.
What role do veterinarian services play in managing screw worm infestations?
Veterinarian services are crucial for diagnosing, treating infestations, and advising on preventative measures to protect livestock.
Can wild animals transmit screw worms to livestock?
Yes, wild animals can harbor screw worms and act as reservoir hosts, potentially transmitting them to livestock.
What climates are favorable to screw worm breeding?
Screw worms thrive in warm and humid climates, which provide ideal conditions for breeding and larval development.
Have there been successful eradication programs for screw worms?
Yes, programs utilizing SIT have successfully eradicated screw worms from North America and other regions, reducing impacts on livestock.
How does climate change potentially affect screw worm populations?
Climate change may expand the geographical range of screw worms by creating more favorable climates for their survival and spread.
Useful Links
This website offers general information and is not a substitute for professional advice.
Always seek guidance from qualified professionals.
If you have any medical concerns or need urgent help, contact a healthcare professional or emergency services immediately.
Some of this content was generated with AI assistance. We’ve done our best to keep it accurate, helpful, and human-friendly.
- Ergsy carfully checks the information in the videos we provide here.
- Videos shown by Youtube after a video has completed, have NOT been reviewed by ERGSY.
- To view, click the arrow in centre of video.
- Most of the videos you find here will have subtitles and/or closed captions available.
- You may need to turn these on, and choose your preferred language.
- Go to the video you'd like to watch.
- If closed captions (CC) are available, settings will be visible on the bottom right of the video player.
- To turn on Captions, click settings .
- To turn off Captions, click settings again.
More Items From Ergsy search
-

What impact do screw worms have on livestock?
Relevance: 100%
-

What are Screw Worms parasites?
Relevance: 83%
-

Can screw worm infestations be prevented?
Relevance: 81%
-

Are there any natural predators of screw worms?
Relevance: 80%
-

How do screw worms reproduce?
Relevance: 79%
-

How do screw worms infest their hosts?
Relevance: 78%
-

Can screw worms cause zoonotic disease?
Relevance: 75%
-

What are the symptoms of a screw worm infestation?
Relevance: 75%
-
Where are screw worms found geographically?
Relevance: 74%
-

Has the screw worm been eradicated in some areas?
Relevance: 74%
-

What methods are used to control screw worm populations?
Relevance: 73%
-
Are screw worms dangerous to humans?
Relevance: 72%
-

What measures are taken during a screw worm outbreak?
Relevance: 71%
-
How are screw worm infestations treated?
Relevance: 69%
-

How long do screw worm larvae typically infest a host?
Relevance: 66%
-

What species of flies produce screw worms?
Relevance: 64%
-

What economic impact do screw worms have?
Relevance: 42%
-
What animals can be affected by screw worms?
Relevance: 37%
-

How can individuals help in the fight against screw worms?
Relevance: 32%
-

How do hosepipe bans affect farmers?
Relevance: 17%
-

Why is screw worm eradication important?
Relevance: 16%
-

How do I install a Ring Doorbell Camera?
Relevance: 12%
-

Is there an impact on short-term rentals?
Relevance: 11%
-

How will the cuts impact landlords?
Relevance: 10%
-

Can whiplash occur at low-speed impacts?
Relevance: 10%
-

What is the impact of director disputes on company morale?
Relevance: 10%
-

What are the environmental impacts of cremation?
Relevance: 10%
-

Impact of Housing Shortage on Local Communities
Relevance: 10%
-

Does screen time impact REM sleep?
Relevance: 10%
-

How can drug offences impact future opportunities?
Relevance: 10%
-

Can diet impact BPH?
Relevance: 10%
-

Can a wealth tax impact economic behavior?
Relevance: 10%
-

What are the health impacts of the US leaving WHO?
Relevance: 10%
-

Impact of Rising Energy Costs on Family Budgets
Relevance: 10%
-

What are the potential long-term impacts of housing benefit cuts?
Relevance: 10%
-

Can sewage pollution impact marine wildlife?
Relevance: 10%
-

Can diet impact postnatal depression?
Relevance: 9%
-

How does the type of case impact the court schedule?
Relevance: 9%
-

What is the impact of obesity on mental health?
Relevance: 9%
-

How Rising Living Costs Are Impacting Family Wellbeing
Relevance: 9%


