
Find Help
More Items From Ergsy search
-

How is flesh-eating disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 100%
-

Is flesh-eating disease contagious?
Relevance: 80%
-
What is a flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 78%
-

Can flesh-eating disease be treated?
Relevance: 77%
-

Who is at risk for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 74%
-

What causes flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 73%
-
Can flesh-eating disease cause long-term complications?
Relevance: 70%
-
Can antibiotics alone cure flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 69%
-

How does flesh-eating disease spread?
Relevance: 69%
-
What is the mortality rate for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 67%
-

Are there any preventative measures for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 67%
-

Can flesh-eating disease recur after treatment?
Relevance: 67%
-
What is the difference between cellulitis and flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 66%
-
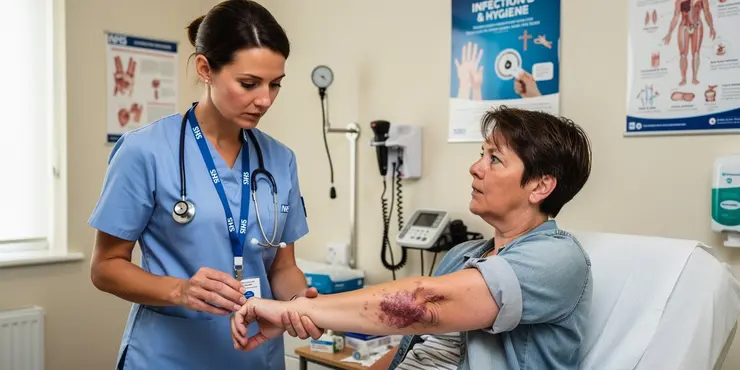
What are the symptoms of flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 64%
-

Can flesh-eating disease occur after common surgical procedures?
Relevance: 63%
-
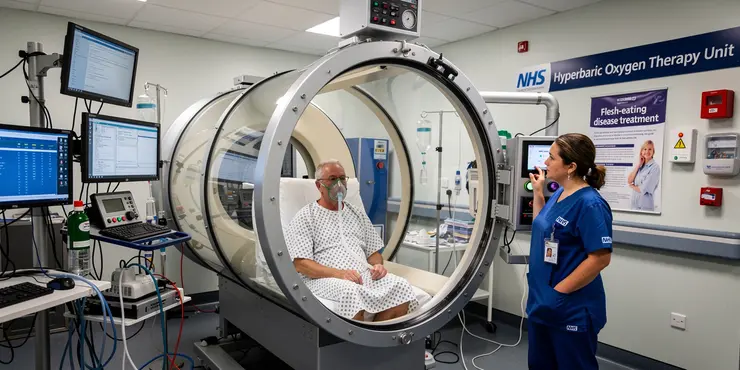
What is the role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in treating flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 63%
-
How quickly does flesh-eating disease progress?
Relevance: 62%
-
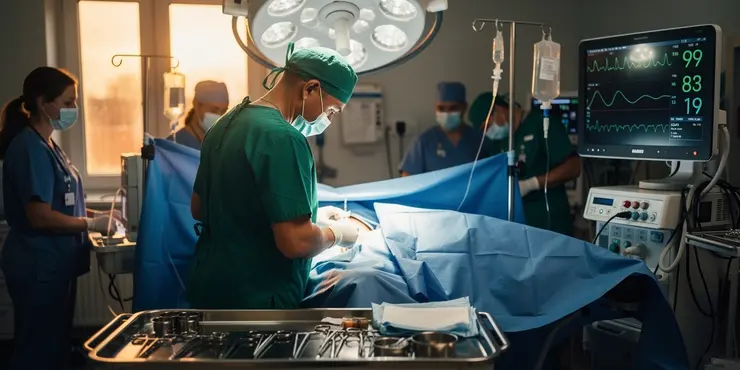
Is surgery always required to treat flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 60%
-

What is a flesh eating disease?
Relevance: 54%
-

How is Crohn's disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 54%
-

How is Huntington's disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 54%
-

How is Alzheimer's disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 53%
-

How is sickle cell disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 51%
-

What tests are available for diagnosing Lyme disease?
Relevance: 49%
-

How is Marburg virus disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 49%
-

Diagnosing Coeliac Disease Updated 2021
Relevance: 49%
-

How is motor neurone disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 48%
-
How can healthcare providers prevent the spread of flesh-eating bacteria in hospitals?
Relevance: 41%
-

How is hypotony diagnosed?
Relevance: 36%
-

How is lupus diagnosed in children?
Relevance: 35%
-
Coeliac Disease: Session 1: What is Coeliac Disease?
Relevance: 35%
-
How is Chikungunya virus infection diagnosed?
Relevance: 34%
-

Coeliac disease
Relevance: 34%
-

How is autism diagnosed?
Relevance: 34%
-
Lyme disease: What is it?
Relevance: 34%
-

How is SAD diagnosed?
Relevance: 34%
-

Diagnosing irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
Relevance: 34%
-

What is Lyme Disease?
Relevance: 34%
-

How is ADHD diagnosed?
Relevance: 34%
-
How is mitochondrial disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 33%
Introduction to Flesh-Eating Disease
Flesh-eating disease, medically known as necrotising fasciitis, is a severe bacterial infection. This condition rapidly destroys soft tissue, causing significant damage.
Prompt diagnosis and treatment are critical as the infection can spread quickly. Misdiagnosis or delayed intervention can lead to serious complications.
Initial Symptoms and Clinical Assessment
The first step in diagnosing flesh-eating disease is recognising early symptoms. Common signs include severe pain, redness, and swelling in the affected area.
General practitioners or emergency department clinicians assess the patient's condition. They evaluate the severity of symptoms and medical history to determine potential causes.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
If necrotising fasciitis is suspected, imaging tests like X-rays or CT scans may be conducted. These tests help reveal the extent of tissue damage and gas presence in tissues.
Blood tests are used to check for elevated white blood cell counts or specific bacteria. These tests can indicate infection presence and guide further analysis.
Tissue Biopsy and Microbial Cultures
In certain cases, a tissue biopsy is necessary. A small tissue sample from the affected area is taken and analysed microscopically for signs of necrosis.
Microbial cultures from tissue or fluid samples are grown in a lab to identify bacteria types. Identifying specific bacteria informs appropriate antibiotic treatment options.
Consultation with Specialists
Consultation with specialists, such as dermatologists or infectious disease experts, may be required. These specialists provide additional insights and recommend targeted treatments.
They may also consider other potential conditions that mimic necrotising fasciitis, helping refine the diagnosis.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Early and accurate diagnosis of flesh-eating disease is vital. A swift diagnosis significantly improves treatment outcomes and reduces complications.
Once diagnosed, immediate medical intervention, usually involving surgery and antibiotics, is essential to combat the infection effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is flesh-eating disease?
Flesh-eating disease, also known as necrotizing fasciitis, is a severe bacterial infection that destroys soft tissue.
How is flesh-eating disease initially suspected?
The disease is initially suspected based on symptoms such as severe pain, swelling, fever, and redness in the affected area.
Can blood tests diagnose flesh-eating disease?
Blood tests alone cannot diagnose necrotizing fasciitis but can suggest an infection and identify bacteria.
What imaging tests help diagnose flesh-eating disease?
MRI, CT scans, and ultrasound can be used to detect gas in tissues and deep infections.
What role does a tissue biopsy play in diagnosis?
A tissue biopsy can confirm necrotizing fasciitis by identifying the bacteria and amount of tissue damage.
Why is early diagnosis crucial for flesh-eating disease?
Early diagnosis is critical to prevent extensive tissue damage and reduce the risk of complications.
Can necrotizing fasciitis be diagnosed through symptoms alone?
While symptoms can suggest necrotizing fasciitis, confirmation requires laboratory and imaging tests.
How does a doctor differentiate necrotizing fasciitis from other infections?
A doctor will assess symptoms, perform imaging studies, and evaluate lab tests and cultures to differentiate.
What kind of cultures are taken for diagnosis?
Tissue and blood cultures are taken to identify the bacteria causing the infection.
How fast can necrotizing fasciitis progress?
Necrotizing fasciitis can progress rapidly, within hours to days, making prompt diagnosis critical.
What laboratory tests are conducted for diagnosis?
Complete blood counts, CRP levels, lactate, and creatine kinase levels are commonly tested.
Is surgery part of the diagnostic process?
Surgery can be necessary both for diagnosis and immediate treatment to remove dead tissue.
How does a CT scan help in diagnosing necrotizing fasciitis?
A CT scan can show soft tissue gas formation, which is indicative of infection.
What bacteria commonly cause flesh-eating disease?
Group A Streptococcus, Clostridium, and others like MRSA can cause necrotizing fasciitis.
Why is necrotizing fasciitis considered a medical emergency?
The rapid progression and potential for severe consequences make it a medical emergency.
What symptom is the most indicative of necrotizing fasciitis?
Sudden, severe pain out of proportion to the appearance of the affected area is a key symptom.
Can examination of the affected area help diagnose necrotizing fasciitis?
Physical examination can reveal signs like skin discoloration and tissue death, aiding diagnosis.
Are there risk factors that aid in clinical suspicion?
Yes, factors like recent surgery, trauma, or immune suppression increase clinical suspicion.
Is patient history important for diagnosis?
Patient history, including any recent injuries or illnesses, is crucial for timely diagnosis.
Can necrotizing fasciitis occur without a visible wound?
Yes, it can occur internally without obvious external wounds; hence symptoms and imaging are important.
Useful Links
This website offers general information and is not a substitute for professional advice.
Always seek guidance from qualified professionals.
If you have any medical concerns or need urgent help, contact a healthcare professional or emergency services immediately.
Some of this content was generated with AI assistance. We’ve done our best to keep it accurate, helpful, and human-friendly.
- Ergsy carfully checks the information in the videos we provide here.
- Videos shown by Youtube after a video has completed, have NOT been reviewed by ERGSY.
- To view, click the arrow in centre of video.
- Most of the videos you find here will have subtitles and/or closed captions available.
- You may need to turn these on, and choose your preferred language.
- Go to the video you'd like to watch.
- If closed captions (CC) are available, settings will be visible on the bottom right of the video player.
- To turn on Captions, click settings .
- To turn off Captions, click settings again.
More Items From Ergsy search
-

How is flesh-eating disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 100%
-

Is flesh-eating disease contagious?
Relevance: 80%
-

What is a flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 78%
-

Can flesh-eating disease be treated?
Relevance: 77%
-

Who is at risk for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 74%
-

What causes flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 73%
-
Can flesh-eating disease cause long-term complications?
Relevance: 70%
-

Can antibiotics alone cure flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 69%
-

How does flesh-eating disease spread?
Relevance: 69%
-

What is the mortality rate for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 67%
-

Are there any preventative measures for flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 67%
-

Can flesh-eating disease recur after treatment?
Relevance: 67%
-

What is the difference between cellulitis and flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 66%
-

What are the symptoms of flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 64%
-

Can flesh-eating disease occur after common surgical procedures?
Relevance: 63%
-

What is the role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in treating flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 63%
-
How quickly does flesh-eating disease progress?
Relevance: 62%
-

Is surgery always required to treat flesh-eating disease?
Relevance: 60%
-

What is a flesh eating disease?
Relevance: 54%
-

How is Crohn's disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 54%
-

How is Huntington's disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 54%
-

How is Alzheimer's disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 53%
-

How is sickle cell disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 51%
-

What tests are available for diagnosing Lyme disease?
Relevance: 49%
-

How is Marburg virus disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 49%
-

Diagnosing Coeliac Disease Updated 2021
Relevance: 49%
-

How is motor neurone disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 48%
-
How can healthcare providers prevent the spread of flesh-eating bacteria in hospitals?
Relevance: 41%
-

How is hypotony diagnosed?
Relevance: 36%
-

How is lupus diagnosed in children?
Relevance: 35%
-

Coeliac Disease: Session 1: What is Coeliac Disease?
Relevance: 35%
-

How is Chikungunya virus infection diagnosed?
Relevance: 34%
-

Coeliac disease
Relevance: 34%
-

How is autism diagnosed?
Relevance: 34%
-

Lyme disease: What is it?
Relevance: 34%
-

How is SAD diagnosed?
Relevance: 34%
-

Diagnosing irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
Relevance: 34%
-

What is Lyme Disease?
Relevance: 34%
-

How is ADHD diagnosed?
Relevance: 34%
-
How is mitochondrial disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 33%


