Find Help
More Items From Ergsy search
-
Are vaccines linked to autism?
Relevance: 100%
-

What causes autism?
Relevance: 71%
-

What is Autism?
Relevance: 69%
-

How prevalent is autism?
Relevance: 65%
-

Is there an autism test?
Relevance: 64%
-

What is the autism spectrum?
Relevance: 63%
-

Is there a genetic component to autism?
Relevance: 62%
-

Can autism be cured?
Relevance: 61%
-

What are the signs of autism?
Relevance: 61%
-

How is autism diagnosed?
Relevance: 60%
-

Autism - My Story - Adrian | NHS
Relevance: 60%
-

Can adults have autism?
Relevance: 59%
-

Autism: Graeme's story | NHS
Relevance: 59%
-

Is paracetamol linked to autism?
Relevance: 59%
-
How effective is the MMR vaccine?
Relevance: 58%
-

Autism - My Story - Rosalind | NHS
Relevance: 58%
-

What can cause autism, if not paracetamol?
Relevance: 57%
-

Is autism more common in boys or girls?
Relevance: 57%
-

Is there any scientific evidence that links paracetamol use to autism?
Relevance: 56%
-

What advice is available for parents concerned about autism risks?
Relevance: 56%
-

How does autism affect communication?
Relevance: 56%
-

What are some common therapies for autism?
Relevance: 56%
-

Can people with autism lead independent lives?
Relevance: 55%
-

What is the difference between autism and Asperger's syndrome?
Relevance: 54%
-

Autism Assessment - What Happens in Your Appointment
Relevance: 53%
-

What role do sensory issues play in autism?
Relevance: 53%
-

How can families support a member with autism?
Relevance: 52%
-

How can early intervention help children with autism?
Relevance: 51%
-

The NHS Long Term Plan for learning disability and autism
Relevance: 51%
-

Why is there concern about paracetamol and autism?
Relevance: 51%
-

Is there any risk of using paracetamol outside of pregnancy with regard to autism?
Relevance: 50%
-
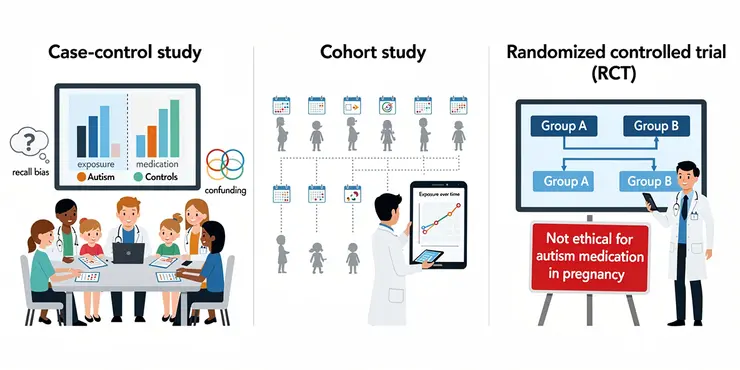
What kind of studies are conducted to investigate links between medications and autism?
Relevance: 50%
-
Children's Vaccination Schedule
Relevance: 49%
-

What is the MMR vaccine?
Relevance: 48%
-

How effective is the MMR vaccine?
Relevance: 46%
-

Transforming Care for people with Learning Disabilities and/ or Autism: Peter's Story
Relevance: 45%
-
Are there vaccines for meningitis?
Relevance: 43%
-

Are vaccines safe?
Relevance: 43%
-

What is a vaccine?
Relevance: 42%
-

Is there a vaccine for H3N2?
Relevance: 42%
The Myth: Vaccines and Autism
The claim that vaccines are linked to autism has been a topic of debate and concern for many parents and health professionals across the world, including the UK. This controversial idea primarily originated from a study published in 1998 by Andrew Wakefield, who suggested a link between the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine and autism. Though the study was later discredited and retracted due to serious procedural errors and ethical violations, the myth persists.
The Scientific Consensus
There is a strong scientific consensus that vaccines do not cause autism. Large-scale studies conducted across various countries and populations consistently show no link between receiving vaccinations and the development of autism spectrum disorders. Organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and Public Health England support these findings, emphasizing the safety and necessity of childhood vaccinations.
Public Health Perspective
Vaccination is a crucial public health tool that protects individuals and communities from infectious diseases. The MMR vaccine, in particular, is essential in preventing outbreaks of measles, mumps, and rubella, diseases that can lead to severe health complications or even death. Vaccination contributes to herd immunity, which protects those who cannot be vaccinated, such as infants and individuals with certain medical conditions.
The Importance of Accurate Information
In the UK, healthcare professionals are working tirelessly to counteract misinformation regarding vaccines and autism. Public Health England and the NHS provide evidence-based resources to educate parents and caregivers. It is vital to rely on credible sources when making health-related decisions, as misinformation can lead to vaccine hesitancy and lower vaccination rates, putting communities at risk.
Continuing Research
Researchers continue to study autism spectrum disorders to better understand their causes and improve treatments. While vaccines do not cause autism, factors such as genetics and environmental influences are being explored. Continuous research and investment in this field are crucial for developing effective intervention strategies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the belief that vaccines are linked to autism is unfounded and refuted by a wealth of scientific evidence. Maintaining high vaccination rates is essential for protecting public health and preventing the resurgence of infectious diseases. The UK remains committed to ensuring the safety and efficacy of vaccines, and addressing vaccine-related myths is a part of maintaining public trust in vaccination programs.
The Myth: Vaccines and Autism
Some people think vaccines cause autism. This idea has worried many parents and doctors. It started from a study in 1998 by a doctor named Andrew Wakefield. He said the vaccine for measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) might cause autism. But later, people found out this study was wrong. They also found problems in how it was done. The study is not trusted anymore, but some people still believe in the idea.
The Scientific Consensus
Scientists agree that vaccines are safe and do not cause autism. Big studies from different countries show no link between vaccines and autism. Important groups like the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) say vaccines are safe. They help protect children from getting sick.
Public Health Perspective
Vaccines are important to keep people healthy. The MMR vaccine stops diseases like measles, mumps, and rubella. These illnesses can make people very sick. Vaccines help protect not just the person who gets the shot but also others who can't get vaccinated, like babies or people with health problems. This is called herd immunity.
The Importance of Accurate Information
In the UK, doctors and nurses work hard to give good information about vaccines. Public Health England and the NHS have trusted information to help parents. It is important to use good sources of information to make health choices. Wrong information can make people scared of vaccines, which can lead to fewer people getting vaccinated. This can be dangerous for everyone.
Continuing Research
Scientists keep studying autism to find out its causes and make better treatments. Vaccines do not cause autism. Instead, they look at genetics (family history) and the environment. It's important to keep doing research to help children with autism.
Conclusion
To finish, vaccines do not cause autism. Science does not support this idea. Getting vaccinated is very important to keep people safe from diseases. The UK makes sure vaccines are safe and works to stop wrong ideas about them. Keeping trust in vaccines helps protect everyone.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are vaccines linked to autism?
No, extensive research has shown there is no link between vaccines and autism.
What study started the vaccine-autism controversy?
The controversy began with a 1998 study by Andrew Wakefield, which has since been discredited.
Has the original study linking vaccines to autism been retracted?
Yes, the 1998 study by Andrew Wakefield was retracted by The Lancet in 2010.
What do major health organizations say about vaccines and autism?
Organizations like the CDC, WHO, and AAP state there is no link between vaccines and autism.
Have further studies been conducted to investigate vaccines and autism?
Yes, numerous studies involving large populations have found no evidence of a link.
What is the role of thimerosal in the vaccine-autism debate?
Thimerosal, a mercury-based preservative, was falsely linked to autism; it has been removed or reduced in vaccines.
Do vaccines cause neurological disorders in children?
There is no scientific evidence supporting a link between vaccines and neurological disorders such as autism.
Why do some parents still believe vaccines cause autism?
Misinformation, anecdotal experiences, and distrust of pharmaceutical companies contribute to these beliefs.
What impact have vaccine-autism myths had on vaccination rates?
These myths have contributed to vaccine hesitancy and outbreaks of preventable diseases.
Can a child be diagnosed with autism shortly after receiving a vaccine?
Timing of diagnosis might coincide with vaccinations, but studies show vaccines do not cause autism.
Have any components in vaccines been found to cause autism?
No components in vaccines have been scientifically shown to cause autism.
How do scientists ensure vaccines are safe concerning autism?
Vaccines undergo rigorous testing and monitoring to ensure safety, including thorough investigations into autism.
What is herd immunity and how is it affected by the vaccine-autism myth?
Herd immunity protects those who cannot be vaccinated; declining vaccination rates due to myths threaten this protection.
What should parents do if they are concerned about vaccines and autism?
Parents should consult with healthcare professionals and rely on reputable sources for vaccine information.
Are there any vaccines that increase the risk of autism?
No, there are no vaccines that have been shown to increase the risk of autism.
Has the autism rate increased due to vaccinations?
Increases in autism diagnoses are not linked to vaccinations, but likely due to broader diagnostic criteria and awareness.
Why is it important to dispel the vaccine-autism myth?
Dispelling this myth is crucial to maintaining public health and preventing outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases.
Did any legal cases validate the link between vaccines and autism?
No legal cases have been upheld that prove a link between vaccines and autism.
Have countries or health organizations issued statements about vaccines and autism?
Yes, many countries and health organizations have publicly stated that vaccines do not cause autism.
How does misinformation about vaccines spread?
Misinformation spreads through social media, some news outlets, and personal anecdotal stories.
Do vaccines cause autism?
No, vaccines do not cause autism. Doctors and scientists have done many studies to check this. They found that vaccines are safe and do not make children autistic.
If you want help understanding this better, you can:
- Ask your doctor for more information.
- Read books or watch videos about how vaccines keep us healthy.
- Talk to someone you trust who knows about health.
No, lots of studies have shown that vaccines do not cause autism.
Which study began the argument about vaccines and autism?
This problem started with a study in 1998 by a man named Andrew Wakefield. People found out later that his study was wrong.
Did scientists take back the study that said vaccines cause autism?
Yes, in 1998, a doctor named Andrew Wakefield did a study.
But in 2010, The Lancet, a big medical magazine, said the study was wrong and took it back.
What do big health groups say about vaccines and autism?
Big health groups, like doctors and scientists, say vaccines are safe. They say vaccines do not cause autism. Autism is something some kids have that makes it hard to talk or understand other people.
If you want more help, you can:
- Ask a doctor or nurse.
- Visit a health clinic.
- Use easy-to-read websites.
Groups like the CDC, WHO, and AAP say vaccines do not cause autism.
Did scientists study vaccines and autism more?
Yes, many big studies have looked into this and found no link.
What does thimerosal do in the vaccine and autism talk?
Some people talk about a thing called "thimerosal" in vaccines. They wonder if it is linked to autism. Autism is when the brain works in a different way, and it can make learning and talking hard.
Thimerosal keeps vaccines safe and stops germs from growing in them. Experts say thimerosal in vaccines is safe. They say thimerosal does not cause autism.
If you want more help understanding, you can:
- Ask a doctor or nurse.
- Read easy books or watch videos about vaccines.
- Use simple apps that explain health in a fun way.
Thimerosal is a safe chemical that was used to help keep vaccines clean. Some people said it caused autism, but that was not true. Thimerosal is now used much less in vaccines.
If you're finding it hard to read, try using a ruler or your finger to help keep your place. You can also ask someone to read it with you.
Can vaccines make children's brains sick?
Vaccines help protect us from getting sick. Sometimes, people worry if vaccines can make children's brains not work well. Scientists have studied this and say vaccines are safe. If you are still worried, you can talk to a doctor or nurse. They can help you understand more.
Using pictures and videos can also help explain how vaccines work. Stories and books about going to the doctor might make learning about vaccines easier and fun.
Scientists say vaccines do not cause brain problems like autism. There is no proof that they are connected.
Why do some parents think vaccines cause autism?
Parents might worry about vaccines and autism because of things they've heard or read.
Sometimes, stories and information can make people feel scared or confused.
Here are some ways to help understand:
- Ask a doctor about vaccines and autism.
- Read information from trustworthy sources.
- Talk to other parents about their experiences.
Remember, doctors and experts say vaccines are safe and do not cause autism.
Some people believe this because they hear wrong information, stories from others, and they do not trust big medicine companies.
How have stories about vaccines causing autism affected how many people get vaccines?
These untrue stories make people scared of vaccines and cause more people to get sick from diseases we can stop with vaccines.
Can a child get diagnosed with autism soon after a vaccine?
Sometimes, a child might be told they have autism after getting a vaccine. But doctors say vaccines do not cause autism.
If you have questions, you can talk to a doctor or a nurse. They can help you understand.
Sometimes, autism is found around the same time a child gets vaccines.
But studies show that vaccines do not cause autism.
Do vaccines have anything in them that causes autism?
Vaccines do not cause autism. Scientists have done many studies to check this.
How do scientists make sure vaccines are safe and do not cause autism?
Vaccines help keep us healthy. Scientists work hard to make sure they are safe. Here’s how they do it: - **Testing:** Before vaccines are used, scientists test them a lot. They check if they are safe for everyone. - **Watching:** After people get a vaccine, scientists watch to make sure there are no problems. - **Studying:** Scientists read many studies. These studies show vaccines do not cause autism. If you have questions, talking to a doctor can help. You can also look at pictures or videos of how vaccines work.Vaccines are tested a lot to make sure they are safe. Experts carefully check them to see if they might cause autism. This helps keep everyone safe.
What is herd immunity and how does the vaccine-autism story affect it?
Herd immunity means most people are safe from a disease because lots of people got a vaccine.
Some people think vaccines cause autism, but this is not true. This false story makes some people afraid to get vaccines.
If not enough people get vaccines, herd immunity does not work well. Then, more people can get sick.
Ask a doctor or nurse if you have questions about vaccines. They can help you understand how vaccines keep you safe.
To learn more, you can read simple books or watch videos made for kids.
Herd immunity helps protect people who can't get vaccines. But when less people get vaccinated because of untrue stories, this protection is in danger.
What can parents do if they are worried about vaccines and autism?
If you are worried about vaccines and autism, here are some steps you can take:
- Talk to your doctor. They can give you good advice and answer your questions.
- Read books or look at websites from trusted health groups to learn more.
- Write down your questions so you can ask your doctor or nurse when you see them.
- Join a support group to talk to other parents who have the same questions.
- Remember, many studies show that vaccines are safe for children.
Use these steps to help you feel better and make good choices for your child.
Parents should talk to doctors or nurses and look at trusted sources to learn about vaccines.
Do any vaccines cause autism?
No, vaccines do not cause autism. Vaccines help keep us safe from sickness.
Here are some tips to understand better:
- Ask a doctor or nurse if you have questions about vaccines.
- Use picture stories to learn how vaccines work.
- Watch videos made for kids about health.
No, vaccines do not cause autism.
Do vaccines make more people have autism?
Vaccines help us not get sick. Some people worry that vaccines can cause autism. But doctors and scientists say that vaccines do not cause autism. If you're not sure, talking to a doctor can help. They can answer questions and make you feel better. Using pictures, simple words, and asking questions can also help understand better.More people know what autism is now, and doctors have better ways to find it. This is why more kids are being told they have autism. It is not because of vaccines. Vaccines do not cause autism.
Why is it important to stop the myth that vaccines cause autism?
Some people believe that vaccines can make children have autism, but this is not true. It is a myth, like a fairy tale. Vaccines help keep people healthy and stop them from getting sick.
It is important to know the truth because:
- Vaccines protect you and your friends from bad diseases.
- If people stop getting vaccines, more people might get sick.
If you want to learn more, you can:
- Ask a doctor or nurse for information.
- Look at trusted websites with adults you trust.
Remember, vaccines are safe and help everyone stay healthy!
It is very important to show that this idea is wrong. This helps keep people healthy and stops diseases that vaccines can prevent from spreading.
Did any courts say vaccines cause autism?
No court cases have shown that vaccines cause autism.
Do countries and health groups talk about vaccines and autism?
Do countries or health groups say things about vaccines and autism? This question is asking if these important groups have made statements on this topic. To understand better, you can:
- Look at news from trusted sources.
- Visit websites of health groups like the World Health Organization.
- Ask a doctor or nurse for more information.
- Use pictures to help you understand complex information.
Yes, many countries and health groups say vaccines do not cause autism.
How does wrong information about vaccines spread?
Sometimes, wrong stories about vaccines can be shared by people. This means telling things about vaccines that are not true.
Here are some ways wrong information can spread:
- People share it on social media, like Facebook or Twitter.
- Someone might say it in a video or on TV.
- Friends or family might tell each other information that isn't right.
Here are some tips to help understand vaccines better:
- Ask a doctor or nurse if you have questions.
- Look for information on trusted websites like health organizations.
- Be careful and check if a story is true before sharing it.
Wrong information can spread on social media, some news sites, and when people share personal stories.
Useful Links
This website offers general information and is not a substitute for professional advice.
Always seek guidance from qualified professionals.
If you have any medical concerns or need urgent help, contact a healthcare professional or emergency services immediately.
Some of this content was generated with AI assistance. We’ve done our best to keep it accurate, helpful, and human-friendly.
- Ergsy carfully checks the information in the videos we provide here.
- Videos shown by Youtube after a video has completed, have NOT been reviewed by ERGSY.
- To view, click the arrow in centre of video.
- Most of the videos you find here will have subtitles and/or closed captions available.
- You may need to turn these on, and choose your preferred language.
- Go to the video you'd like to watch.
- If closed captions (CC) are available, settings will be visible on the bottom right of the video player.
- To turn on Captions, click settings .
- To turn off Captions, click settings again.
More Items From Ergsy search
-

Are vaccines linked to autism?
Relevance: 100%
-

What causes autism?
Relevance: 71%
-

What is Autism?
Relevance: 69%
-

How prevalent is autism?
Relevance: 65%
-

Is there an autism test?
Relevance: 64%
-

What is the autism spectrum?
Relevance: 63%
-

Is there a genetic component to autism?
Relevance: 62%
-

Can autism be cured?
Relevance: 61%
-

What are the signs of autism?
Relevance: 61%
-

How is autism diagnosed?
Relevance: 60%
-

Autism - My Story - Adrian | NHS
Relevance: 60%
-

Can adults have autism?
Relevance: 59%
-

Autism: Graeme's story | NHS
Relevance: 59%
-

Is paracetamol linked to autism?
Relevance: 59%
-

How effective is the MMR vaccine?
Relevance: 58%
-

Autism - My Story - Rosalind | NHS
Relevance: 58%
-

What can cause autism, if not paracetamol?
Relevance: 57%
-

Is autism more common in boys or girls?
Relevance: 57%
-

Is there any scientific evidence that links paracetamol use to autism?
Relevance: 56%
-

What advice is available for parents concerned about autism risks?
Relevance: 56%
-

How does autism affect communication?
Relevance: 56%
-

What are some common therapies for autism?
Relevance: 56%
-

Can people with autism lead independent lives?
Relevance: 55%
-

What is the difference between autism and Asperger's syndrome?
Relevance: 54%
-

Autism Assessment - What Happens in Your Appointment
Relevance: 53%
-

What role do sensory issues play in autism?
Relevance: 53%
-

How can families support a member with autism?
Relevance: 52%
-

How can early intervention help children with autism?
Relevance: 51%
-

The NHS Long Term Plan for learning disability and autism
Relevance: 51%
-

Why is there concern about paracetamol and autism?
Relevance: 51%
-

Is there any risk of using paracetamol outside of pregnancy with regard to autism?
Relevance: 50%
-

What kind of studies are conducted to investigate links between medications and autism?
Relevance: 50%
-

Children's Vaccination Schedule
Relevance: 49%
-

What is the MMR vaccine?
Relevance: 48%
-

How effective is the MMR vaccine?
Relevance: 46%
-

Transforming Care for people with Learning Disabilities and/ or Autism: Peter's Story
Relevance: 45%
-

Are there vaccines for meningitis?
Relevance: 43%
-

Are vaccines safe?
Relevance: 43%
-

What is a vaccine?
Relevance: 42%
-

Is there a vaccine for H3N2?
Relevance: 42%


