
Find Help
More Items From Ergsy search
-

What are the signs of autism?
Relevance: 100%
-

Is there an autism test?
Relevance: 74%
-

What is Autism?
Relevance: 73%
-

What is the autism spectrum?
Relevance: 71%
-

Autism - My Story - Rosalind | NHS
Relevance: 67%
-

How is autism diagnosed?
Relevance: 65%
-

Autism: Graeme's story | NHS
Relevance: 64%
-

Can adults have autism?
Relevance: 64%
-

What advice is available for parents concerned about autism risks?
Relevance: 63%
-

Is there a genetic component to autism?
Relevance: 63%
-

Autism - My Story - Adrian | NHS
Relevance: 62%
-

How prevalent is autism?
Relevance: 62%
-

What causes autism?
Relevance: 62%
-

Can autism be cured?
Relevance: 62%
-

Is autism more common in boys or girls?
Relevance: 61%
-
Are vaccines linked to autism?
Relevance: 61%
-

Is paracetamol linked to autism?
Relevance: 60%
-

What can cause autism, if not paracetamol?
Relevance: 58%
-

How can early intervention help children with autism?
Relevance: 57%
-

How does autism affect communication?
Relevance: 57%
-

The NHS Long Term Plan for learning disability and autism
Relevance: 57%
-

What are some common therapies for autism?
Relevance: 57%
-

Autism Assessment - What Happens in Your Appointment
Relevance: 57%
-

Can people with autism lead independent lives?
Relevance: 55%
-

What is the difference between autism and Asperger's syndrome?
Relevance: 55%
-

What role do sensory issues play in autism?
Relevance: 53%
-

How can families support a member with autism?
Relevance: 53%
-

Is there any scientific evidence that links paracetamol use to autism?
Relevance: 53%
-

Why is there concern about paracetamol and autism?
Relevance: 52%
-

Is there any risk of using paracetamol outside of pregnancy with regard to autism?
Relevance: 51%
-
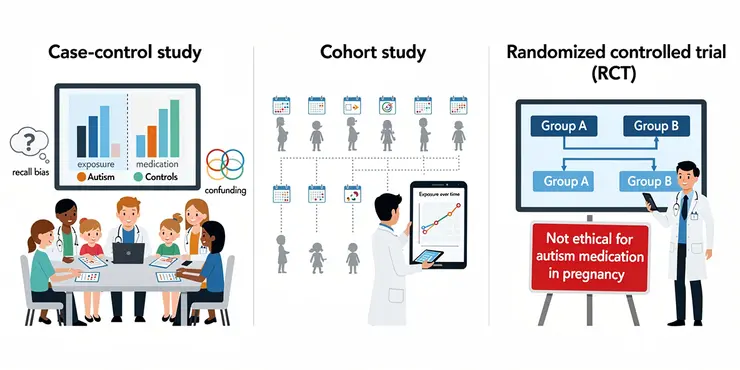
What kind of studies are conducted to investigate links between medications and autism?
Relevance: 51%
-

Transforming Care for people with Learning Disabilities and/ or Autism: Peter's Story
Relevance: 46%
-

We are autistic | NHS
Relevance: 43%
-

Dyspraxia Symptoms & Signs
Relevance: 40%
-

NHS-led Provider Collaboratives: improving mental health, learning disability and autism services
Relevance: 39%
-

What are the limitations of studies examining paracetamol use and autism?
Relevance: 37%
-

What are the signs of meningitis in infants?
Relevance: 37%
-

Dyspraxia Symptoms & Signs
Relevance: 36%
-

What are the signs of heat exhaustion?
Relevance: 36%
-

How do you sign up for the Postcode Lottery?
Relevance: 35%
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a developmental disorder that affects communication, behaviour, and social interactions. Diagnosing autism can be complex due to the wide range of symptoms and their varying degrees of intensity. Recognizing the signs early can lead to timely intervention, offering better support for individuals with autism.
Signs of Autism in Young Children
Children with autism may show signs in early infancy. Some of these signs include a lack of eye contact, not responding to their name, or not showing interest in objects or people. They might not smile back or engage in back-and-forth play. Additionally, the child may engage in repetitive movements, like rocking or flapping their hands, and have unusual reactions to sensory experiences, such as sounds, lights, or textures.
Communication Challenges
Children and adults with autism often experience difficulties in communication. This can manifest as delayed speaking, using a flat or monotonous tone, or repeating phrases and scripts. There may be challenges in understanding and using non-verbal communication, such as facial expressions, gestures, or body language. Some individuals with autism might avoid eye contact during interactions.
Social Interactions
Autistic individuals may struggle with social interactions. They might find it difficult to understand social cues, initiate or sustain conversations, or develop peer relationships. An apparent lack of interest in peers and difficulty in sharing and taking turns could also be observed. In some cases, individuals may prefer to play alone or alongside others without engaging in interactive play.
Restrictive and Repetitive Behaviors
A characteristic feature of autism is engaging in restricted or repetitive behaviours. This could involve adherence to specific routines or rituals, an intense focus on certain interests or topics, and resistance to changes in environment or schedules. Stereotyped behaviours like arranging objects in a specific order or repeating the same action multiple times are common.
Sensory Sensitivities
Sensory issues are prevalent among individuals with autism. This might present as heightened or reduced sensitivity to sensory inputs. For example, some individuals may be overly sensitive to loud noises or bright lights, while others might have a high pain threshold. Unusual interest in sensory aspects of the environment, such as the texture of objects or spinning objects, may also be observed.
Conclusion
While these signs can indicate autism, it is important to remember that each individual is unique, and the presence of these signs does not necessarily confirm an autism diagnosis. Professional evaluation by healthcare providers specialising in developmental disorders is crucial for an accurate diagnosis. Understanding these signs can help in seeking appropriate guidance and support, which can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals and families affected by autism.
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a condition that changes how people talk, act, and interact with others. It can be hard to figure out if someone has autism because the signs can be different for each person. If you notice the signs early, you can get help sooner, which is better for people with autism.
Signs of Autism in Young Children
Kids with autism might show signs when they are very young. They might not look at you when you talk to them, not turn when you say their name, or not be interested in toys or people. They might not smile back or play games where you take turns. They might do the same movement over and over, like rocking or flapping hands. They might also react differently to things like sounds, lights, or the way things feel.
Communication Challenges
Kids and adults with autism might have trouble talking and understanding others. They might start talking later than other kids, use a flat voice, or say the same words many times. They might find it hard to understand facial expressions or gestures. They might also not look others in the eye when talking.
Social Interactions
People with autism might have trouble with social interactions. They might not understand social clues or know how to start or keep a conversation. They might not show much interest in playing with other kids or taking turns. Sometimes, they might like to play alone or alongside others without really playing together.
Restrictive and Repetitive Behaviors
Many people with autism do things in a pattern or repeat actions a lot. They might like to follow a strict routine or be very interested in certain topics. They might not like changes in their schedule or surroundings. They might enjoy arranging objects in a certain way or repeating an action again and again.
Sensory Sensitivities
People with autism often have sensory issues. They might be too sensitive to loud sounds or bright lights, or they might not feel pain like others do. They might be very interested in how things feel or like watching things spin.
Conclusion
These signs can help you notice autism, but remember every person is different. Having these signs doesn't mean someone definitely has autism. It's important to talk to a doctor who knows about these conditions to be sure. Knowing these signs can help get the right help, making life better for people with autism and their families.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are common signs of autism in young children?
Common signs include delayed speech and language skills, difficulty making eye contact, limited interest in social interactions, and repetitive behaviors or routines.
How might autism manifest in school-aged children?
In school-aged children, autism may present as difficulty understanding social cues, problems with peer relationships, a strong interest in specific topics, or challenges with transitions and changes in routine.
What social differences might suggest autism?
Social differences can include avoidance of eye contact, lack of interest in peer interactions, difficulty understanding emotions, and challenges in expressing empathy.
How can communication skills be affected by autism?
Children with autism may experience delays in speech development, use repetitive language, have difficulty with conversation, or prefer non-verbal communication methods.
Are repetitive behaviors a sign of autism?
Yes, repetitive behaviors such as hand-flapping, rocking, lining up toys, or insistence on specific routines can be signs of autism.
Can sensory sensitivities indicate autism?
Sensory sensitivities, including strong reactions to sounds, lights, textures, or smells, are often associated with autism.
What are some early signs of autism in infants?
Early signs in infants may include limited eye contact, not responding to their name, minimal babbling or gesturing, and little interest in interactive play.
How can play behavior indicate autism?
Children with autism may show limited imaginative play, prefer playing alone, or focus intensely on parts of toys rather than the whole.
Do children with autism have difficulty with changes in routine?
Yes, many children with autism find changes in routine distressing and may react negatively or with anxiety when faced with new situations.
Can difficulty understanding jokes and sarcasm be a sign of autism?
Yes, difficulty comprehending non-literal language, such as jokes and sarcasm, can be a sign of autism.
Is there a link between autism and exceptional skills or interests?
Some individuals with autism may demonstrate exceptional skills or intense interests in specific areas, often referred to as 'splinter skills'.
What behavioral signs in toddlers might indicate autism?
Behavioral signs in toddlers can include limited use of gestures, difficulty imitating actions or words, and extreme focus on a single interest or object.
How might autism affect emotional regulation in children?
Children with autism may struggle with emotional regulation, leading to frequent outbursts, tantrums, or difficulty calming down.
Do children with autism show a preference for solitude?
Many children with autism may prefer solitary activities and may not seek out social interactions as frequently as their peers.
Can resistance to physical touch be a sign of autism?
Some individuals with autism might avoid physical touch due to sensory sensitivities, which can include discomfort with hugs or certain textures.
What are some cognitive characteristics associated with autism?
Cognitive characteristics may include strong memory skills, a detail-oriented focus, and varying abilities across different tasks or subjects.
How are problem-solving skills affected by autism?
Problem-solving can be affected in various ways, with some individuals excelling in logical and structured tasks while struggling with open-ended or abstract problems.
Can difficulties in coordination be related to autism?
Yes, some individuals with autism may experience issues with motor skills, coordination, or physical clumsiness.
How is anxiety related to autism?
Anxiety is common in individuals with autism and may be linked to difficulties in handling change, sensory overload, or social situations.
Is there a connection between autism and dietary preferences?
Children with autism may have strong food preferences or aversions, often related to sensory sensitivities around taste, texture, or smell.
What signs show autism in young children?
Autism is something that affects how kids learn and communicate. Here are some things to look for:
- Talking: A child might not talk as much as other kids.
- Playing: A child might not play pretend games.
- Understanding: A child might not understand jokes or feelings.
- Reactions: A child might react strongly to lights or sounds.
- Routine: A child might get upset if something changes in their routine.
If you notice these signs, talking to a doctor can help.
Other Tips:
- Use pictures to help kids understand better.
- Play calm music to help them relax.
- Stick to a daily routine to make them feel safe.
Here are some things to look out for:
- Talking and understanding words later than other kids.
- Having a hard time looking people in the eye.
- Not wanting to play with other kids much.
- Doing the same thing over and over again.
Tools that might help:
- Use pictures to help understand and learn words.
- Games that help with making eye contact.
- Practice playing and talking with others in small groups.
- Make a schedule to help with routines.
What are the signs of autism in children at school?
Children with autism might:
- Have trouble talking with other children.
- Find it hard to make friends.
- Like to do the same thing over and over.
- Not like changes to their routine.
- Have a strong interest in one topic or hobby.
- Sometimes get upset by loud noises or bright lights.
If you notice these signs, talk to a teacher or doctor. They can help.
Tools like picture cards can help children understand and communicate better.
Children in school with autism might find it hard to understand how other people feel. They may have trouble making friends. They might really like certain things a lot and find it hard when plans change. Tools like picture schedules can help make changes easier. Talking to a teacher or helper can also support them.
What are signs of autism in social situations?
Some people show social differences. This means they might:
- Not look people in the eye.
- Not want to play or talk with other kids.
- Find it hard to know what others are feeling.
- Have trouble showing that they care.
Using pictures or simple stories can help you understand feelings. Talking with an adult about your feelings can be helpful too!
How does autism change the way people talk?
Some children with autism might take longer to learn to talk. They might say the same words over and over. Talking with others can be hard for them. They might like to use other ways to communicate, like using pictures or gestures.
Do people with autism sometimes do the same things again and again?
Yes, some people with autism like to do the same things over and over. This is called repetitive behavior. It is common for them.
If you want to learn more about autism, you can try watching videos or using pictures. These tools can help you understand better.
Yes, doing the same things over and over, like waving hands, rocking back and forth, putting toys in a line, or needing things to be done in a certain way can be signs of autism.
Do people with autism have strong feelings to sounds, lights, or touches?
People with autism might have strong feelings about sounds, lights, textures, or smells.
What are early signs of autism in babies?
Here are some things to look for in babies:
- They do not smile back at you.
- They do not look at you.
- They do not make sounds to get your attention.
- They do not like being held or cuddled.
- They do not follow things with their eyes.
If you think your baby has some of these signs, talk to a doctor. You can also use picture books to help your baby learn. Point to things in the book and talk about them. Play simple games like peek-a-boo to help them connect with you.
Early signs in babies can include not looking at people, not turning when you say their name, not making many sounds or movements with their hands, and not wanting to play with others.
How Can Play Show Autism?
Some kids play in ways that can show they have autism. This means they may play differently than other kids.
Here is how play might be different:
- They like playing alone and don’t want to play with other kids.
- They play with toys in the same way over and over again.
- They like to line up toys instead of playing pretend games.
If you think a child might show signs of autism, it is good to talk to a doctor. They can help you understand more.
For help, you can use pictures, videos, or apps that show how to play with others. These can make learning to play more fun and easier.
Children with autism might not use their imagination much when they play. They might like to play by themselves. Sometimes, they pay close attention to small parts of toys instead of the whole toy.
Here are some ways to help:
- Play with them and show them how to use their imagination.
- Give them toys that can be used in different ways.
- Use pictures or stories to help them understand play ideas.
Do kids with autism find it hard when routines change?
Some kids with autism may find it hard when things change. Changes, like a different plan or a new teacher, can be tricky.
Here are some ways to help:
- Use pictures to show what will happen next.
- Talk about changes before they happen.
- Try to keep some things the same every day.
Yes, many children with autism do not like changes. Changes can make them upset or worried. They might get nervous when something new happens.
Can having trouble understanding jokes and sarcasm mean someone has autism?
Some people find it hard to understand jokes and sarcasm. This can sometimes be a sign of autism. Autism is a condition that affects how people understand and interact with others.
If you or someone you know finds jokes and sarcasm confusing, here are some ways to help:
- Ask someone to explain the joke or sarcasm in a simple way.
- Use pictures or drawings to show what the joke means.
- Practice telling jokes with a friend or family member.
- Watch shows or videos that explain jokes and sarcasm.
If you are worried, talk to a doctor or a teacher for help. They can support you and answer your questions.
Having trouble understanding jokes and sarcasm can be a sign of autism.
Are some people with autism very good at special skills or have strong interests?
Some people with autism are really good at certain things. They might have special skills or strong interests. These are called 'splinter skills'.
What signs in young children might mean autism?
Young children with autism might do things differently. Here are some signs to look out for:
- They don’t respond when you call their name.
- They don’t point at things to show interest.
- They might not play pretend games.
- They like to do the same thing over and over.
- They might not talk as much as other children.
- They might not look you in the eyes when they talk to you.
If you are worried, talk to a doctor or a specialist. They can help you understand your child better. Using pictures or sign language might also help your child communicate. There are also apps and toys designed to support learning and play.
Signs in young children can be:
- Not using many hand movements.
- Finding it hard to copy what others do or say.
- Being really focused on one thing.
Here’s what can help:
- Use simple language.
- Use pictures to show actions.
- Play and talk about different things.
How does autism change how kids handle feelings?
Some kids have autism. Autism can make it hard for them to know their feelings. It can also make it hard to calm down when they feel upset.
Things that might help:
- Using a feelings chart can help kids say what they feel.
- Taking deep breaths can help kids relax.
- Having a quiet space to calm down can be good.
Children with autism might have a hard time controlling their emotions. This can make them upset easily, have tantrums, or find it hard to calm down.
To help, you can:
- Use pictures or charts to show feelings.
- Practice deep breathing to relax.
- Give them a quiet space to calm down.
- Teach them to count to 10 when upset.
- Use a timer to help with waiting.
Do children with autism like being alone?
Many children with autism might like to play alone. They might not want to play with other children as much as other kids do.
Does not liking hugs or touches mean autism?
Some people with autism might not like to be touched. This is because their senses can be very sensitive. Things like hugs or different textures might not feel nice to them.
What are some thinking and learning traits linked to autism?
Autism can affect how people think and learn. Here are some traits that might be seen:
- Focus on details: People might notice small things that others miss.
- Strong memory: They might remember lots of facts or details.
- Different ways of learning: Some learn better with pictures or hands-on activities.
- Fixated interests: They might have special interests they think about a lot.
- Trouble with changes: Changes in routine might be hard for them.
To help, you can:
- Use visual aids like pictures and charts.
- Make a daily schedule to follow.
- Break tasks into small steps.
People might have a great memory. They might notice little details. They can be good at some tasks but find others harder.
How does autism change the way people solve problems?
People with autism might solve problems differently. This means they might find some things easy and other things hard.
Their brains work in a unique way. They might find it hard to change plans or think quickly. But they might also be really good at noticing details or following routines.
To help, it's good to break tasks into small steps and use pictures or lists. Someone can also use tools like timers to help manage time.
People can be good at solving problems in different ways. Some people are really good at solving puzzles that have clear steps, like math problems. But the same people might find it hard to solve problems when there is no clear answer or when the problem is more about ideas.
Can troubles with movement be linked to autism?
Yes, some people with autism might find it hard to move their bodies easily. They might seem clumsy and have trouble with things like balance or coordination.
How are feeling worried and autism connected?
Some people with autism can also feel very worried or anxious. This is called having anxiety.
Autism can make it harder to understand the world. This can make a person feel nervous or scared.
There are ways to help feel less anxious:
- Talk to someone you trust about your feelings.
- Try deep breathing exercises to calm down.
- Use pictures or a schedule to know what will happen next.
A grown-up or a teacher can help you with these steps.
People with autism often feel worried or scared. This might happen when things change, when there are too many loud noises or bright lights, or when they are around other people.
Do people with autism like some foods more?
Children with autism might like or dislike certain foods a lot. This can happen because of how the food tastes, feels, or smells.
Useful Links
This website offers general information and is not a substitute for professional advice.
Always seek guidance from qualified professionals.
If you have any medical concerns or need urgent help, contact a healthcare professional or emergency services immediately.
Some of this content was generated with AI assistance. We’ve done our best to keep it accurate, helpful, and human-friendly.
- Ergsy carfully checks the information in the videos we provide here.
- Videos shown by Youtube after a video has completed, have NOT been reviewed by ERGSY.
- To view, click the arrow in centre of video.
- Most of the videos you find here will have subtitles and/or closed captions available.
- You may need to turn these on, and choose your preferred language.
- Go to the video you'd like to watch.
- If closed captions (CC) are available, settings will be visible on the bottom right of the video player.
- To turn on Captions, click settings .
- To turn off Captions, click settings again.
More Items From Ergsy search
-

What are the signs of autism?
Relevance: 100%
-

Is there an autism test?
Relevance: 74%
-

What is Autism?
Relevance: 73%
-

What is the autism spectrum?
Relevance: 71%
-

Autism - My Story - Rosalind | NHS
Relevance: 67%
-

How is autism diagnosed?
Relevance: 65%
-

Autism: Graeme's story | NHS
Relevance: 64%
-

Can adults have autism?
Relevance: 64%
-

What advice is available for parents concerned about autism risks?
Relevance: 63%
-

Is there a genetic component to autism?
Relevance: 63%
-

Autism - My Story - Adrian | NHS
Relevance: 62%
-

How prevalent is autism?
Relevance: 62%
-

What causes autism?
Relevance: 62%
-

Can autism be cured?
Relevance: 62%
-

Is autism more common in boys or girls?
Relevance: 61%
-

Are vaccines linked to autism?
Relevance: 61%
-

Is paracetamol linked to autism?
Relevance: 60%
-

What can cause autism, if not paracetamol?
Relevance: 58%
-

How can early intervention help children with autism?
Relevance: 57%
-

How does autism affect communication?
Relevance: 57%
-

The NHS Long Term Plan for learning disability and autism
Relevance: 57%
-

What are some common therapies for autism?
Relevance: 57%
-

Autism Assessment - What Happens in Your Appointment
Relevance: 57%
-

Can people with autism lead independent lives?
Relevance: 55%
-

What is the difference between autism and Asperger's syndrome?
Relevance: 55%
-

What role do sensory issues play in autism?
Relevance: 53%
-

How can families support a member with autism?
Relevance: 53%
-

Is there any scientific evidence that links paracetamol use to autism?
Relevance: 53%
-

Why is there concern about paracetamol and autism?
Relevance: 52%
-

Is there any risk of using paracetamol outside of pregnancy with regard to autism?
Relevance: 51%
-

What kind of studies are conducted to investigate links between medications and autism?
Relevance: 51%
-

Transforming Care for people with Learning Disabilities and/ or Autism: Peter's Story
Relevance: 46%
-

We are autistic | NHS
Relevance: 43%
-

Dyspraxia Symptoms & Signs
Relevance: 40%
-

NHS-led Provider Collaboratives: improving mental health, learning disability and autism services
Relevance: 39%
-

What are the limitations of studies examining paracetamol use and autism?
Relevance: 37%
-

What are the signs of meningitis in infants?
Relevance: 37%
-

Dyspraxia Symptoms & Signs
Relevance: 36%
-

What are the signs of heat exhaustion?
Relevance: 36%
-

How do you sign up for the Postcode Lottery?
Relevance: 35%


