Find Help
More Items From Ergsy search
-

Childhood dyspraxia: James' story | NHS
Relevance: 100%
-

Dyspraxia Symptoms & Signs
Relevance: 73%
-

Dyspraxia Symptoms & Signs
Relevance: 71%
-

What is Dyspraxia? (Short Version)
Relevance: 71%
-

Children With Co-ordination Difficulties and Dyspraxia
Relevance: 69%
-
What is Dyspraxia (DCD)?
Relevance: 66%
-

Dyspraxia Children: How to Help
Relevance: 64%
-

Dyslexia, Dyspraxia & Overlapping Learning Difficulties
Relevance: 63%
-

Is childhood obesity a concern in the United Kingdom?
Relevance: 48%
-
What are the current statistics on childhood obesity in the UK?
Relevance: 46%
-

Is childhood obesity a concern in the United Kingdom?
Relevance: 46%
-

Childhood squint | NHS
Relevance: 44%
-

The effective treatment of childhood constipation according to NICE guidelines.
Relevance: 39%
-

Study Finds Alarming Increase in Childhood Obesity Rates Post-Pandemic
Relevance: 38%
-

Dealing with Common Childhood Illnesses
Relevance: 32%
-

Rise in Childhood Asthma Linked to Air Pollution in Urban Areas
Relevance: 30%
-

Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD) for Children and Young People
Relevance: 23%
-

Is asthma more common in certain age groups?
Relevance: 21%
-

Can chickenpox be prevented?
Relevance: 19%
-

Can children outgrow asthma?
Relevance: 18%
-
Is obesity more prevalent in certain regions of the UK?
Relevance: 17%
-

What causes ADHD?
Relevance: 16%
-

Has the sugar tax affected the sugar content in drinks?
Relevance: 15%
-

Should I test my child for high blood pressure?
Relevance: 15%
-
What causes asthma?
Relevance: 13%
-

Can ADHD be inherited?
Relevance: 13%
-

Can adults have autism?
Relevance: 13%
-

Can Rubella be prevented?
Relevance: 13%
-

What is Short-Sightedness?
Relevance: 12%
-

Who should receive the MMR vaccine?
Relevance: 12%
-

What health risks are associated with obesity?
Relevance: 12%
-
Can genetics influence obesity?
Relevance: 12%
-

What type of anxiety do children and teenagers experience?
Relevance: 12%
-

BSL - Causes of panic disorder
Relevance: 12%
-

What is Asthma?
Relevance: 12%
-

Obesity
Relevance: 12%
-
How are children defined for the purpose of this ban?
Relevance: 11%
-
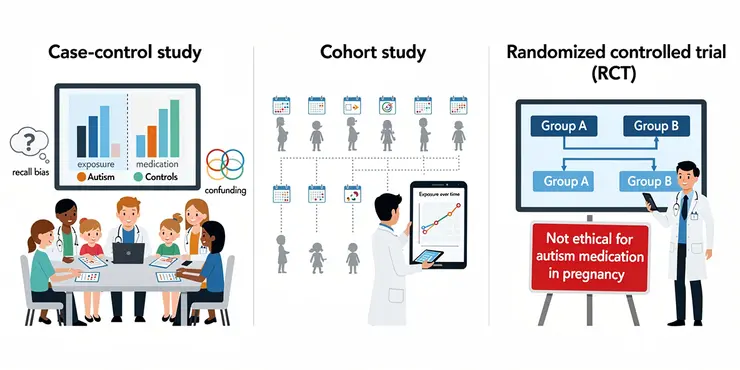
What kind of studies are conducted to investigate links between medications and autism?
Relevance: 11%
-

Are vaccines safe?
Relevance: 11%
-

Should I get the chickenpox vaccine?
Relevance: 11%
Childhood Dyspraxia: James' Story | NHS
Understanding Childhood Dyspraxia
Childhood dyspraxia, also known as Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD), is a condition affecting physical coordination. Children with dyspraxia often struggle with tasks requiring balance, fine motor skills, and spatial awareness, leading to difficulties in everyday activities.
James' Early Challenges
James was diagnosed with dyspraxia at the age of 5 when his parents noticed he had trouble with tasks such as tying shoes, writing, and even playing with toys that required hand-eye coordination. In school, James found it hard to keep up with his peers, becoming easily frustrated by his limitations.
Interventions and Support
Upon diagnosis, James' parents sought help from healthcare professionals. The NHS provided occupational therapy to help him improve his motor skills. James also received support from his school, where teachers adapted physical activities and provided additional learning resources to accommodate his needs.
James' Progress and Achievements
With continuous support and intervention, James began to show significant improvement. His confidence grew as he mastered tasks that once seemed impossible. James learned to ride a bike, participate in sports with modifications, and improved his handwriting. His achievements were celebrated, motivating him to keep trying.
Ongoing Support and Future Outlook
James' journey with dyspraxia is ongoing. His parents remain in close contact with NHS healthcare providers to monitor his progress and adjust his support plan as needed. The support from family, school, and healthcare professionals has been crucial in helping James navigate daily challenges and succeed in his personal activities.
Resources for Families
Families in the United Kingdom facing similar challenges can access various resources through the NHS. These include occupational therapy, educational support, and community support groups. Early intervention and consistent support are key to helping children with dyspraxia thrive.
Childhood Dyspraxia: James' Story | NHS
What is Childhood Dyspraxia?
Childhood dyspraxia is also called Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD). It makes it hard for kids to move and balance. Kids with dyspraxia find things like tying shoes and drawing hard to do.
James' Early Challenges
James found out he had dyspraxia when he was 5 years old. His mom and dad saw he had trouble playing with toys, tying his shoes, and writing. In school, James got upset because he couldn't do things as fast as other kids.
Getting Help for James
When James found out he had dyspraxia, his parents got help from healthcare workers. The NHS gave James therapy to help him move better. His school also helped by changing activities to make them easier for James.
James' Progress and Success
James got better with help and support. He became more confident. He learned how to ride a bike and play sports with some changes. His writing got better too. Every little win made him want to keep trying.
Ongoing Help and Future for James
James still needs help for his dyspraxia. His parents talk often with NHS workers to see how he is doing. Support from his family, school, and doctors helps him do well each day.
Help for Other Families
Families in the UK can get help from the NHS. They offer therapy and school support. There are also groups where families can meet and help each other. Getting help early and often is important for kids with dyspraxia.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is childhood dyspraxia?
Childhood dyspraxia, also known as Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD), is a condition affecting physical coordination, making everyday tasks difficult.
How was James diagnosed with dyspraxia?
James was diagnosed with dyspraxia after assessments by healthcare professionals who noted his difficulties with coordination, movement, and daily activities.
What are some common symptoms of dyspraxia in children?
Common symptoms include difficulty with motor tasks, clumsiness, problems with balance, and challenges with tasks like tying shoelaces or using cutlery.
How does dyspraxia affect children at school?
Children with dyspraxia may struggle with handwriting, physical education, and following instructions, which can affect their academic performance and self-esteem.
Can dyspraxia be cured?
There is no cure for dyspraxia, but various therapies and interventions can help manage the symptoms and improve coordination and daily functioning.
What types of therapies can help children with dyspraxia?
Occupational therapy and physical therapy are common interventions that can help children develop motor skills and improve coordination.
How can parents support a child with dyspraxia?
Parents can support their child by being patient, encouraging them, working closely with their school, and seeking professional help like occupational therapy.
What role do schools play in supporting children with dyspraxia?
Schools can provide tailored support, such as specialized teaching strategies and physical accommodations, to help children with dyspraxia succeed academically.
Can dyspraxia co-exist with other conditions?
Yes, dyspraxia can co-exist with other developmental disorders such as ADHD, dyslexia, and autism spectrum disorders.
What are some daily challenges children with dyspraxia might face?
Daily challenges can include difficulties with dressing, eating, writing, and participating in sports or playground activities.
Are there any famous people with dyspraxia?
Yes, several famous individuals, including actor Daniel Radcliffe and singer Florence Welch, have publicly shared their experiences with dyspraxia.
What are the long-term prospects for children with dyspraxia?
With the right support and interventions, many children with dyspraxia can lead successful and fulfilling lives into adulthood.
How is dyspraxia different from other coordination disorders?
Dyspraxia specifically affects planning and executing movements, whereas other coordination disorders might involve different areas of motor control or cognitive function.
What resources are available for parents of children with dyspraxia in the UK?
Resources include support groups, NHS services, educational psychologists, and organisations like the Dyspraxia Foundation.
How can friends and family help children with dyspraxia?
Friends and family can help by understanding the condition, being supportive and patient, and assisting with tasks that the child finds difficult.
What is childhood dyspraxia?
Childhood dyspraxia is a problem some kids have. It makes it hard for them to do things like tying shoelaces or writing. It is not because they are not trying, but because their bodies do not follow what their brains tell them to do.
Here are some ways to help:
- Practicing small steps each day.
- Using special tools like thicker pencils.
- Playing games that help with movement, like dancing or hopping.
Support from parents and teachers is very important. They can give lots of help and practice to make things easier.
Childhood dyspraxia is also called Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD). It makes it hard for kids to move and do things.
How did doctors find out James has dyspraxia?
James found out he has dyspraxia. Dyspraxia makes it hard for him to move and do everyday things. Doctors and helpers figured this out after some checks.
What signs of dyspraxia can you see in children?
Dyspraxia can make things tricky for kids. Here are some signs:
- Trouble running, jumping, or playing sports.
- Finding it hard to hold a pencil or write.
- Being messy when eating or dressing.
- Having trouble speaking clearly.
- Finding it hard to keep up at school.
If you think your child might have dyspraxia, it's a good idea to talk to a doctor or teacher. They can help find ways to make things easier at home and school. Tools like special grips for pencils or extra time to move can help.
Here are some common signs:
- Having trouble moving certain ways.
- Being clumsy.
- Finding it hard to keep your balance.
- Struggling with things like tying shoelaces or using a knife and fork.
If you find any of these things hard, you can ask for help. Using special tools or practicing with a friend might make it easier.
How does dyspraxia affect children at school?
Dyspraxia can make school hard for children. It can be tough for them to write neatly or play sports. They may find it tricky to focus in class or keep up with others. Kids with dyspraxia might need extra time and help to learn new things.
Tools like special keyboards or tablet apps can help them. Teachers can offer short breaks and easy-to-understand instructions. Sometimes, working with a friendly tutor can also make a big difference.
Children with dyspraxia might find it hard to write neatly, do sports, and follow directions. This can make school tough and make them feel not so good about themselves.
Can dyspraxia be cured?
Dyspraxia is a condition that makes it hard for some people to move their bodies smoothly. It affects things like balance and coordination. While there is no "cure" for dyspraxia, people can get help to make things easier.
Supportive tools and techniques can help. For example, special exercises and practicing certain activities can help people manage dyspraxia. Occupational therapists, who are trained to help with movement skills, can be very helpful. They can teach new ways to do things and suggest tools that make tasks easier.
With the right support, many people with dyspraxia can get better at the things they find hard. It is important to talk with a doctor or a therapist to find the best help.
There is no way to completely fix dyspraxia, but there are ways to help. Different therapies and activities can make the symptoms better and help with moving and doing everyday things.
Here are some helpful tools:
- Occupational Therapy: This helps with daily tasks like getting dressed or writing.
- Physical Therapy: This helps you get better at moving and being active.
- Speech Therapy: This helps with talking and making communication easier.
- Use checklists and routines to keep things organized and remember tasks.
- Practice fun games that improve hand-eye coordination.
What therapies can help children with dyspraxia?
Dyspraxia is when kids find it hard to do physical movements.
There are ways to help:
- Occupational Therapy: This can help kids learn everyday tasks like tying shoes and writing.
- Physical Therapy: This helps with balance and coordination, making it easier to play and move around.
- Speech and Language Therapy: This helps children talk and understand others better.
- Using Tools: Special tools like pencil grips can make writing easier.
- Games and Exercises: Fun activities can help build coordination and strength.
These therapies can make life easier for children with dyspraxia.
Occupational therapy and physical therapy are types of help. They can help kids move better and do things with their bodies. This can help them learn how to do things like pick up toys and play games.
How can parents help a child with dyspraxia?
Here are some ways parents can help:
- Practice skills: Do fun activities to practice things like holding a pencil or catching a ball.
- Break tasks into steps: Make big jobs smaller and easier by breaking them into steps.
- Use tools: Try using special tools, like thick pencils or toys with big parts, to make things easier.
- Stay positive: Encourage your child and celebrate small successes.
- Ask for help: Talk to teachers, doctors, or therapists who know about dyspraxia.
Remember, every child is different. Be patient and find what works best for your child.
Mums and dads can help their child by being patient, cheering them on, talking to their teachers, and getting help from experts like an occupational therapist.
How do schools help children with dyspraxia?
Schools can help children with dyspraxia in many ways. They can give extra support in class and help with writing and movement skills. Teachers can use special tools like pencil grips and give more time for tasks.
It helps if teachers understand dyspraxia and know how to help. Schools can also work with families to support the child at home and at school.
Using simple technology, like tablets or laptops, can be useful too. It can help with typing and organizing work.
Schools can help children with dyspraxia do well in their studies.
They can use special ways of teaching and make changes in the classroom.
Can a person have dyspraxia and other conditions at the same time?
Yes, a person can have dyspraxia and other conditions together. This means that if someone has dyspraxia, they might have other difficulties too. For example, a person with dyspraxia might also have ADHD or dyslexia.
It can help to talk to a doctor or specialist if someone has more than one condition. They can offer advice and help to make things easier.
Using tools like a planner or asking for help in school can also be very useful. It is important to understand that it's okay to ask for support.
Yes, dyspraxia can happen alongside other learning difficulties. These include ADHD, dyslexia, and autism.
What are some daily challenges for children with dyspraxia?
Dyspraxia is a condition that makes it hard to move and do things.
Children with dyspraxia might have trouble with:
- Writing neatly
- Using scissors
- Catching a ball
- Getting dressed
- Keeping their desk tidy
- Riding a bike
They may also find it hard to remember what to do next.
It can be easier with help like:
- Using a planner for remembering tasks
- Extra time to finish things
- Practicing skills slowly and step-by-step
Every day, some things can be hard. Like putting on clothes, eating, writing, and playing sports or games.
Do any famous people have dyspraxia?
Yes! Some famous people have dyspraxia. Dyspraxia is when someone finds it hard to move and do things easily.
People with dyspraxia can be very talented at other things. They might be good at writing, acting, or even playing music.
It helps to know that even famous people can have struggles. It shows that you can do great things, no matter what!
If you find it hard to read about dyspraxia, tools like audio books and simple stories can help. Talking to someone who understands can also make reading easier.
Yes, some famous people have talked about having dyspraxia. Actor Daniel Radcliffe and singer Florence Welch have shared their stories.
What will life be like for children with dyspraxia when they grow up?
Dyspraxia is a condition that makes it hard to move and do things like writing and playing. Here’s what might help:
- Children often get better at things as they grow older.
- Teachers and parents can help by using special tools, like big pencils and keyboards.
- Taking breaks and practicing can make tasks easier.
- Staying positive and trying hard is important.
With help, kids with dyspraxia can do well and be happy as they grow up.
With the right help, kids with dyspraxia can grow up happy and do well in life.
What makes dyspraxia different from other movement problems?
Dyspraxia is a special kind of movement problem. Here is how it is different:
- Clumsiness: People with dyspraxia might seem clumsy. This means they bump into things or drop things a lot.
- Tasks are hard: Simple tasks like getting dressed or using a pencil can be tricky.
- Other problems: Sometimes people with dyspraxia also have trouble with speech or learning new things.
Other movement problems might not have these same issues. They can be caused by different things.
If you need help to understand more, you can:
- Ask a teacher or a helper. They can tell you more.
- Look at a picture book about dyspraxia.
- Use a computer or tablet to watch videos that explain it.
Dyspraxia makes it hard to think about and do movements. Other problems with body control might affect different parts of the brain or thinking skills.
What help can parents in the UK get if their child has dyspraxia?
You can get help from support groups, NHS services, educational psychologists, and groups like the Dyspraxia Foundation.
How can friends and family help kids with dyspraxia?
Friends and family can help kids with dyspraxia in these ways:
- Be Patient: Give the child extra time to do things.
- Give Simple Instructions: Use short and clear sentences.
- Practice Together: Help them practice activities like tying shoes or riding a bike.
- Encourage Them: Say nice things to make them feel good.
- Listen: Let them talk about their feelings and listen carefully.
- Use Tools: Use things like special grips on pencils that make writing easier.
Friends and family can also talk to teachers for more ideas.
Friends and family can help by learning about the child's condition, being kind and patient, and helping with things that are hard for the child.
Useful Links
This website offers general information and is not a substitute for professional advice.
Always seek guidance from qualified professionals.
If you have any medical concerns or need urgent help, contact a healthcare professional or emergency services immediately.
Some of this content was generated with AI assistance. We’ve done our best to keep it accurate, helpful, and human-friendly.
- Ergsy carfully checks the information in the videos we provide here.
- Videos shown by Youtube after a video has completed, have NOT been reviewed by ERGSY.
- To view, click the arrow in centre of video.
- Most of the videos you find here will have subtitles and/or closed captions available.
- You may need to turn these on, and choose your preferred language.
- Go to the video you'd like to watch.
- If closed captions (CC) are available, settings will be visible on the bottom right of the video player.
- To turn on Captions, click settings .
- To turn off Captions, click settings again.
More Items From Ergsy search
-

Childhood dyspraxia: James' story | NHS
Relevance: 100%
-

Dyspraxia Symptoms & Signs
Relevance: 73%
-

Dyspraxia Symptoms & Signs
Relevance: 71%
-

What is Dyspraxia? (Short Version)
Relevance: 71%
-

Children With Co-ordination Difficulties and Dyspraxia
Relevance: 69%
-
What is Dyspraxia (DCD)?
Relevance: 66%
-

Dyspraxia Children: How to Help
Relevance: 64%
-

Dyslexia, Dyspraxia & Overlapping Learning Difficulties
Relevance: 63%
-

Is childhood obesity a concern in the United Kingdom?
Relevance: 48%
-

What are the current statistics on childhood obesity in the UK?
Relevance: 46%
-

Is childhood obesity a concern in the United Kingdom?
Relevance: 46%
-

Childhood squint | NHS
Relevance: 44%
-

The effective treatment of childhood constipation according to NICE guidelines.
Relevance: 39%
-

Study Finds Alarming Increase in Childhood Obesity Rates Post-Pandemic
Relevance: 38%
-

Dealing with Common Childhood Illnesses
Relevance: 32%
-

Rise in Childhood Asthma Linked to Air Pollution in Urban Areas
Relevance: 30%
-

Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD) for Children and Young People
Relevance: 23%
-

Is asthma more common in certain age groups?
Relevance: 21%
-

Can chickenpox be prevented?
Relevance: 19%
-

Can children outgrow asthma?
Relevance: 18%
-

Is obesity more prevalent in certain regions of the UK?
Relevance: 17%
-

What causes ADHD?
Relevance: 16%
-

Has the sugar tax affected the sugar content in drinks?
Relevance: 15%
-

Should I test my child for high blood pressure?
Relevance: 15%
-

What causes asthma?
Relevance: 13%
-

Can ADHD be inherited?
Relevance: 13%
-

Can adults have autism?
Relevance: 13%
-

Can Rubella be prevented?
Relevance: 13%
-

What is Short-Sightedness?
Relevance: 12%
-

Who should receive the MMR vaccine?
Relevance: 12%
-

What health risks are associated with obesity?
Relevance: 12%
-

Can genetics influence obesity?
Relevance: 12%
-

What type of anxiety do children and teenagers experience?
Relevance: 12%
-

BSL - Causes of panic disorder
Relevance: 12%
-

What is Asthma?
Relevance: 12%
-

Obesity
Relevance: 12%
-
How are children defined for the purpose of this ban?
Relevance: 11%
-

What kind of studies are conducted to investigate links between medications and autism?
Relevance: 11%
-

Are vaccines safe?
Relevance: 11%
-

Should I get the chickenpox vaccine?
Relevance: 11%


