
Find Help
More Items From Ergsy search
-

What is Chikungunya virus infection?
Relevance: 100%
-

Can Chikungunya virus infection be treated?
Relevance: 96%
-
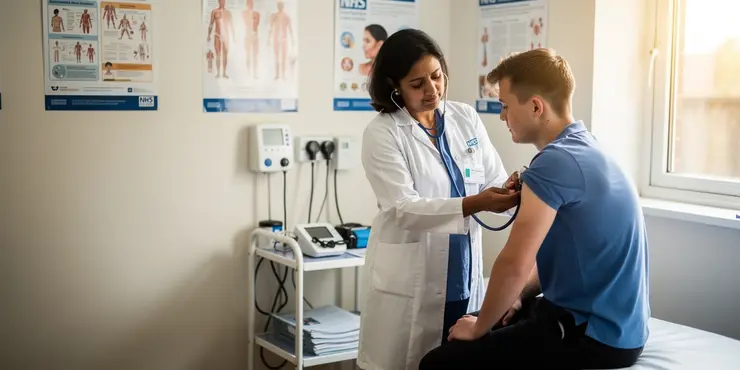
How is Chikungunya virus infection diagnosed?
Relevance: 96%
-

How is Chikungunya virus transmitted?
Relevance: 88%
-

Who is at risk for severe Chikungunya infection?
Relevance: 78%
-
Can Chikungunya be transmitted from person to person?
Relevance: 72%
-

How can Chikungunya virus be prevented?
Relevance: 70%
-

Are there any long-term effects of Chikungunya infection?
Relevance: 67%
-

Is Chikungunya fatal?
Relevance: 60%
-

Where do Chikungunya outbreaks typically occur?
Relevance: 57%
-

How long will I feel ill with chikungunya?
Relevance: 55%
-

What are the symptoms of Zika virus?
Relevance: 53%
-

What are the symptoms of Nipah Virus infection?
Relevance: 50%
-

What are the symptoms of Chikungunya virus infection?
Relevance: 50%
-

What is the mortality rate of Nipah Virus infection?
Relevance: 47%
-

What should someone do if they suspect Nipah Virus infection?
Relevance: 46%
-

Can men in the UK transmit Zika virus if infected?
Relevance: 46%
-

What preventive measures can reduce the risk of Nipah Virus infection?
Relevance: 44%
-

Is there a vaccine for Chikungunya virus?
Relevance: 42%
-

How can healthcare workers protect themselves from Marburg virus infection?
Relevance: 41%
-

Is the Marburg virus related to the Ebola virus?
Relevance: 41%
-

Is there a cure for Nipah Virus?
Relevance: 40%
-

What is Nipah Virus?
Relevance: 40%
-

Has chikungunya virus been reported in the UK?
Relevance: 39%
-

Can Zika virus affect pregnancy?
Relevance: 39%
-

Do antibiotics work on viral infections?
Relevance: 39%
-

How is Nipah Virus transmitted?
Relevance: 39%
-

Can Nipah Virus cause outbreaks?
Relevance: 39%
-

Can Nipah Virus cause neurological complications?
Relevance: 39%
-

How is West Nile Virus transmitted?
Relevance: 38%
-
What is the Marburg Virus?
Relevance: 38%
-

Can animals be infected with H3N2?
Relevance: 38%
-

What is West Nile Virus?
Relevance: 38%
-

How is Nipah Virus diagnosed?
Relevance: 37%
-

Are there treatments for West Nile Virus?
Relevance: 37%
-

How is the Zika virus transmitted?
Relevance: 37%
-

What other viruses are tested for in blood donations?
Relevance: 37%
-

How is Marburg virus disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 37%
-
Which animals are known to carry Nipah Virus?
Relevance: 37%
-

Is the UK government providing guidance on Zika virus for travelers?
Relevance: 36%
Introduction to Chikungunya Virus Infection
Chikungunya is a viral infection caused by the Chikungunya virus (CHIKV), which is primarily spread to humans through the bite of an infected Aedes mosquito, predominantly Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. These mosquitos are also responsible for transmitting other viral diseases such as dengue and Zika. The word "Chikungunya" is derived from a Tanzanian language, meaning "to become contorted," describing the stooped appearance of sufferers with joint pain.
Symptoms and Clinical Features
The onset of Chikungunya is usually sudden, typically 2-7 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. The most common symptoms include high fever, joint pain, muscle pain, headache, nausea, fatigue, and rash. While joint pain can be debilitating, it usually lasts for a few days or weeks, though some individuals experience prolonged joint pain for months. Chikungunya is rarely fatal but can significantly affect quality of life and lead to chronic health issues.
Transmission and Risk Factors
The Chikungunya virus is not transmitted from person to person but through the bites of infected mosquitos. These mosquitos thrive in tropical and subtropical climates and are usually active during daylight hours, especially at dawn and dusk. Areas with poor mosquito control and standing water present a higher risk of Chikungunya outbreaks. International travel has also facilitated the spread of the virus to non-endemic regions, increasing global exposure risk.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis of Chikungunya is primarily based on the symptoms and travel history. Definitive diagnosis can be confirmed through laboratory tests that detect the virus-specific antibodies or RNA in a patient's blood. There is currently no specific antiviral treatment for Chikungunya; management focuses on relieving symptoms. Pain relief and anti-inflammatory medication are commonly prescribed to ease fever and joint pain. Patients are also advised to stay hydrated and rest adequately.
Prevention and Control
Preventing Chikungunya infection hinges on reducing mosquito bites, as there is no vaccine available. Individuals are encouraged to use mosquito repellents, wear long sleeves and trousers, and ensure window and door screens are intact. Reducing mosquito breeding sites by eliminating standing water around homes is vital. Public health measures, including vector control programs, community awareness, and travel advisories, play crucial roles in mitigating the spread of Chikungunya.
Conclusion
While the UK is not a high-risk area for Chikungunya due to its temperate climate, awareness is essential for travelers to endemic regions. Understanding the symptoms, transmission, and preventive measures can help reduce personal risk and limit the virus's impact globally. Continued research and public health efforts are pivotal in addressing the challenges posed by the Chikungunya virus.
Introduction to Chikungunya Virus Infection
Chikungunya is an illness caused by a virus. This virus spreads to people when a special kind of mosquito bites them. The mosquitos that spread Chikungunya are called Aedes mosquitos. They can also carry other illnesses like dengue and Zika. The word "Chikungunya" comes from a language in Tanzania and it means "to become bent over". This is because people with this illness often have bad joint pain and bend over in pain.
Symptoms and How It Feels
Chikungunya sickness starts quickly, usually 2 to 7 days after a mosquito bite. Common signs are high fever, joint pain, sore muscles, headache, feeling sick, feeling tired, and a rash. The joint pain can be very bad but mostly lasts just a few days or weeks. Some people might have this pain for many months. Chikungunya doesn’t often cause death, but it can make people feel very bad for a long time.
How It Spreads and Who Is at Risk
People don’t spread Chikungunya to each other. Only mosquito bites can spread it. These mosquitos like warm, wet places and bite mostly during the day, especially in the morning and evening. Places with lots of mosquitos and still water have a higher chance of a Chikungunya outbreak. Traveling can bring the virus to places it didn’t used to be, so more people around the world can be at risk.
Finding Out if You Have It and How to Feel Better
Doctors check for Chikungunya by looking at what symptoms you have and where you have traveled. They can also do tests on your blood to be sure. There is no special medicine to cure Chikungunya. Doctors help you feel better by giving medicines for pain and fever, like painkillers and anti-swelling drugs. It's important to drink lots of water and get plenty of rest.
How to Stay Safe
Since there is no vaccine for Chikungunya, stopping mosquito bites is very important. Use bug spray, wear long shirts and pants, and make sure windows and doors have screens. Get rid of still water around your home to stop mosquitos from breeding. Public health workers help by controlling mosquitos and teaching people about safety. Travelers should be careful and pay attention to travel warnings.
Conclusion
The UK isn’t a high-risk place for Chikungunya because of its cooler weather, but people who travel should be careful. Knowing the signs of Chikungunya, how it spreads, and how to prevent it can help keep people safe. Scientists and health experts continue to work hard to understand and fight against the Chikungunya virus.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Chikungunya virus infection?
Chikungunya virus infection is a mosquito-borne viral disease caused by the Chikungunya virus, leading to fever and joint pain.
How is Chikungunya virus transmitted?
Chikungunya virus is primarily transmitted to humans through the bites of infected Aedes mosquitoes, primarily Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus.
What are the symptoms of Chikungunya virus infection?
Symptoms include sudden onset of fever, joint pain, muscle pain, headache, nausea, fatigue, and rash.
How long do Chikungunya symptoms last?
Symptoms typically appear within 4-8 days after an infected mosquito bite and can last for several days to weeks. Joint pain may persist for months.
Is there a vaccine for Chikungunya virus?
As of now, there is no specific vaccine available for Chikungunya virus infection.
How is Chikungunya virus infection diagnosed?
Diagnosis is made based on clinical symptoms and confirmed through laboratory tests like PCR, virus isolation, or serology.
Can Chikungunya virus infection be treated?
There is no specific antiviral treatment for Chikungunya. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms, such as pain and fever, using medication like paracetamol.
Who is at risk for severe Chikungunya infection?
Newborns, older adults, and individuals with underlying health conditions are at higher risk for severe symptoms.
Can Chikungunya be transmitted from person to person?
Chikungunya is primarily spread by mosquito bites and does not spread directly from person to person.
How can Chikungunya virus be prevented?
Prevention includes avoiding mosquito bites through repellents, wearing long-sleeved clothing, and eliminating mosquito breeding sites.
Are there any long-term effects of Chikungunya infection?
Some individuals may experience prolonged joint pain or arthritis after the acute phase of the illness has resolved.
Where do Chikungunya outbreaks typically occur?
Chikungunya outbreaks have occurred in Africa, Asia, Europe, and the Americas; typically in tropical and subtropical regions.
Is Chikungunya fatal?
Chikungunya is rarely fatal, but symptoms can be severe and disabling, affecting daily life.
How is Chikungunya different from Dengue and Zika?
All three are mosquito-borne but caused by different viruses. They have overlapping symptoms, but Chikungunya is known for severe joint pain.
What should I do if I suspect I have Chikungunya?
Seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and symptomatic treatment. Rest and stay hydrated.
Can Chikungunya affect travelers?
Yes, travelers to areas where Chikungunya is present can be at risk, especially in tropical regions.
How long does immunity last after a Chikungunya infection?
Immunity after infection is believed to be long-lasting, providing protection against future infections.
Are there any specific populations that should avoid travel to Chikungunya endemic areas?
Pregnant women, very young children, and individuals with weakened immune systems should take extra precautions or avoid travel.
What is the origin of the name 'Chikungunya'?
The name 'Chikungunya' comes from the Makonde language of East Africa, meaning 'to become contorted', referring to the hunched appearance of those suffering from joint pain.
Can climate change affect the spread of Chikungunya?
Yes, climate change can influence the distribution of Aedes mosquitoes, potentially increasing the spread of Chikungunya.
What is Chikungunya virus infection?
Chikungunya is a sickness caused by a virus. It can make you feel very sick.
What causes it?
The virus comes from mosquito bites. Mosquitoes carry the virus and can pass it to people they bite.
How to know if you have it?
People who get Chikungunya may have a fever or feel lots of pain in their joints. You might also feel tired or have a rash.
What can help?
If you think you have Chikungunya, seeing a doctor is a good idea. They can help you feel better.
It is important to stay away from mosquitoes. You can use bug spray and wear long sleeves to keep them away.
Using a calendar or reminders on your phone can help you remember to take medicine or go to doctor appointments.
Chikungunya virus is a sickness you get from a mosquito bite. It makes you have a fever and your joints hurt.
How does the Chikungunya virus spread?
The Chikungunya virus spreads through mosquito bites. If a mosquito bites someone who has the virus, and then bites someone else, the virus can spread. To protect yourself, you can use mosquito repellent and wear long sleeves and pants.
The Chikungunya virus spreads to people when they are bitten by mosquitoes. The mosquitoes that spread this virus are mainly called Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus.
What happens when you have the Chikungunya virus?
When someone gets the Chikungunya virus, they might feel:
- Bad pain in their joints (places where the bones meet).
- Really tired and sleepy.
- Headaches.
- Fever (feeling hot).
- Rashes (red spots on the skin).
If you feel this way, it is important to tell a grown-up or a doctor. They can help you feel better. Using pictures can help you understand how you feel.
Signs you might feel: sudden high body heat, hurt in your joints, sore muscles, head pain, feeling sick, very tired, and spots or bumps on your skin.
How long do Chikungunya symptoms last?
Chikungunya is an illness you can feel when you get sick. It makes you feel achy and tired.
Most people start to feel better in about 1 week. But some people might still feel a bit sore and tired for a few more weeks or even months.
Here are some tips to feel better:
- Rest a lot.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Ask someone to help you if you feel tired.
- Tell a grown-up if you don't feel better.
If reading is hard, you can use audiobooks or picture stories to help you understand better.
Signs you are sick usually start 4 to 8 days after a mosquito bite. You might feel sick for a few days or even weeks. Your joints might hurt for months.
Is there a vaccine for Chikungunya virus?
No, there is no vaccine for Chikungunya virus yet.
If you want to stay safe, here's what you can do:
- Use bug spray to keep mosquitoes away.
- Wear long-sleeved shirts and pants.
- Stay inside when there are lots of mosquitoes around.
These tools can help you understand better:
- Ask an adult if you have questions.
- Use apps that read text out loud.
- Watch videos that explain about the virus.
Right now, there is no special shot to stop Chikungunya virus.
How do doctors know if someone has Chikungunya?
Doctors find out what's wrong by looking at how you feel and checking with tests. These tests are called PCR, virus isolation, or serology. They help be sure about what's making you sick.
Can we treat Chikungunya virus?
If someone gets Chikungunya, doctors can help them feel better.
There is no special medicine to cure it, but there are things you can do:
- Get lots of rest.
- Drink lots of water.
- Take medicine to stop pain and fever. Ask a doctor which medicine is safe.
Some people might find using pictures or a helper to understand this information better. Talking to a nurse or doctor can also help.
There is no special medicine to cure Chikungunya. To help feel better, people take medicine like paracetamol to stop pain and fever.
Who can get very sick from Chikungunya?
Babies, older people, and people who are already sick can get sicker more easily.
Can you catch Chikungunya from another person?
No, you cannot catch Chikungunya from someone else. It spreads through mosquito bites, not from being near people who have it.
You can use pictures or videos to learn more about Chikungunya. Ask a friend or family member if you have questions.
Chikungunya is mainly spread by mosquito bites. It does not spread from one person to another.
How can we stop the Chikungunya virus?
Here are some easy tips:
- Wear long clothes.
- Use bug spray.
- Cover windows with nets.
- Stay indoors when mosquitoes are out.
- Keep water covered.
These tips can help you stay safe. Ask an adult for help if you need it.
To stop mosquito bites, you can do some simple things. Use sprays or creams that keep mosquitoes away. Wear clothes that cover your arms and legs. Get rid of places where mosquitoes can lay eggs, like standing water.
What happens if you have Chikungunya for a long time?
Some people may have joint pain or arthritis that lasts a long time after being sick.
Where do Chikungunya outbreaks usually happen?
Chikungunya is a sickness you can get from mosquito bites. Here is where it usually happens: - **Hot Places**: It often happens in places that are warm and hot. - **Countries**: It can happen in Africa, Asia, and some parts of America. If you want to know more, try looking at a map together with a friend or use a globe. You could also ask an adult for help to find these places.Chikungunya happens in places like Africa, Asia, Europe, and the Americas. It usually happens where it is warm, like in tropical and subtropical places.
Can Chikungunya cause death?
Chikungunya is an illness caused by a virus. It spreads through mosquito bites.
Most people who get Chikungunya feel very sick, but they usually get better after a few weeks.
It is not usually deadly. Most people do not die from it.
If someone is very old or already sick, they might have more trouble.
If you get Chikungunya, it is important to rest, drink water, and take medicine for pain.
If you are worried, talk to a doctor. They can help you.
Chikungunya doesn't usually cause death, but it can make you feel very sick and tired. This can make it hard to do things you normally do every day.
Tools like pictures and videos can help you understand more about Chikungunya. You can also ask someone you trust to explain it to you.
What is the difference between Chikungunya, Dengue, and Zika?
Chikungunya, Dengue, and Zika are all illnesses you can get from mosquito bites. Here is how they are different:
- Chikungunya: This can make your joints and muscles hurt a lot. You may also get a fever and a rash.
- Dengue: This often causes high fever, headache, and pain behind the eyes. You can also get a skin rash and feel very tired.
- Zika: This can be mild with a fever and rash. It is more dangerous for pregnant women because it can harm the baby.
To help understand better, try reading the text out loud or ask someone to read it to you. Using pictures to explain these differences can also be helpful.
All three are spread by mosquitoes, but they come from different viruses. They have similar symptoms, but Chikungunya causes very bad joint pain.
What to do if you think you have Chikungunya
If you feel sick and think it might be Chikungunya, here are some steps you can take:
- Tell an adult you trust, like a parent or a teacher.
- Ask to see a doctor or nurse to check if you are sick.
- Rest a lot and drink water.
- Use simple words when talking about how you feel.
- Write down your symptoms or draw pictures to show the doctor.
Ask for help using pictures or diagrams if it makes it easier for you.
Talk to a doctor to find out what is wrong and how to feel better. Make sure you rest and drink lots of water.
Can travelers get Chikungunya?
Yes, people who travel to places with Chikungunya can be at risk. This is more common in hot, tropical places.
How long do you stay protected after getting Chikungunya?
If you get Chikungunya, your body learns how to fight it. This means you usually won't get it again.
To understand more, you can:
- Talk to a doctor or nurse.
- Read simple books or ask someone to read to you.
- Use apps that help you learn more about staying healthy.
When you get sick, your body learns to fight the illness. This means you might not get the same sickness again for a long time.
Who should not travel to places with Chikungunya?
Some people should not go to places where Chikungunya is common. Here is a list of people who should be careful:
- Pregnant women
- Young children
- Older people
- People who are sick or have weak health
Ask a doctor for advice if you are not sure about traveling.
Women who are going to have a baby, very young kids, and people who get sick easily need to be extra careful or not travel.
Where does the name 'Chikungunya' come from?
The name 'Chikungunya' is from a language in East Africa called Makonde. It means 'to become bent or twisted.' This is because people with Chikungunya often look like they are bent over because their joints hurt.
Can Climate Change Spread Chikungunya?
Climate change can make the world warmer. When it is warmer, mosquitoes can live in more places. Mosquitoes spread the disease called Chikungunya. So, if there are more mosquitoes, more people might get sick.
Using pictures or videos can help you understand this better. You can also ask a friend or helper to explain it to you.
Yes, climate change can change where Aedes mosquitoes live. This might make it easier for them to spread Chikungunya.
Useful Links
This website offers general information and is not a substitute for professional advice.
Always seek guidance from qualified professionals.
If you have any medical concerns or need urgent help, contact a healthcare professional or emergency services immediately.
Some of this content was generated with AI assistance. We’ve done our best to keep it accurate, helpful, and human-friendly.
- Ergsy carfully checks the information in the videos we provide here.
- Videos shown by Youtube after a video has completed, have NOT been reviewed by ERGSY.
- To view, click the arrow in centre of video.
- Most of the videos you find here will have subtitles and/or closed captions available.
- You may need to turn these on, and choose your preferred language.
- Go to the video you'd like to watch.
- If closed captions (CC) are available, settings will be visible on the bottom right of the video player.
- To turn on Captions, click settings .
- To turn off Captions, click settings again.
More Items From Ergsy search
-

What is Chikungunya virus infection?
Relevance: 100%
-

Can Chikungunya virus infection be treated?
Relevance: 96%
-

How is Chikungunya virus infection diagnosed?
Relevance: 96%
-

How is Chikungunya virus transmitted?
Relevance: 88%
-

Who is at risk for severe Chikungunya infection?
Relevance: 78%
-

Can Chikungunya be transmitted from person to person?
Relevance: 72%
-

How can Chikungunya virus be prevented?
Relevance: 70%
-

Are there any long-term effects of Chikungunya infection?
Relevance: 67%
-

Is Chikungunya fatal?
Relevance: 60%
-

Where do Chikungunya outbreaks typically occur?
Relevance: 57%
-

How long will I feel ill with chikungunya?
Relevance: 55%
-

What are the symptoms of Zika virus?
Relevance: 53%
-

What are the symptoms of Nipah Virus infection?
Relevance: 50%
-

What are the symptoms of Chikungunya virus infection?
Relevance: 50%
-

What is the mortality rate of Nipah Virus infection?
Relevance: 47%
-

What should someone do if they suspect Nipah Virus infection?
Relevance: 46%
-

Can men in the UK transmit Zika virus if infected?
Relevance: 46%
-

What preventive measures can reduce the risk of Nipah Virus infection?
Relevance: 44%
-

Is there a vaccine for Chikungunya virus?
Relevance: 42%
-

How can healthcare workers protect themselves from Marburg virus infection?
Relevance: 41%
-

Is the Marburg virus related to the Ebola virus?
Relevance: 41%
-

Is there a cure for Nipah Virus?
Relevance: 40%
-

What is Nipah Virus?
Relevance: 40%
-

Has chikungunya virus been reported in the UK?
Relevance: 39%
-

Can Zika virus affect pregnancy?
Relevance: 39%
-

Do antibiotics work on viral infections?
Relevance: 39%
-

How is Nipah Virus transmitted?
Relevance: 39%
-

Can Nipah Virus cause outbreaks?
Relevance: 39%
-

Can Nipah Virus cause neurological complications?
Relevance: 39%
-

How is West Nile Virus transmitted?
Relevance: 38%
-

What is the Marburg Virus?
Relevance: 38%
-

Can animals be infected with H3N2?
Relevance: 38%
-

What is West Nile Virus?
Relevance: 38%
-

How is Nipah Virus diagnosed?
Relevance: 37%
-

Are there treatments for West Nile Virus?
Relevance: 37%
-

How is the Zika virus transmitted?
Relevance: 37%
-

What other viruses are tested for in blood donations?
Relevance: 37%
-

How is Marburg virus disease diagnosed?
Relevance: 37%
-

Which animals are known to carry Nipah Virus?
Relevance: 37%
-

Is the UK government providing guidance on Zika virus for travelers?
Relevance: 36%


