Find Help
More Items From Ergsy search
-

Neurophysiology EEG Patient Information
Relevance: 100%
-
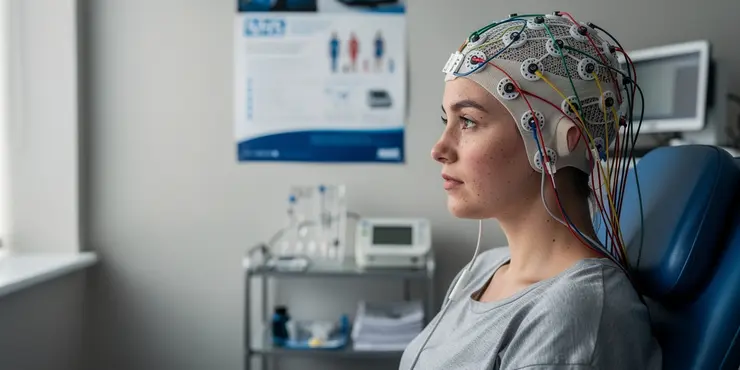
Epilepsy research: EEG | NHS
Relevance: 45%
-

Epilepsy research: EEG | NHS
Relevance: 44%
-
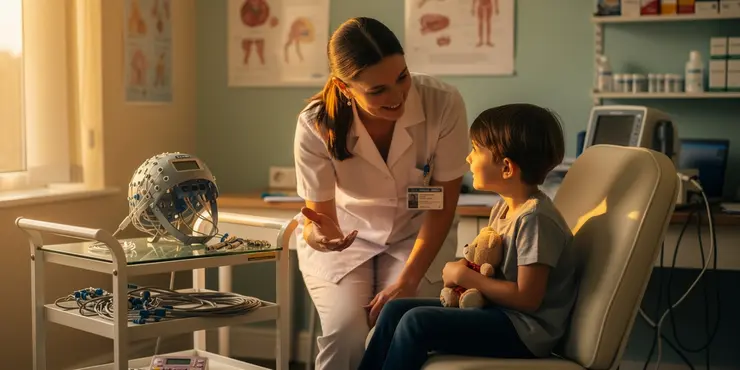
What happens when my child has an EEG?
Relevance: 39%
-
Cornea transplant patient Information
Relevance: 28%
-
Can online patient forums provide reliable information on waiting times?
Relevance: 26%
-

Infertility - IVF Treatment and Patient Information
Relevance: 26%
-

Useful information for patients with lower back pain
Relevance: 24%
-
Useful information for patients with lower back pain
Relevance: 23%
-

Finding out about Fibroids - information for patients
Relevance: 23%
-

Patient Information Video - Leeds Stress Echocardiography Service
Relevance: 22%
-

Information for all cancer patients receiving Chemotherapy or Targeted Therapy at HDFT.
Relevance: 21%
-

Gaining consent from stroke patients
Relevance: 20%
-
Positioning for Breathless Patient
Relevance: 19%
-
Neuroendocrine tumour patient video
Relevance: 19%
-

Are virtual wards suitable for elderly patients?
Relevance: 19%
-

What support is available for carers of Alzheimer's patients?
Relevance: 18%
-

Are there online support services for prostate cancer patients on the NHS?
Relevance: 18%
-

What legal rights do I have as a medical patient in the EU?
Relevance: 18%
-

Sean's Story - There is another way. Information for prescribers
Relevance: 17%
-

Assessing the stroke patient
Relevance: 17%
-

What legal resources are available for carers of Alzheimer's patients?
Relevance: 17%
-

Are there financial support programs for carers of Alzheimer's patients?
Relevance: 17%
-

Can technology aid in the care of Alzheimer's patients?
Relevance: 17%
-

NHS Utilizes AI to Prioritize High-Risk Patients on Waiting Lists
Relevance: 17%
-

Chemotherapy - the patient journey
Relevance: 17%
-
Exercise in patients with a neuropathy
Relevance: 17%
-

Breakthrough Cancer Treatment Shows Promise for NHS Patients
Relevance: 17%
-

What is self-testing for eye patients?
Relevance: 17%
-

Can Baxdrostat be used in patients with renal impairment?
Relevance: 17%
-

Delirium: A Patient Story at Leicester's Hospitals
Relevance: 17%
-
What if there are no NHS dentists accepting new patients?
Relevance: 17%
-

Sickle cell patients share their experiences.
Relevance: 17%
-
How can I find information on waiting times for an operation in my area?
Relevance: 16%
-

Fallsafe - Put the patient first. Preventing falls in Hospital.
Relevance: 16%
-

How do virtual wards improve patient outcomes?
Relevance: 16%
-

Can I access prostate cancer information online through the NHS?
Relevance: 16%
-

Are there specific apps or tools to help carers of Alzheimer's patients?
Relevance: 16%
-

How can primary care support workers contribute to patient care improvement?
Relevance: 16%
-
Can I get information on average waiting times for operations?
Relevance: 16%
Neurophysiology EEG Patient Information
What is an EEG?
An Electroencephalogram (EEG) is a diagnostic test that measures the electrical activity of your brain. Small sensors, called electrodes, are attached to your scalp to detect tiny electrical charges produced by brain cells. The resulting brain wave patterns are recorded and can help diagnose a variety of neurological conditions.
Why Might I Need an EEG?
EEGs are commonly used to investigate epilepsy and other seizure disorders. They can also help diagnose sleep disorders, head injuries, brain infections, degenerative diseases, and brain tumours. Your doctor may recommend an EEG if you are experiencing symptoms such as persistent headaches, unexplained fainting spells, or memory problems.
How to Prepare for an EEG
In the days leading up to your EEG, avoid consuming caffeine as it can affect brain activity. Ensure your hair is clean and free of oils, sprays, or creams on the day of the test, as greasy hair can interfere with the electrodes. Continue to take your prescribed medications unless advised otherwise by your doctor.
What to Expect During the EEG
An EEG is non-invasive and painless. You will be asked to lie down and relax while a technician places electrodes on your scalp. You may be asked to open and close your eyes, breathe deeply, or look at a flashing light during the test. The EEG typically takes about 30 to 60 minutes, although it may be longer if a sleep EEG is required.
After the EEG
Once the test is complete, the electrodes will be removed, and you can go about your daily activities as normal. There are no after-effects from the test, and you can resume driving and returning to work immediately. The results will be analysed by a neurologist and discussed with you at a follow-up appointment.
Getting Your Results
Your EEG results will usually be ready within a week. If the test was conducted as part of an emergency, your doctor might request an expedited analysis. The neurologist will review the brain wave patterns for any abnormalities that could indicate a specific neurological condition and will explain what the results mean for your health and potential treatment options.
Important Considerations
If you have any concerns or require special assistance on the day of your EEG, do not hesitate to contact the hospital or clinic beforehand. Always follow medical advice and attend all scheduled appointments to ensure the best care and accurate diagnosis.
Neurophysiology EEG Patient Information
What is an EEG?
An EEG is a test that looks at how your brain works. Small sensors, called electrodes, are put on your head. These sensors check the tiny electrical charges made by your brain. The test helps doctors understand if there are any problems with the brain.
Why Might I Need an EEG?
Doctors use EEGs to look for problems like epilepsy and seizures. They also use it for sleep problems, head injuries, and brain sicknesses. You might need an EEG if you have bad headaches, fainting, or memory troubles.
How to Prepare for an EEG
A few days before your EEG, do not drink anything with caffeine like coffee or cola. These can change how your brain works. Wash your hair before the test, but do not use any hair products. This helps the sensors stick to your scalp. Keep taking your medicine unless your doctor tells you not to.
What to Expect During the EEG
The EEG does not hurt. You will lie on a bed while the sensors are put on your head. You might be asked to open and close your eyes, breathe deeply, or look at a flashing light. The test usually takes about half an hour to an hour. It might be longer if the doctor wants to do a sleep test.
After the EEG
After the test, the sensors will be taken off. You can go back to your usual activities, like driving and working. The test does not have any side effects. A doctor will look at the results and talk to you about them in another appointment.
Getting Your Results
You should get your EEG results in about a week. If it was an emergency test, the doctor might get the results faster. A special brain doctor, called a neurologist, will look at the wave patterns from your brain. They will explain what the results mean for your health and any treatment you might need.
Important Considerations
If you are worried or need help on the test day, call the hospital or clinic. Always do what your doctor tells you and go to all your appointments to make sure you get the best care and the right answers to your health problems.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an EEG?
An EEG, or electroencephalogram, is a test that measures the electrical activity of your brain using small sensors attached to your scalp.
Why do I need an EEG?
An EEG can help diagnose conditions such as epilepsy, sleep disorders, and other brain-related conditions by capturing the electrical signals in the brain.
How should I prepare for my EEG?
Before your EEG, avoid consuming caffeine for 8-12 hours. Wash your hair with shampoo but do not use conditioner or oils. Continue taking your medication unless otherwise instructed by your doctor.
Can I eat or drink before the EEG?
Yes, you can eat and drink as usual before the test. However, avoid any foods or drinks with caffeine as it can affect the results.
Will the EEG hurt?
No, an EEG is a painless test. The sensors attached to your scalp only record electrical activity and do not emit any electrical charges.
How long does an EEG take?
An EEG test usually takes about 1 to 2 hours, including preparation time. The actual recording of brain activity usually lasts 20 to 40 minutes.
What should I wear to my EEG appointment?
Wear comfortable clothing, but avoid any metallic accessories or hairstyles that involve hair products. It is best to leave jewellery at home.
Can I drive after an EEG test?
Yes, you can usually drive after an EEG, unless you are advised otherwise by your doctor. If you were given sedation for the test, you should arrange for someone to drive you home.
Will I need to stay overnight for an EEG?
Typically, an EEG is an outpatient procedure, meaning you won't need to stay overnight unless it combines with other tests requiring observation.
What happens during the EEG?
During the EEG, you will be asked to lie down or sit comfortably. Small sensors (electrodes) will be attached to your scalp, and the recording will begin. You may be asked to do simple tasks such as breathing deeply or looking at flashing lights.
Are there any side effects of an EEG?
EEGs are very safe with minimal risks. Some people might experience slight skin irritation where the electrodes were attached, but this is temporary.
When will I get my EEG results?
The results of your EEG will usually be available within a few days. Your consultant will discuss the findings with you and explain what they mean.
Can children have an EEG?
Yes, children can have an EEG. The procedure is safe and painless for patients of all ages. Specific instructions will be provided for preparing your child for the test.
What if I fall asleep during an EEG?
Falling asleep during an EEG is not uncommon and can actually be useful, since it may help capture different types of brain activity. Some EEG tests might even specifically require you to sleep.
Will my medication affect my EEG results?
Some medications can affect EEG results. It is important to provide a full list of current medications to your doctor. Do not stop taking your medications unless instructed.
What is an EEG?
An EEG is a test that looks at how the brain works. It checks the signals in your brain. It does not hurt, and it can help doctors understand more about how your brain is doing.
If you find reading hard, you might use pictures or videos to help understand better. You can also ask someone to read with you. If you have questions, you can ask a teacher or an adult to help explain.
An EEG is a special test that looks at how your brain works. It checks the little signals your brain makes. To do this, tiny parts are put on your head.
Why Do I Need an EEG Test?
An EEG test looks at your brain. It checks how your brain is working.
Doctors use it to find out why you might be having problems like headaches or seizures.
The test can help doctors know what to do next to help you feel better.
If you find reading hard, use a ruler or your finger to follow the words.
An EEG is a test that looks at brain waves. It can help find problems like epilepsy, sleep troubles, and other brain problems. This test works by catching tiny electrical signals from the brain.
How to Get Ready for Your EEG
Before your EEG test, don't have drinks with caffeine for 8 to 12 hours. Wash your hair with shampoo, but don't use conditioner or oils. Keep taking your medicine unless your doctor tells you to stop.
Can I eat or drink before the EEG?
Yes, you can eat and drink before your EEG. It is okay to have your breakfast, lunch, or snacks.
Here are some tips to help you:
- Drink water or juice if you are thirsty.
- Avoid drinks with caffeine like coffee, tea, or cola.
- If you are unsure, ask someone for help.
Remember, if you need more help, you can talk to your doctor or nurse.
Yes, you can eat and drink like you usually do before the test. But, try not to have any food or drinks with caffeine because it can change the results.
Will the EEG hurt?
No, an EEG will not hurt. An EEG is a test to see how your brain works. It uses special patches put on your head, but they do not hurt.
If you feel worried, you can try some things to feel better:
- Bring a toy or book you like.
- Ask someone to stay with you.
- Take deep breaths to stay calm.
No, an EEG does not hurt. It is a test that does not cause pain. Small sensors are placed on your head. They just record signals from your brain. They do not give off any electricity.
Tip: If you feel worried, try deep breathing to relax.
How long does an EEG take?
An EEG is a test that looks at how the brain works. It usually takes about 1 to 2 hours.
If you need help understanding the test, ask someone to explain it to you. You can also talk to the person who is doing your test.
An EEG test usually takes about 1 to 2 hours. This includes getting everything ready. The part where they record what your brain is doing usually takes 20 to 40 minutes.
Sometimes, having someone with you can help you feel more comfortable. You can also try to relax by taking deep breaths before the test starts.
What clothes should I wear to my EEG appointment?
Here are some tips to help you:
- Wear a shirt or top that buttons or zips in the front. This makes it easy to change.
- Avoid clothes with metal, like zippers or big jewelry.
- Wear something comfortable so you can relax.
You might want to use a calendar or set a reminder so you don't forget your appointment.
Wear clothes that feel good and are easy to move in. Don't wear things like metal jewelry or hair spray. It's a good idea to leave your jewelry at home.
Can I drive after my brain test?
A brain test is called an EEG. It looks at how your brain is working.
After the EEG, ask your doctor if you can drive. They know what is best for you.
If you feel tired or dizzy after the test, do not drive.
Driving when you are not feeling good is not safe.
Ask a friend or family member to help you get home.
You can also use a taxi or a bus.
Yes, you can drive after an EEG test, unless your doctor tells you not to. If you got medicine to make you sleepy during the test, ask someone to drive you home.
Do I need to sleep at the hospital for an EEG test?
An EEG is a test that checks your brain. You can usually have it done and go home the same day. You only need to stay overnight if you have other tests that need more watching.
What happens during the EEG?
An EEG test looks at how your brain works. Here is what happens during the test:
- You will go to a special room.
- A person will put small stickers on your head. These are called electrodes.
- The electrodes check the electrical activity in your brain. They do not hurt.
- You might need to sit still, close your eyes, or do some simple things during the test.
- The test is safe and usually takes about one hour.
If you feel worried or unsure about anything, you can ask the person doing the test.
Tools that might help you:
- Ask a friend or family to come with you.
- Bring a toy or something that comforts you.
- Practice relaxing by taking deep breaths.
When you have the EEG test, you will need to sit or lie down quietly. Tiny sensors, called electrodes, will be put on your head. The test will start. You might be asked to do easy things like take big breaths or look at lights that flash on and off.
Here are some tips to help you:
- Bring someone with you who can explain things and give you support.
- Ask the doctor to explain any parts that are confusing.
- Use a breathing app to practice deep breaths at home.
Are there any side effects of an EEG?
An EEG is a test that checks your brain. It does not hurt. Most people do not feel any different after the test. Some people feel a little tired, but this goes away soon. You can watch TV or listen to music to relax after. If you feel worried, ask someone to go with you.
EEGs are very safe. They do not cause problems. Some people might get a little itchy skin where the sensors are put on, but this feeling goes away quickly.
When will I see my EEG results?
Your EEG test results will take some time. You might get them in a few days. If you have not heard anything after a week, ask the doctor. The doctor will say what the EEG shows.
Here are some tips to help you:
- Bring a friend or family member to the appointment. They can help you ask questions.
- Write down any questions you want to ask the doctor.
- Use a calendar to keep track of dates and reminders.
You will get your EEG test results in a few days. Your doctor will talk to you about what they mean.
Can children have an EEG?
Yes, children can have an EEG.
An EEG is a safe and easy test. It looks at brain waves.
To help children feel calm:
- Explain what will happen.
- Let them bring a favorite toy or blanket.
Parents can stay with their child during the test.
If you have questions, ask the doctor or nurse.
Yes, kids can have an EEG. It is safe and does not hurt. The doctor will tell you what to do to get your child ready for the test.
What happens if I fall asleep during an EEG?
If you fall asleep during an EEG, it's okay! The EEG can still work while you are sleeping. It watches your brain's activity. Sleeping might even help the doctors see more things about your brain. You can relax and let the test happen.
To feel better, you can:
- Bring a favorite blanket or toy to feel comfy.
- Ask someone you trust to stay with you.
- Listen to calming music if the doctor says it's okay.
It is normal to fall asleep during an EEG test. This can be helpful because it lets the doctors see different brain activity. Some EEG tests might ask you to sleep on purpose.
If you need help, try using soft music or a calming story. You can also hug a stuffed toy or use a cozy blanket.
Will my medicine change my EEG test?
Some medicines can change EEG test results. It is important to tell your doctor all the medicines you are taking. Do not stop taking your medicines unless your doctor says it is okay.
Useful Links
This website offers general information and is not a substitute for professional advice.
Always seek guidance from qualified professionals.
If you have any medical concerns or need urgent help, contact a healthcare professional or emergency services immediately.
Some of this content was generated with AI assistance. We’ve done our best to keep it accurate, helpful, and human-friendly.
- Ergsy carfully checks the information in the videos we provide here.
- Videos shown by Youtube after a video has completed, have NOT been reviewed by ERGSY.
- To view, click the arrow in centre of video.
- Most of the videos you find here will have subtitles and/or closed captions available.
- You may need to turn these on, and choose your preferred language.
- Go to the video you'd like to watch.
- If closed captions (CC) are available, settings will be visible on the bottom right of the video player.
- To turn on Captions, click settings .
- To turn off Captions, click settings again.
More Items From Ergsy search
-

Neurophysiology EEG Patient Information
Relevance: 100%
-

Epilepsy research: EEG | NHS
Relevance: 45%
-

Epilepsy research: EEG | NHS
Relevance: 44%
-
What happens when my child has an EEG?
Relevance: 39%
-

Cornea transplant patient Information
Relevance: 28%
-
Can online patient forums provide reliable information on waiting times?
Relevance: 26%
-

Infertility - IVF Treatment and Patient Information
Relevance: 26%
-

Useful information for patients with lower back pain
Relevance: 24%
-

Useful information for patients with lower back pain
Relevance: 23%
-

Finding out about Fibroids - information for patients
Relevance: 23%
-

Patient Information Video - Leeds Stress Echocardiography Service
Relevance: 22%
-

Information for all cancer patients receiving Chemotherapy or Targeted Therapy at HDFT.
Relevance: 21%
-

Gaining consent from stroke patients
Relevance: 20%
-

Positioning for Breathless Patient
Relevance: 19%
-

Neuroendocrine tumour patient video
Relevance: 19%
-

Are virtual wards suitable for elderly patients?
Relevance: 19%
-

What support is available for carers of Alzheimer's patients?
Relevance: 18%
-

Are there online support services for prostate cancer patients on the NHS?
Relevance: 18%
-

What legal rights do I have as a medical patient in the EU?
Relevance: 18%
-

Sean's Story - There is another way. Information for prescribers
Relevance: 17%
-

Assessing the stroke patient
Relevance: 17%
-

What legal resources are available for carers of Alzheimer's patients?
Relevance: 17%
-

Are there financial support programs for carers of Alzheimer's patients?
Relevance: 17%
-

Can technology aid in the care of Alzheimer's patients?
Relevance: 17%
-

NHS Utilizes AI to Prioritize High-Risk Patients on Waiting Lists
Relevance: 17%
-

Chemotherapy - the patient journey
Relevance: 17%
-

Exercise in patients with a neuropathy
Relevance: 17%
-

Breakthrough Cancer Treatment Shows Promise for NHS Patients
Relevance: 17%
-

What is self-testing for eye patients?
Relevance: 17%
-

Can Baxdrostat be used in patients with renal impairment?
Relevance: 17%
-

Delirium: A Patient Story at Leicester's Hospitals
Relevance: 17%
-
What if there are no NHS dentists accepting new patients?
Relevance: 17%
-

Sickle cell patients share their experiences.
Relevance: 17%
-
How can I find information on waiting times for an operation in my area?
Relevance: 16%
-

Fallsafe - Put the patient first. Preventing falls in Hospital.
Relevance: 16%
-

How do virtual wards improve patient outcomes?
Relevance: 16%
-

Can I access prostate cancer information online through the NHS?
Relevance: 16%
-

Are there specific apps or tools to help carers of Alzheimer's patients?
Relevance: 16%
-

How can primary care support workers contribute to patient care improvement?
Relevance: 16%
-
Can I get information on average waiting times for operations?
Relevance: 16%


