Find Help
More Items From Ergsy search
-

A guide to hospital-acquired deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism
Relevance: 100%
-

What is a pulmonary embolism?
Relevance: 64%
-

What are the symptoms of deep vein thrombosis (DVT)?
Relevance: 59%
-
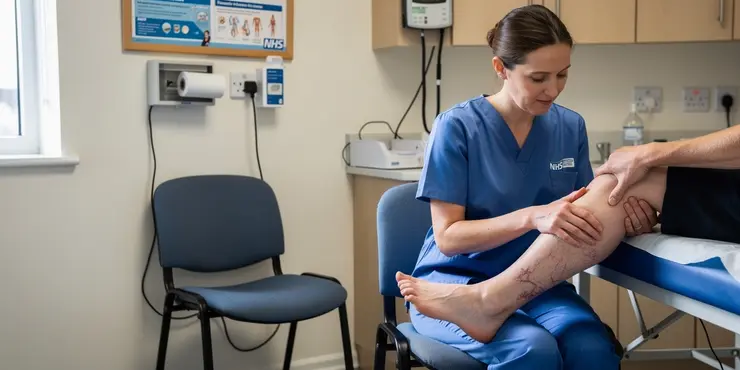
What are the types of thrombosis?
Relevance: 54%
-

What is thrombosis?
Relevance: 48%
-
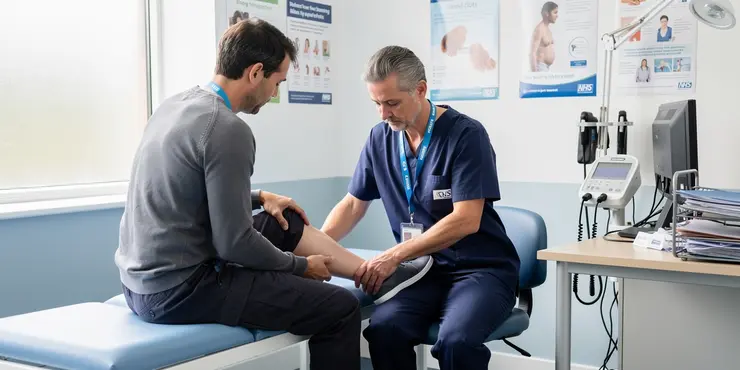
How is thrombosis diagnosed?
Relevance: 40%
-

How is thrombosis treated?
Relevance: 36%
-

What causes thrombosis?
Relevance: 34%
-

Why is thrombosis dangerous?
Relevance: 30%
-

What are the risk factors for thrombosis?
Relevance: 29%
-
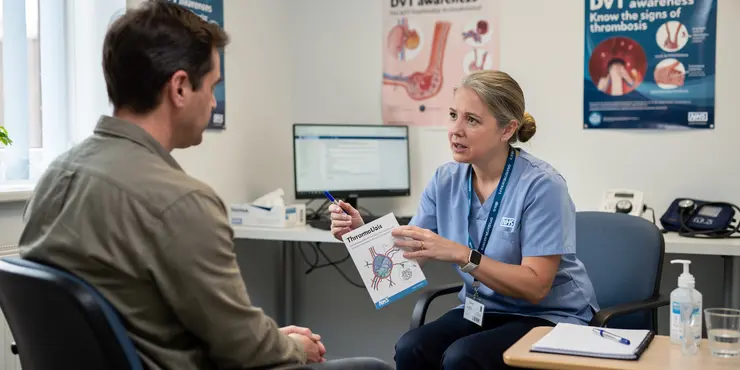
Is thrombosis a common condition?
Relevance: 27%
-

Who is at higher risk for thrombosis?
Relevance: 22%
-

Pulmonary rehabilitation | NHS
Relevance: 22%
-

What are the symptoms of arterial thrombosis?
Relevance: 20%
-

What lifestyle changes can help manage thrombosis risk?
Relevance: 20%
-

Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) research
Relevance: 18%
-
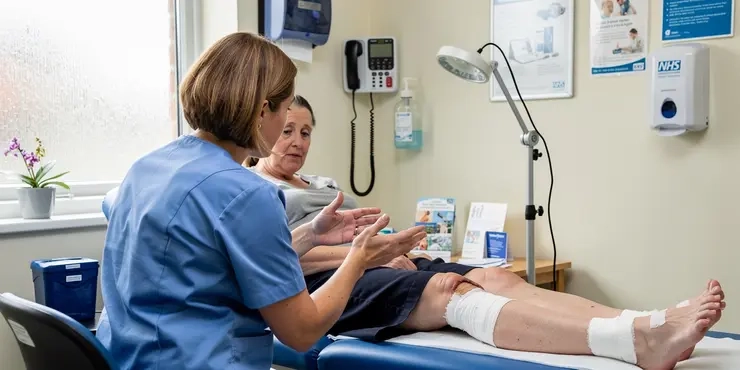
Leg ulcer see Venous leg ulcer
Relevance: 14%
-
What are the risks associated with hip replacement surgery?
Relevance: 13%
-

Can thrombosis be prevented?
Relevance: 10%
-

Can thrombosis recur?
Relevance: 10%
-

Can heart failure affect other organs?
Relevance: 9%
-

2 episodes of cellulitis and been given antibiotics but the redness doesn't seem to be improving?
Relevance: 8%
-
COPD | NHS
Relevance: 8%
-
What is an incentive spirometer in air physiotherapy?
Relevance: 8%
-
Are there any risks associated with traveling to the EU for medical treatment?
Relevance: 8%
-

An Introduction to Decompression Illness: Signs & Symptoms”. Dr Roland Armes
Relevance: 7%
-

Enhanced Recovery After Surgery in Forth Valley
Relevance: 7%
-

Enhanced Recovery - Hip
Relevance: 7%
-
What are minimally invasive procedures for BPH?
Relevance: 7%
-

Breathlessness after COVID-19 - helpful techniques
Relevance: 7%
-

How does air physiotherapy work?
Relevance: 7%
-
What to do about red legs
Relevance: 6%
-

Can air physiotherapy prevent respiratory infections?
Relevance: 6%
-

Are anticoagulants effective in reducing stroke risk?
Relevance: 6%
-

Cardiac Physiology Walkthrough
Relevance: 6%
-

High Air Pollution Levels Linked to Rising Cases of Respiratory Issues
Relevance: 6%
-
Eye Injections at Royal Bournemouth Hospital
Relevance: 6%
-
Are there any exercises involved in air physiotherapy?
Relevance: 5%
-

Clearing Your Chest with Breathing Exercises
Relevance: 5%
-

Who can benefit from air physiotherapy?
Relevance: 5%
Guide to Hospital-Acquired Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) refers to the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, typically in the legs. It is a serious condition that can lead to complications if the clot dislodges and travels to the lungs, resulting in a pulmonary embolism.
Understanding Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Pulmonary Embolism (PE) occurs when a blood clot from a DVT travels to the lungs, blocking one or more pulmonary arteries. This can impede blood flow, reducing oxygen levels and potentially causing severe lung damage or even death.
Risk Factors for Hospital-Acquired DVT and PE
Hospital patients are at increased risk of DVT and PE due to prolonged immobility, surgical procedures, or specific medical conditions. Older age, obesity, a history of clotting disorders, and major surgeries, such as hip or knee replacements, further elevate this risk.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing hospital-acquired DVT and PE involves multiple strategies. Use of anticoagulant medications, mechanical compression devices like compression stockings or inflatable cuffs, and encouraging early mobilisation and physical activity are common preventive measures.
Recognising Symptoms
Common symptoms of DVT include leg pain, swelling, and redness. Symptoms of PE may include sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, rapid pulse, and coughing (sometimes with blood). Early recognition and prompt medical intervention are crucial.
Treatment Options
Treatment for DVT and PE typically involves anticoagulant medications to stop the clot from growing and reduce the risk of new clots. Severe cases may require thrombolytic therapy to dissolve clots or surgical procedures to remove them.
Conclusion
Hospital-acquired DVT and PE are preventable and treatable conditions. Awareness, early detection, and a proactive approach involving preventive measures can significantly reduce the incidence and improve patient outcomes.
Guide to Hospital-Acquired Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
Deep Vein Thrombosis or DVT is when a blood clot forms in a deep vein. This usually happens in the legs. It can be very serious. If the clot moves, it can go to the lungs and cause problems.
Understanding Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Pulmonary Embolism or PE happens when a clot from a DVT goes to the lungs. This blocks blood flow in the lungs. It can make it hard to breathe and is very dangerous.
Risk Factors for Hospital-Acquired DVT and PE
People in the hospital have a higher chance of getting DVT and PE. This can happen if they are in bed for a long time or have surgery. Older people, people who are very overweight, and those who have had blood clots before are at higher risk, too.
Prevention Strategies
There are ways to stop DVT and PE in the hospital. Doctors might give medicine to thin the blood. They may use special socks or cuffs to help blood flow in the legs. Getting up and moving around as soon as you can is also important.
Recognising Symptoms
DVT might cause pain, swelling, or redness in the leg. PE might make you feel short of breath or have chest pain. You might have a fast heartbeat or cough. If you notice these signs, tell a doctor straight away.
Treatment Options
To treat DVT and PE, doctors use medicines that help stop clots from growing. In some cases, they might use medicine to break up clots or even do surgery to remove them.
Conclusion
DVT and PE can often be prevented and treated. Knowing the signs and acting fast is important. Preventive steps can keep you safe and help you get better faster.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a deep vein thrombosis (DVT)?
A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in a deep vein, typically in the legs. It can cause pain, swelling, and redness in the affected leg.
What is a pulmonary embolism (PE)?
A pulmonary embolism (PE) occurs when a blood clot that has formed elsewhere in the body, often in the legs, travels to the lungs and causes a blockage. This can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
How common are DVT and PE in hospitals?
DVT and PE are relatively common complications in hospitalized patients, especially those who undergo surgery, are immobile for prolonged periods, or have certain medical conditions.
What are the risk factors for hospital-acquired DVT and PE?
Risk factors include prolonged immobility, major surgery, certain medical conditions (e.g., cancer, heart failure), obesity, smoking, and a history of previous blood clots.
How can DVT be prevented in hospitalized patients?
Preventive measures include using blood-thinning medications, wearing compression stockings, and encouraging mobility when possible. Proper hydration and leg exercises can also help.
What are the symptoms of a DVT?
Symptoms of a DVT can include pain, swelling, tenderness, and redness in the affected leg. In some cases, there may be no noticeable symptoms.
What are the symptoms of a PE?
Symptoms of a PE can include sudden shortness of breath, chest pain that may worsen with deep breaths, rapid heart rate, and coughing, sometimes with bloody sputum.
How is DVT diagnosed?
DVT is typically diagnosed through a combination of a physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests such as an ultrasound. Blood tests may also be used to check for clotting abnormalities.
How is PE diagnosed?
PE diagnosis may involve imaging tests such as a CT scan or a ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) scan, along with blood tests and a review of the patient's clinical symptoms and medical history.
What treatments are available for DVT?
Treatment options for DVT include anticoagulant (blood thinner) medications to prevent further clotting, thrombolytic therapy to dissolve clots, and in some cases, surgical intervention.
What treatments are available for PE?
PE treatments often involve anticoagulant medications, thrombolytic therapy, and in severe cases, surgical procedures such as catheter-directed thrombolysis or surgical embolectomy to remove the clot.
Is DVT and PE preventable?
While not all cases can be prevented, many DVTs and PEs can be avoided with appropriate preventive measures, especially in hospitalized patients with known risk factors.
What should I do if I suspect I have a DVT or PE?
If you suspect a DVT or PE, seek immediate medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent serious complications.
Can lifestyle changes reduce the risk of DVT and PE?
Yes, lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, avoiding prolonged periods of immobility, quitting smoking, and staying hydrated can help reduce the risk.
Are there long-term effects of DVT and PE?
Long-term effects can include post-thrombotic syndrome (chronic pain and swelling in the affected limb) and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (high blood pressure in the lungs caused by unresolved clots). Monitoring and ongoing medical care are important.
What is a deep vein thrombosis (DVT)?
A deep vein thrombosis, or DVT, is something that happens in your body. It is a blood clot, like a lump of thick blood, that forms in a deep vein. Deep veins are veins that are inside your body, not the ones you see under your skin. This can happen in places like your leg.
When you have a DVT, blood can't flow like it should. This can be serious because if the clot moves, it can go to your lungs and cause big problems.
If you want to understand more about DVT, you can use pictures and videos to help. Talk to a doctor or nurse if you have questions. They can explain things to make them easier to understand.
A deep vein thrombosis, or DVT, is when a blood clot forms in a deep vein. This usually happens in the legs. It can cause the leg to hurt, swell, and turn red.
What is a pulmonary embolism (PE)?
A pulmonary embolism (PE) is when a blood clot gets stuck in the blood vessels of the lungs. This can make it hard to breathe and can be very serious.
If you are finding it hard to understand, try using tools like text-to-speech to listen to the information. Pictures and videos can also help explain things better.
If you are worried about PE, ask a doctor or nurse to explain it to you.
A pulmonary embolism, or PE, happens when a blood clot moves to the lungs. It often starts in the legs. This clot blocks the blood flow in the lungs. It can be very dangerous if not treated quickly.
How often do DVT and PE happen in hospitals?
DVT stands for deep vein thrombosis. It means a blood clot in a vein. PE stands for pulmonary embolism. It means a blood clot in the lungs. Both are serious and can happen in hospitals.
Lots of people in hospitals can get blood clots. It is important to be careful and watch for signs.
Here are some tools and tips to help:
- Ask the doctor or nurse to check for blood clots.
- Move around as much as you can to help blood flow.
- Wear special stockings that help blood move in your legs.
- Take medicine that the doctor gives you to stop clots.
DVT and PE are health problems that can happen in people in the hospital. This often happens to people who have had surgery, are not moving much, or have some health issues.
What makes DVT and PE more likely in a hospital?
Some things can make it more likely for someone to get DVT (blood clots in the legs) or PE (blood clots in the lungs) while in the hospital. Here are a few:
- Being in bed and not moving a lot
- Having surgery
- Being older
- Having a history of blood clots
- Being overweight
- Having cancer
If you or someone you know is in the hospital, talk to a doctor or nurse about ways to prevent blood clots. They may suggest moving more, wearing special socks, or taking medicine.
Here are some things that can make blood clots more likely:
- Not moving for a long time
- Big surgeries
- Certain health problems like cancer or heart issues
- Being very overweight
- Smoking
- Having blood clots before
Here are some tips to help understand and read better:
- Take breaks often to rest your eyes.
- Ask someone to read with you or help explain.
- Use audiobooks or reading apps that can read aloud to you.
How can we stop DVT in patients who are in the hospital?
DVT means "Deep Vein Thrombosis," which is a blood clot in the leg. Here’s how to help stop it:
- Move Around: Help patients move their legs and feet often.
- Special Stockings: Use tight socks called compression stockings that help blood flow.
- Medicine: Sometimes doctors give special medicine to help stop clots.
- Raise Legs: Keep the legs up with pillows to help blood move better.
You can use pictures or videos to understand these steps better.
To stay healthy, you can do some simple things:
- Take special medicine that keeps your blood from getting too thick.
- Wear tight socks called compression stockings.
- Try to move around when you can.
- Drink lots of water.
- Do exercises for your legs.
These tips can help you feel better!
What are the signs of a DVT?
If you have a DVT, your leg might hurt, get bigger, feel sore, or turn red. Sometimes, you might not notice anything is wrong.
What are the signs of a PE?
A PE is a blockage in the lung. Here are some signs to look for:
- It's hard to breathe.
- Breathing hurts.
- You cough up blood.
- Your heart beats very fast.
It helps to use pictures or videos to understand more. A friend or family member can also help explain this.
If you have a blood clot in your lung, you might feel these things:
- It suddenly gets hard to breathe.
- Your chest hurts, especially when you take a deep breath.
- Your heart beats very fast.
- You start coughing and might see some blood when you cough.
These things can be scary. If you feel them, tell a grown-up and go to the doctor. They can help you feel better.
To make reading easier, you can:
- Read slowly and take your time.
- Use your finger to follow along with the words.
- Ask someone to read it with you.
How do doctors find out if you have DVT?
Doctors find out if someone has DVT in a few ways. They will check your body and ask about your health. They might use a special machine called an ultrasound to look inside your body. Sometimes, they will also take a blood test to see if your blood is clotting the right way.
To make things easier, you can use tools like text readers that read words out loud. Or you can use pictures to help understand the words better.
How do doctors find out if someone has PE?
To find out if someone has PE, doctors might do special picture tests like a CT scan or a V/Q scan. They also take blood tests and check how the person feels and any past health problems.
What can help if you have DVT?
Ways to help with DVT (blood clots in veins) are:
- Medicine that makes the blood thinner and stops more clots from forming.
- Medicine that breaks up the clots.
- Sometimes, doctors might need to do surgery.
What can help if you have PE?
PE stands for a problem where some boys finish too early during sex. Here are some things that can help:
- Talk to a doctor: They can give you advice.
- Practice relaxing: Calm down by breathing slowly.
- Therapy: Talking to someone can help.
- Medicines: Some pills can help. Ask a doctor.
Using pictures or videos can also help make things clearer. You can also ask an adult you trust to help you understand.
PE treatments help to get rid of blood clots. People often use medicine to stop clots from getting bigger. This medicine is called 'blood thinners'.
In some cases, people need special treatments to break up the clot. This might be strong medicine or a small operation to take away the clot.
If things are very serious, doctors might do a bigger operation to quickly remove the clot.
If you need help reading, you can use tools like text-to-speech apps or ask someone to read with you. They can help make things easier to understand.
Can We Stop DVT and PE from Happening?
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) are conditions that can be harmful. But there are ways to help stop them.
Here are some tips:
- Ask your doctor about medicines that can help.
- Move around regularly. Don’t sit still for too long.
- Wear special socks called compression stockings.
- Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated.
If you need help, you can use pictures or apps that remind you to move, or ask someone you trust to help you understand.
Sometimes, blood clots can't be stopped. But many clots can be avoided. This is true, especially for people in the hospital who are already at risk.
What should I do if I think I have a DVT or PE?
If you think you have a DVT (blood clot in your leg) or a PE (blood clot in your lung), talk to a doctor right away.
Here are some things you can do:
- Tell an adult you trust that you are worried.
- Call or visit your doctor quickly.
- Ask someone to help you get to a doctor if you need it.
The doctor can help you know what to do next. You are not alone, and people are ready to help you.
If you think you have a blood clot in your leg or lung, go to the doctor right away. It is very important to find and treat it early to stop any big problems.
Can changing how you live make DVT and PE less likely?
Yes, there are some things you can do to stay healthy.
Here are some tips:
- Keep a healthy body weight.
- Move your body and exercise.
- Don't sit still for too long.
- Quit smoking.
- Drink lots of water.
These tips can help you stay healthy.
Can DVT and PE cause problems in the future?
DVT means a blood clot in a vein, usually in the leg. PE is a clot that goes to the lungs. These clots can cause problems later. Here is how:
- DVT can cause leg pain and swelling.
- PE can make it hard to breathe.
- Both can mean you might need more treatments later on.
If you or someone you care for has DVT or PE, talk to a doctor.
Tools that might help:
- A doctor or nurse can help explain things.
- Easy-to-read medical info on trusted websites.
Over time, there can be problems like post-thrombotic syndrome, which means having pain and swelling for a long time in the arm or leg.
There can also be chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension, which means having high blood pressure in your lungs because clots didn't clear up.
It is important to keep checking with your doctor and getting care.
Using pictures, speaking with others, or listening to information may help understanding. Ask for help if you need it!
Useful Links
This website offers general information and is not a substitute for professional advice.
Always seek guidance from qualified professionals.
If you have any medical concerns or need urgent help, contact a healthcare professional or emergency services immediately.
Some of this content was generated with AI assistance. We’ve done our best to keep it accurate, helpful, and human-friendly.
- Ergsy carfully checks the information in the videos we provide here.
- Videos shown by Youtube after a video has completed, have NOT been reviewed by ERGSY.
- To view, click the arrow in centre of video.
- Most of the videos you find here will have subtitles and/or closed captions available.
- You may need to turn these on, and choose your preferred language.
- Go to the video you'd like to watch.
- If closed captions (CC) are available, settings will be visible on the bottom right of the video player.
- To turn on Captions, click settings .
- To turn off Captions, click settings again.
More Items From Ergsy search
-

A guide to hospital-acquired deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism
Relevance: 100%
-

What is a pulmonary embolism?
Relevance: 64%
-

What are the symptoms of deep vein thrombosis (DVT)?
Relevance: 59%
-

What are the types of thrombosis?
Relevance: 54%
-

What is thrombosis?
Relevance: 48%
-

How is thrombosis diagnosed?
Relevance: 40%
-

How is thrombosis treated?
Relevance: 36%
-

What causes thrombosis?
Relevance: 34%
-

Why is thrombosis dangerous?
Relevance: 30%
-

What are the risk factors for thrombosis?
Relevance: 29%
-

Is thrombosis a common condition?
Relevance: 27%
-

Who is at higher risk for thrombosis?
Relevance: 22%
-

Pulmonary rehabilitation | NHS
Relevance: 22%
-

What are the symptoms of arterial thrombosis?
Relevance: 20%
-

What lifestyle changes can help manage thrombosis risk?
Relevance: 20%
-

Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) research
Relevance: 18%
-

Leg ulcer see Venous leg ulcer
Relevance: 14%
-

What are the risks associated with hip replacement surgery?
Relevance: 13%
-

Can thrombosis be prevented?
Relevance: 10%
-

Can thrombosis recur?
Relevance: 10%
-

Can heart failure affect other organs?
Relevance: 9%
-

2 episodes of cellulitis and been given antibiotics but the redness doesn't seem to be improving?
Relevance: 8%
-

COPD | NHS
Relevance: 8%
-

What is an incentive spirometer in air physiotherapy?
Relevance: 8%
-

Are there any risks associated with traveling to the EU for medical treatment?
Relevance: 8%
-

An Introduction to Decompression Illness: Signs & Symptoms”. Dr Roland Armes
Relevance: 7%
-

Enhanced Recovery After Surgery in Forth Valley
Relevance: 7%
-

Enhanced Recovery - Hip
Relevance: 7%
-

What are minimally invasive procedures for BPH?
Relevance: 7%
-

Breathlessness after COVID-19 - helpful techniques
Relevance: 7%
-

How does air physiotherapy work?
Relevance: 7%
-

What to do about red legs
Relevance: 6%
-

Can air physiotherapy prevent respiratory infections?
Relevance: 6%
-

Are anticoagulants effective in reducing stroke risk?
Relevance: 6%
-

Cardiac Physiology Walkthrough
Relevance: 6%
-

High Air Pollution Levels Linked to Rising Cases of Respiratory Issues
Relevance: 6%
-

Eye Injections at Royal Bournemouth Hospital
Relevance: 6%
-

Are there any exercises involved in air physiotherapy?
Relevance: 5%
-

Clearing Your Chest with Breathing Exercises
Relevance: 5%
-

Who can benefit from air physiotherapy?
Relevance: 5%


